Granola vs Oatmeal: Both Have Oats So What’s The Difference?
As a Certified Health Coach many of my clients ask about granola and oatmeal, two popular breakfast foods. Granola contains oats causing many people to wonder about their differences. Let’s answer, what’s the difference between granola and oatmeal?
Granola is made from dried oats and wheat bound together with a sweetener like honey. Oatmeal is made by hulling and steaming whole oat grains which are rolled or chopped. It is consumed by cooking or soaking the oats in water or milk while granola is typically consumed dry.
This article will include a side-by-side comparison of the nutrients contained in both. In addition, I’ll examine their tastes, textures, glycemic index, satiety index, prices, storage methods and health benefits.
In addition to coaching clients about them, I’ve purchased, researched and consumed both prior to, during and sometimes after writing this article.

Granola vs Oatmeal: The Difference
Before we compare the nutrients of both foods, let’s take a deeper look at their differences.
Granola consists of dried oats, wheat and is bound together with a sweetener like honey or maple syrup.There are different variations with some containing raisins, chopped nuts, seeds and different oils.
Oat Granola
Some, the healthier version called oat granola, is made only with oats and honey to hold it all together.
Granola is typically served for breakfast, added to yogurts or made into snack bars. For this reason, it is mostly consumed all day long. It is mostly eaten cold but can be hot when mixed into baked goods.
Oats
Because it is the primary ingredient in oatmeal, the different types come down to how the oat is flattened and sliced.
There are four main types of oats:
- Rolled: Rolled oats are the classic oat used in most varieties. These are also called regular or old-fashioned.
- Steel-cut: Steel-cut oats is typically chewier and heartier. You can also use these as a substitution for traditional rice dishes, like risotto.
- Stone-ground: Stone-ground oats make the creamiest type.
- Quick: Quick oats, often called instant, are thinner rolled oats. These are often used in instant and microwavable versions because they don’t take as long to cook.
It is mostly served for breakfast and is not typically consumed during the day or even. It is mostly eaten hot but can be served cold like when making the overnight type.
People often add chopped nuts, fruit or cinnamon.
Because both foods are ate for breakfast and have some of the same ingredients, many people often place them into the same food category.
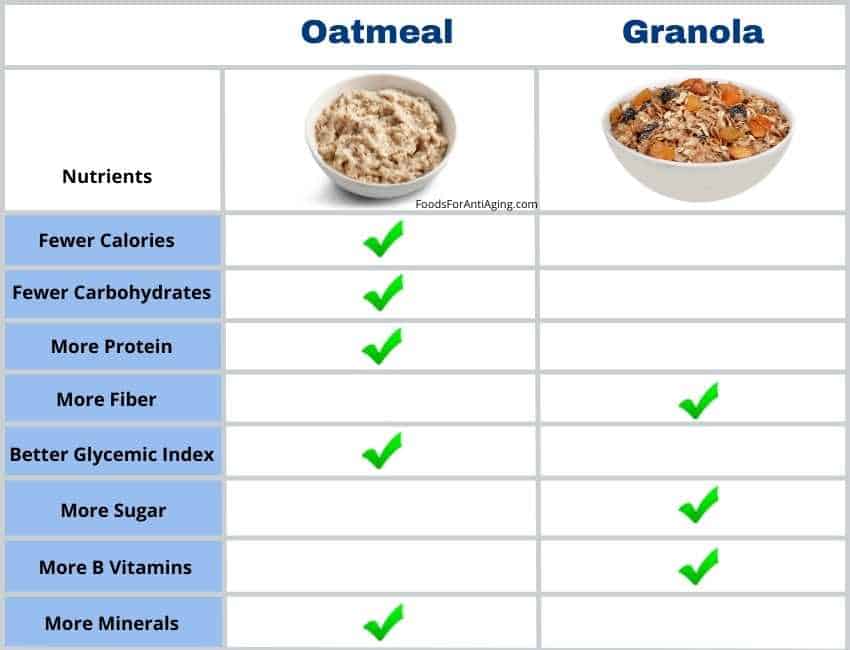
Granola vs Oatmeal: Nutrient Comparison
Both can be made with different ingredients which change their nutritional values.
For example, granola can be made with nuts or without. Some may contain coconut oil and honey while others may have just the honey.
Sometimes people add banana, apple or mixed nuts to their oatmeal. Each different version has more nutrients added. Cooking it compared to soaking it over night also changes the nutritional value.
To keep the comparison as fair as possible, the table below will compare dry oats since most granola is consumed dry also. The granola only contains natural granola, oats, wheat and honey. The meal is unfortified and does not contain added ingredients.
The following table is a side-by-side comparison of the nutrients contained in both.
| Oatmeal Dry (100 g) | Granola (100 g) | |
| Calories | 379 | 421 |
| Protein | 13.2 g | 10.6 g |
| Carbohydrates | 67.7 g | 73.6 g |
| Fiber | 10.1 g | 10.2 g |
| Fat | 6.52 g | 11.6 g |
| Sugar | 0.99 g | 20.3 g |
| Vitamin A | 0 IU | 8 IU |
| Beta-carotene | 0 mcg | 1 mcg |
| Vitamin C | 0 mg | 0.2 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.10 mg | 0.23 mg |
| Vitamin B9 (Folate) | 32 mcg | 37 mcg |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 0.46 mg | 0.41 mg |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0.15 mg | 0.28 mg |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | 1.12 mg | 2.31 mg |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | 1.12 mg | 1.34 mg |
| Magnesium | 138 mg | 121 mg |
| Phosphorous | 410 mg | 392 mg |
| Potassium | 362 mg | 483 mg |
| Iron | 4.25 mg | 2.81 mg |
| Copper | 0.39 mg | 0.31 mg |
| Calcium | 52 mg | 109 mg |
| Zinc | 3.64 mg | 2.95 mg |
Is Granola or Oatmeal Healthier?
Both oatmeal and granola contain the same types of nutrients. At first it’s difficult to determine which one provides a higher percentage than the other. This causes many people to ask, which is more healthier?
Oatmeal is healthier than granola due to its fewer calories, sugar, carbohydrates and a higher percentage of protein and minerals. It provides a higher percentage of thiamin, magnesium, phosphorus, iron, copper and zinc. Granola contains more calories, total fat and 1,950% more sugar.
In moderation granola is also healthy and contains many beneficial nutrients. It provides a higher percentage of B6, folate, riboflavin, niacin, B5, potassium and calcium.
I mostly eat oatmeal than the alternative. I find it healthier and I enjoy it more. I always try to consume it for breakfast on gym days for the extra carbs.
Choosing one or the other may depend on your particular goal. One of these goals may be weight loss.
Weight Loss
Oatmeal is better for weight loss due to its fewer calories, total fat and sugar. It contains 11% less calories per 100 grams than granola.
Fiber
Granola contains more fiber. It provides 10.2 grams of fiber per 100 grams while oatmeal provides 10.1 grams.
Protein
Oatmeal contains more protein per serving. It provides 13.2 grams of protein per 100 gram serving while granola provides 10.6 grams.
Bodybuilding: Workouts and Fitness
Granola is better for building muscle and athletic performance due to its higher percentage of carbohydrates and calories. The extra calories and protein help to gain weight, muscle and repair muscle. The extra carbs help to provide energy while lifting weights.
Carbohydrates
Granola contains 73.6 grams of carbohydrates per 100 gram serving. If you’re on a low carb or Keto diet, oatmeal, which contains 5.9 fewer grams, is the better choice.
Taste and Texture of Granola and Oatmeal
It’s not always about the nutrients provided. Many times people choose one food over the other because of its taste or according to their mood.
Since there are some similarities between the two, many people wonder and ask, do they taste the same?
Oatmeal is blander and has less flavor than granola. Granola tastes sweeter due to the added honey. If the granola has fruit added it can taste fruity and sweet. Oatmeal’s texture is not smooth, but granola is harder and crunchier. Granola is drier than oatmeal which is more moist or wet.
Granola has a sweet taste due to the honey and sugar added to its oats. The type containing fruit tastes sweet and fruity. Its taste will change depending on the ingredients added. Its texture is dry and crunchy and consists of small and larger clusters.
Old-fashioned rolled oats have a chewier texture than the smoother instant type of meal.
To conduct original research, I polled some of my readers and people in food groups I belong to. I asked, which do you prefer the taste of?
- 42% said they preferred the taste of granola.
- 40% said they preferred the taste of oatmeal.
- 18% said they had no preference.
To conduct more original research I thought it would be fun to set up my own taste test at home. Nuts and bananas were added to the meal which we tried at breakfast. 75% picked the oatmeal making it the winner at home but a loser in the poll.
Find out how brown rice compared in my article here.

Glycemic Index
The Glycemic Index (GI) is a scale measuring how fast a particular food raises the blood sugar in the blood3. Blood sugar spikes can lead to health complications with the heart, nerves, kidneys and eyes4.
Foods on the GI scale are categorized as:
- Low-GI foods: 55 or under
- Medium-GI foods: 56-69
- High-GI foods: 70 or over
How blood sugars levels are affected:
- Foods with a glycemic index 70 or more cause a quicker spike in blood sugar levels.
- Foods with a glycemic index 56 to 69 cause a moderate spike in blood sugar levels.
- Foods with a glycemic index 55 or less cause a slow spike in blood sugar levels.
Having more knowledge of the glycemic index of food and how it raises blood sugar, many people wonder which food has a higher GI.
Oatmeal and granola are both a medium-GI food. Although granola with much added sugar has a higher GI than oatmeal. Rolled oats have a GI of 55. Instant has a GI of 79. Steel-cut has a low GI under 55.
The more added high sugar ingredients, the more GI.
Steel-cut has a lower GI because they are the least processed. Rolled oats are a little higher because they’ve been partially cooked. Quick oats have been steamed and rolled into thinner pieces to cook quicker. This process increases their GI.
Find out how white rice compared in my article here.
Satiety Index
Satiety is a term used to explain the feeling of being full and the loss of appetite which occurs after eating food. The satiety index is a scale showing how full a person feels after eating a certain food.
The satiety index was developed in 1995 from a study which tested 38 foods. The foods were ranked how they satisfied a person’s hunger. Foods scoring under 100 are considered less filling and foods scoring above 100 are considered more filling ((National Center for Biotechnology Information: A satiety index of common foods)).
The table below shows the satiety scores of some foods.
| Food | Satiety Index Score |
| Muesli | 100% |
| Brown rice | 132% |
| Lentils | 133% |
| Wholemeal Bread | 157% |
| Brown pasta | 188% |
| Oatmeal w/milk | 209% |
Comparing the table above will help answer the question, which food keeps you full longer?
Compared to granola, oatmeal will keep you full longer after breakfast due to its higher satiety index of 209%. Granola has a satiety score of 100%.
Of all the 38 foods, it scored the fourth highest only beat by oranges, ling fish and boiled potatoes.
High satiety foods are likely to have a high satiety score for the following reasons:
- High in protein.
- High in fiber.
- High in volume (foods containing a lot of water or air).
- Low in energy density (foods low in calories for their weight).
Cooked, it seems to fit into all four listed above which is why oatmeal is more likely to satisfy your hunger.
Granola contains many calories for its light weight and doesn’t have as much water. These two factors make them less filling.
Find out if grits have the better satiety in my article.
Costs
It seems every time I check out at the supermarket the price is higher than the last time and I have less groceries in my cart. The price of food certainly matters to most, especially with the rising costs of everything.
The price may sway your decision about which one to use in your meals more often. Therefore, let’s take a closer look at which costs more.
Granola costs more per serving than oatmeal. The average price for quick oats is $0.25 per 1/2 cup serving. The average price for granola is $0.62 per 1/2 cup serving.
To conduct more original research, I decided to visit various different stores to compare the price of both.
I first visited the Shoprite supermarket for the prices:
- Wholesome Pantry Oats & Honey Granola
- $4.49 per 12 oz bag (6 servings) equaling $0.74 per 1/2 cup serving
- Quaker quick oats
- $4.99 per 18 oz container (13 servings) equaling $0.38 per 1/2 cup serving
I then checked Walmart:
- Oats & Honey Granola (Store brand)
- $2.36 per 11 oz bag (6 servings) equaling $0.39 per 1/2 cup serving
- Nature Valley Oats & Honey Granola
- $4.38 per 11 oz bag (5 servings) equaling $0.73 per 1/2 cup serving
- Quaker quick oats
- $4.98 per 42 oz container (30 servings) equaling $0.17 per 1/2 cup serving
- Quaker quick oats
- $2.73 per 18 oz container (13 servings) equaling $0.21 per 1/2 cup serving
Find out how quinoa compared in my article here.
How To Store Oats
Whichever you choose or have on hand, proper storage is crucial. How you store items can affect how long they last before going bad and how they taste.
Storing Granola
The best way to store unopened or opened granola is to keep it in a cool, dry place away from the sun or indirect heat. After opening, it should be transferred to a tightly covered glass container, plastic container or a resealable bag. Opened, uncooked does not have to be refrigerated.
Opened it should be transferred out of its original bag or packaging. An airtight container prevents exposure to the outside air which may cause staleness sooner.
Storing it in the refrigerator may cause it to turn soggy. Granola can be stored in a cool area up to six months.
For longer-term storage, it can be frozen. Place it into a plastic freezer bag and remove all the excess air. Date the bag and store it in the freezer for up to eight months.
The best way to remove the excess air is to use a vacuum sealer. They are one of those items making you wonder how you did without one before purchasing it.
Store unopened dry oatmeal in a cool, dry place away from the heat and sun. Opened it should be tightly covered in its original container, glass or plastic container or resealable bag. Opened, uncooked does not have to be refrigerated.
Opened it should be stored up to one year. Always check the dates on the packaging. Typically, the “best if used by date” is a quality suggestion5.
I store mine at home in a cool cabinet away from the heat. Below is a picture of my opened container in my kitchen cabinet.

I compared everything to Cream of Wheat in my article here.
Health Benefits of Granola
Potassium
- Granola contains more potassium per 100 g.
Some medical experts recommend the potassium to sodium ratio of 4:1. Consuming too much sodium or not enough potassium throws off the delicate balance the kidneys need to remove the excess water6.
Potassium helps the body get rid of excess sodium reducing fluid build-up. These help keep systolic and diastolic blood pressure lower ((American Heart Association: How Potassium Can Help Control High Blood Pressure)).
According to Harvard Health, a number of studies have shown a connection between low potassium levels and high blood pressure7. The more potassium, the more sodium your body will lose.
Fiber
- Granola contains 10.2 grams of fiber per 100 g.
Both foods are high in soluble fiber, which is helpful for many reasons ((National Center for Biotechnology Information: Mechanisms linking dietary fiber, gut microbiota and colon cancer prevention)). What makes fiber soluble is it dissolves in water.
Soluble fiber is known for the following:
- Help overall digestive health.
- Decrease the risk of diabetes by managing the blood glucose levels.
- Helps avoid constipation and have a more regular stool.
- Aids greatly in weight management because it allows you to feel full faster and eat less.
Calcium
- Granola contains 109 mg of calcium per 100 g.
Calcium is important for the heart and blood pressure. Harvard Health reports calcium helps maintain blood pressure by helping in the controlling of the relaxing and tightening of blood vessels8.
Calcium also helps the following:
- Help the muscles to function properly.
- Helps nerve function.
- Build and maintain strong bones.
Is there a difference between overnight and regular? Find out in my article.

B Vitamins
Of the six B vitamins listed below, granola provides a higher percentage of five of them compared.
The B vitamins provided include the following:
- B1 (thiamin)
- B2 (riboflavin)
- B3 (niacin)
- B5
- B6
- B9 (folate)
B vitamins help support the following:
- Digestion.
- Nerve function.
- Cardiovascular disease.
- Red blood cells.
- Brain function.
- Energy levels.
A lack of B vitamins has been associated with oxidative stress and neural inflammation. In a study released in 2018 32 healthy adults were given B vitamin supplementation for six months. The results indicated preliminary evidence B vitamin supplementation reduced oxidative stress and inflammation9.
Health Benefits of Oatmeal
Iron
- Oatmeal has more iron, 4.25 mg of iron per 100 g.
Much higher in iron than other grains, it is an excellent choice if you need to get your daily value of iron. Iron is essential in the creation of red blood cells and is a necessary part of any healthy diet.
Iron is also vital for growth and development, as some hormones need iron to be appropriately balanced10.
Find out if there is a difference in benefits between steel cut and regular in my article.
Phosphorus
- It contains 410 mg of phosphorus per 100 g.
Phosphorus has been shown in scientific studies to help with the following:
- Help the body store and manage energy.
- Promote healthy nerve conduction.
- Promote bone and teeth strength.
- Muscle contraction.
- Muscle recovery.
- Help the kidneys remove waste.
Magnesium
- It contains 138 mg of magnesium per 100 g.
Magnesium helps keep blood pressure levels stable and balanced. Recent scientific research examined previous studies and concluded magnesium supplementation decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure11.
Magnesium helps control the following:
- Insomnia
- Muscle
- Blood pressure
- Blood sugar
- Nerve function
In the heart and muscles, magnesium competes with calcium to help the muscles relax after contracting. When the body is low in magnesium, calcium can over stimulate the heart muscle’s cells causing a rapid or irregular heartbeat12.
One reason many people supplement with magnesium in the evening is because it helps calm the whole body including blood vessels.
Gluten-Free
Oats and granola made with oats and honey are naturally gluten-free and might be a great substitute to other gluten-heavy items of a similar taste. Even those who don’t have a completely gluten-free diet may benefit from cutting down on their gluten.
Some granola may contain wheat, wheat flour or other ingredients not gluten-free. This type wouldn’t be gluten free. Always check the label of your food product.
Recently it has been discussed many more people have at least a small amount of gluten intolerance and are unaware of it. Having less gluten in your diet is a good choice for most.
Important: Although oats and granola made from just oats and honey are gluten free, they may come in contact with gluten-containing grains in storage or during transportation. Most of the Quaker products have solved this issue and label those products gluten free. Always check the label of your products to determine if its gluten free.
Saturated Fat
Unsweetened, both foods don’t have much unhealthy saturated fat. On the other hand, when unhealthy additives are added into the lower quality varieties, it can change the equation.
You’re more likely to find the unhealthier ingredients in granola bars. These are the kind mostly found in gas station food shelves people will grab for breakfast, living on the go.
Cholesterol
The ingredients in some of the unhealthy bars have been shown in some scientific studies about how they raised cholesterol. Oatmeal has done the opposite and has been shown to lower bad cholesterol.
Is eggs the better breakfast? Find out in my article here, Eggs – Which Is Better? Let’s Compare.
Read Next – More Food Articles!
Muesli vs Oatmeal – What’s The Difference? Let’s Compare
Oatmeal vs Porridge: Are They The Same?
Oatmeal Vs. Oat Bran: A Comparison
Bread vs Oatmeal: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison
If you have any questions about this article don’t hesitate to email us. You can find an email on our contact page.
- USDA: Cereals, oats, regular and quick, not fortified, dry [↩]
- USDA: Cereals ready-to-eat, Quaker, 100% Natural Granola, Oats, Wheat and Honey [↩]
- Harvard Health Publishing: Glycemic index for 60+ foods [↩]
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Know Your Blood Sugar Numbers: Use Them to Manage Your Diabetes [↩]
- Michigan State University: Dry needs careful handling [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: The Effect of the Sodium to Potassium Ratio on Hypertension Prevalence: A Propensity Score Matching Approach [↩]
- Harvard Health: Potassium lowers blood pressure [↩]
- Harvard Health: Key minerals to help control blood pressure [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: The Effect of a High-Dose Vitamin B Multivitamin Supplement on the Relationship between Brain Metabolism and Blood Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress: A Randomized Control Trial [↩]
- National Institutes of Health: Iron [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure: a meta-analysis [↩]
- National Institutes of Health: Magnesium [↩]
