Frozen Spinach vs Fresh Spinach: Which is Better?
Spinach is a superfood available in frozen and fresh. Between the two you may be wondering if it matters which one you place in your shopping cart. Many of my health coaching clients asks about them during our sessions. Let’s answer, is frozen spinach better than fresh spinach?
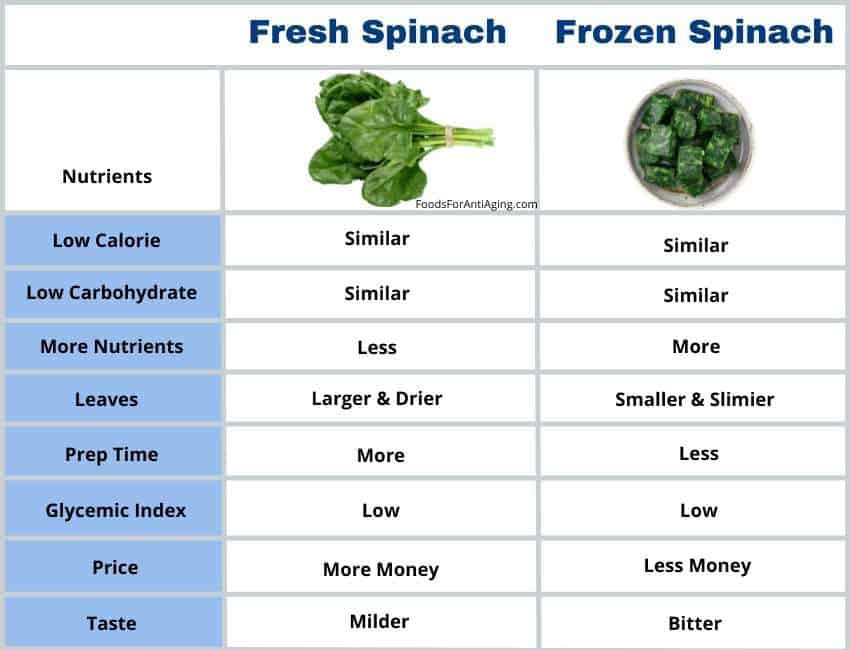
Frozen spinach is better than fresh due to its higher percentage of macronutrients and longer shelf life. Frozen spinach costs less than fresh making it more affordable. Frozen spinach involves less prepping time than fresh spinach which needs to be washed and sometimes trimmed.
This article will examine their tastes, textures, prices, which is better for a particular dish and how to substitute one for the other. In addition, I’ll include and examine their nutrients side-by-side and discuss their health benefits.
In addition to coaching clients about them, I’ve purchased, researched and consumed both prior to, during and after writing this article. I include both in my daily nutrition plan.
Frozen Spinach vs Fresh Spinach: Nutrients
The following table compares the nutrients contained in each per 100 grams.
| Spinach, raw (100 g) | Frozen Spinach, raw (100 g) | |
| Calories | 23 | 29 |
| Protein | 2.86 g | 3.63 g |
| Carbohydrates | 3.63 g | 4.21 g |
| Fiber | 2.2 g | 2.9 g |
| Fat | 0.39 g | 0.57 g |
| Sugar | 0.42 g | 0.65 g |
| Vitamin A | 9,380 IU | 11,700 IU |
| Beta-carotene | 5,630 mcg | 7,040 mcg |
| Vitamin C | 28.1 mg | 5.5 mg |
| Vitamin K | 483 mcg | 372 mcg |
| Vitamin D | 0 IU | 0 IU |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.19 mg | 0.17 mg |
| Vitamin B9 (Folate) | 194 mcg | 145 mcg |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 0.08 mg | 0.09 mg |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0.19 mg | 0.22 mg |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | 0.72 mg | 0.50 mg |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | 0.07 mg | 0.09 mg |
| Magnesium | 79 mg | 75 mg |
| Phosphorous | 49 mg | 49 mg |
| Potassium | 558 mg | 346 mg |
| Iron | 2.71 mg | 1.89 mg |
| Copper | 0.13 mg | 0.14 mg |
| Calcium | 99 mg | 129 mg |
| Zinc | 0.53 mg | 0.56 mg |
Looking at the nutrient table above it’s difficult to determine if one provides more overall nutrients than the other. Let’s examine which is healthier.
Frozen spinach and fresh are nutrients dense and provide a similar number of nutrients. For this reason, they are equally healthy and both should be part of a well-rounded, healthy diet.
Frozen spinach provides a higher percentage of the following:
- Protein
- Fiber
- Vitamin A
- Beta carotene
- Thiamin
- Riboflavin
- B5
- Copper
- Calcium
- Zinc
Fresh spinach provides a higher percentage of the following:
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin K
- B6
- Folate
- Niacin
- Magnesium
- Potassium
- Iron
This video compares fresh and frozen spinach.
The fresh spinach contains a significant amount more vitamin C to start. In a study published in the Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, researchers found freshly picked vegetables consistently contained the highest numbers of vitamin C3.
However, the researchers found fresh spinach loses some of its vitamins and folate over time. Stored at room temperature, it lost 100% of its vitamin C in less than four days. Frozen spinach is flash frozen within hours of being picked. Therefore, it retains more of its vitamin C than fresh spinach.
In addition, a Pennsylvania State University study showed fresh spinach lost much of its folate when sitting in a truck for transport or in the refrigerator. So much folate is lost, frozen spinach ends up with more than fresh4.
Check down further in the article to find out about the health benefits of these two superfoods obtained from these nutrients. Choosing one over the other may depend on the nutrients for your particular goals. Let’s examine some of those goals next.
I choose and use both frozen and fresh in my nutrition plan. I often use fresh spinach for my salads and add frozen spinach into my smoothies.
Spinach is a frozen vegetable with flavor that holds up to the freezing process.
Frozen or Fresh: Which to Choose?
Choosing one food over the other sometimes comes down to your goals. Some popular goals are:
- Weight loss
- Low-carb or Keto diets
- Gluten free
- Bodybuilding
The calories, protein and carbohydrates are similar between the two. Therefore, both are good choices for weight loss, low-carb diets and bodybuilding.
Spinach is gluten free. Therefore, frozen or fresh is a good option for those who have to consume a gluten free diet.
Taste and Texture
Let’s face it, sometimes nothing else matters about the food we choose to eat other than the taste. Some healthy food remains on the store shelves because people find it undesirable to eat.
Therefore, let’s compare the taste of the two vegetables.
When frozen spinach is thawed or cooked, it has a stronger and more bitter taste than fresh spinach leaves. The texture of fresh spinach is crispier and drier than frozen spinach which softens and becomes stringier and fibrous when defrosted or cooked.
I wanted to conduct original research and find out what real people, like you, thought about the taste. So, I polled my clients, readers and members of food groups. I asked, which one tastes better?
- 52% said they preferred the taste of fresh spinach.
- 38% said they preferred the taste of frozen spinach.
- 10% said they had no preference.
To conduct more research I setup and participated in a taste test at home. All three of us chose the fresh spinach due to its crispier and less bitter taste.
The battle of taste was won by fresh spinach in the poll and in my own taste test.
Substitute Fresh or Frozen
When cooking fresh spinach the amount of spinach started with drastically reduces when it is finished cooking. In other words, if you start cooking with one cup, the cooked amount when finished is less than one cup.
Like many leafy greens, it contains much water in the leaves. This water gets cooked out when applied to heat. This makes it shrink down to the end result and softens the leaves.
Commercially sold frozen spinach has already been boiled or blanched and then flash frozen. Therefore when substituting one for the other, the substitutions cannot be made using a one to one ratio or equal amounts of each.
Therefore, many people wonder if one can substitute for the other.
Frozen spinach and fresh spinach can substitute for each although the texture may differ depending on the dish prepared. Substituting frozen for fresh in raw preparations like salads is unrecommended. The two cannot substitute for each other in equal amounts because one pound of fresh spinach equals 10 ounces of frozen spinach.
The following handy formula works well for most people and will help you make spinach substitutions easier in the future. Bookmark this article now, so you can access the formula anytime you need it.
- A 10 ounce package of frozen spinach is equivalent to one pound (16 ounces) of fresh spinach.
- A 10 ounce package of frozen spinach is equivalent to 1 1/2 cups after draining.
- One pound (16 ounces) of fresh spinach after being cooked is equivalent to 1 1/2 cups.
10 ounces of frozen spinach or one pound (16 ounces) of fresh spinach cooked equals 1.5 cups drained.
How to substitute fresh spinach for frozen spinach?
Substitute one pound (16 ounces) of fresh spinach per 10 ounces of frozen spinach.
How to substitute frozen spinach for fresh spinach?
Substitute 10 ounces of frozen spinach for one pound (16 ounces) of fresh spinach.
The following video describes how to make healthy creamed spinach.
A Spinach Time Saver
One benefit of frozen vegetables and spinach is it is ready to add straight from the freezer to your recipes. Fresh requires a few steps before you’re prepared to work with it:
- A thorough cleaning. It holds onto some dirt. To avoid an unpleasant texture, you must soak the leaves before using them.
- Trimming the leaves. The leaves have long stems which may be unpleasant to include in your recipes.
- Cook time. Unless you’re planning to use it raw, you’ll need to add cooking time before adding it to your recipe.
Using frozen vegetables is better for the following dishes:
- Soups
- Eggs
- Spinach appetizers
- Casseroles
Fresh is better to use in the following dishes:
- Salads
- Sandwiches
- Wraps
- Sauteed
- Creamed spinach
- Dips
- Juices
- Smoothies

Spinach Prices
How much food cost is important to most people. Lately, it seems the price of grocery items keeps getting higher. Therefore, let’s take a close look at the prices of both foods.
Fresh spinach costs more money per ounce than frozen spinach. The cost for frozen spinach averages $0.12 per ounce and fresh spinach averages $0.16 per ounce.
The difference in cost is more than the $0.04 difference per ounce because it takes 16 ounces of fresh spinach to equal 10 ounces of frozen spinach when cooked. That would equal $2.56 for fresh and $1.20 for frozen.
To conduct some original research, I visited some local supermarkets and checked the prices of each one. Here are my findings.
First I visited a Walmart Supercenter:
- Marketside bagged fresh spinach
- 10 ounce bag for $1.98. Equals $0.20 per ounce
- Birds Eye frozen spinach
- 10 ounce container for $1.37. Equals $0.14 per ounce
I then checked my local Shoprite supermarket:
- Bowl and basket chopped spinach
- 10 ounce bag for $1.29. Equals $0.13 per ounce
- Bowl and basket frozen spinach
- 20 ounce bag for $2.29. Equals $0.11 per ounce

Compare the benefits of these varieties in my article, Baby Spinach vs Spinach: Which is Better? A Comparison.
Storage
Storing Frozen Spinach
Whether you pick it up frozen or freeze your own supply, it lasts months longer than the fresh alternative. Frozen, it will stay in your freezer safely for up to 12 months.
In a seldomly disturbed deep freezer, the shelf life can be even longer.
Once it has been opened, if you haven’t used the entire package how you store it makes a difference. If the bag contains air, it will build a freezer burn and lower the quality.
Transfer any unused to a plastic freezer bag and remove all the excess air. Date the package so you know how long it’s been in the freezer.
Storing Fresh Spinach
Fresh spinach lasts in the refrigerator for about 5-7 days. This is assuming it is appropriately stored in a sealed plastic bag, wrapped in paper towels and hasn’t already been washed.
To maintain its life, don’t wash the leaves until you’re ready to cook or consume them. I used to make the mistake of washing them the moment I got home from the supermarket. This is okay if you’re using all of them that day.
Once it has been cooked, it will last 3-5 days in the refrigerator. Or you can store it in the freezer for up to a year. Check out my article, How to Freeze Spinach.

Glycemic Index
Blood sugar spikes may lead to health complications over time ((National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Know Your Blood Sugar Numbers: Use Them to Manage Your Diabetes)). For this reason, avoiding blood sugar spikes as often as possible is an important part of a healthy diet.
The glycemic index measures how fast food raises blood sugar levels ((Harvard Health Publishing: Glycemic index for 60+ foods)). Foods on the GI scale are categorized as:
- Low-GI foods: 55 or under
- Medium-GI foods: 56-69
- High-GI foods: 70 or over
Frozen and fresh spinach are both low glycemic foods and shouldn’t cause any spikes in blood sugar. In addition, it doesn’t matter if you consume it raw or cooked.
Find out if kale had more nutrients in my article, Kale vs Spinach: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison.
Health Benefits
The nutrients provided by both are similar and therefore the health benefits gained from them are also similar. Let’s examine the nutrients provided and how they benefit health.
Potassium
- Fresh spinach contains more potassium.
According to Harvard Health, a number of studies have shown a connection between low potassium levels and high blood pressure5. The more potassium, the more sodium your body will lose.
Potassium helps the body reduce excess fluid and blood pressure6.
Some medical experts recommend the potassium to sodium ratio of 4:1. Consuming too much sodium or not enough potassium throws off the delicate balance the kidneys need to remove the excess water7.
Magnesium
- Fresh contains 4 mg more of magnesium per 100 grams.
Magnesium helps the body control the following:
- Insomnia
- Muscle function
- Blood sugar
- Systolic and diastolic blood pressure
- Nerve function
Magnesium helps keep blood pressure levels stable and balanced. Recent scientific research examined previous studies and concluded magnesium supplementation decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure8.
One reason many people supplement with magnesium in the evening is because it helps calm the whole body including blood vessels.
Calcium
- Frozen contains 30 mg more of calcium per 100 grams.
Calcium helps the following:
- Help the muscles to function properly.
- Helps nerve function.
- Maintain and build strong bones.
- Heart
- Blood pressure
Harvard Health reports calcium helps maintain blood pressure by helping in the controlling of the relaxing and tightening of blood vessels9.

Vitamin A & Beta Carotene
- Frozen spinach contains more vitamin A and beta-carotene per 100 grams.
Beta-carotene is a compound present in both foods. The body converts beta-carotene into vitamin A.
Vitamin A is a powerful antioxidant that can help reduce cellular damage by controlling the negative effects of free radicals10.
An increased number of vitamin A has been shown to fight and prevent cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of death in the United States11.
But what about the eyes? According to scientific studies, vitamin A helps the eyes when it comes to dim light vision and dry eyes ((National Center for Biotechnology Information: Nutrients for the aging eye)).
B Vitamins
The B vitamins provided by both varieties include the following:
- B1 (thiamin)
- B2 (riboflavin)
- B3 (niacin)
- B5
- B6
- B9 (folate)
B vitamins help support the following:
- Digestion.
- Nerve function.
- Brain function.
- Red blood cells.
- Energy levels.
- Cardiovascular disease.
The following video explains when to use fresh or frozen.
Find out if collard greens are better in my article, Collard Greens vs Spinach: Which is Better? A Comparison.
If you have any questions about this article don’t hesitate to email us. You can find an email on our contact page.
Read More Spinach Food vs Food Articles
Spinach vs Broccoli: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison
Raw Spinach vs Cooked Spinach: Which is Better? A Comparison
Arugula vs Spinach: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison
Organic Spinach vs. Regular Spinach: What’s The Difference?
Spinach vs Lettuce: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison
- USDA: Spinach, raw [↩]
- USDA: Spinach, frozen, chopped or leaf, unprepared [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Impact of Innovative Technologies on the Content of Vitamin C and Its Bioavailability from Processed Fruit and Vegetable Products [↩]
- PennState: Storage time and temperature effects nutrients in spinach [↩]
- Harvard Health: Potassium lowers blood pressure [↩]
- American Heart Association: How Potassium Can Help Control High Blood Pressure [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: The Effect of the Sodium to Potassium Ratio on Hypertension Prevalence: A Propensity Score Matching Approach [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure: a meta-analysis [↩]
- Harvard Health: Key minerals to help control blood pressure [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Antioxidant potentials of vitamin A and carotenoids and their relevance to heart disease [↩]
