Grits vs Oatmeal: Corn or Oats – Which is Better?
Since I specialize in nutrition, during my Heath Coaching sessions many people ask about oatmeal. Itself and grits have their own nutritional values causing many people to ask if one is better than the other. Let’s answer, grits vs oatmeal, which is better?
Oatmeal is better due to its higher percentage of fiber, protein and minerals. It has a little more natural flavor than grits which need more flavor additions. Grits take longer to cook and have a higher glycemic index score.
This article will include a side-by-side comparison of the nutrients contained in both. In addition, I’ll examine their tastes, textures, glycemic index, satiety index, prices, storage methods and health benefits.
I’ve purchased, researched and consumed both of these prior to, during and sometimes after writing this article.
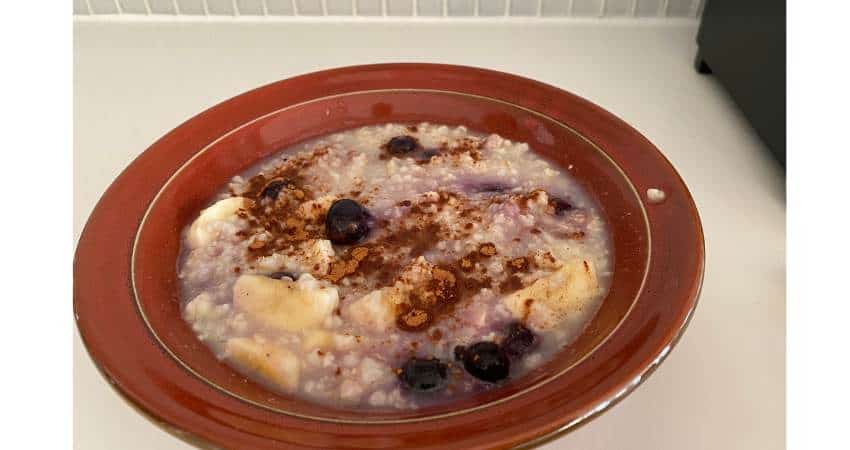

Grits vs Oatmeal: The Difference
Depending on what area you’re from, one of these two foods may be unfamiliar with you. Grits are more popular in the south and are on every menu. Up north, most menus don’t offer them as an option, but you’ll find the other. For this reason, some people don’t know much about one of them.
Let’s discuss some of their differences.
Grits are made by removing the hull and germ of dried kernels of corn and then ground. Oatmeal is made by hulling and steaming whole oat grains which are chopped or rolled. Oatmeal cooks faster than grits. Grits are more often served for breakfast, lunch or dinner while oatmeal is primarily served at breakfast.
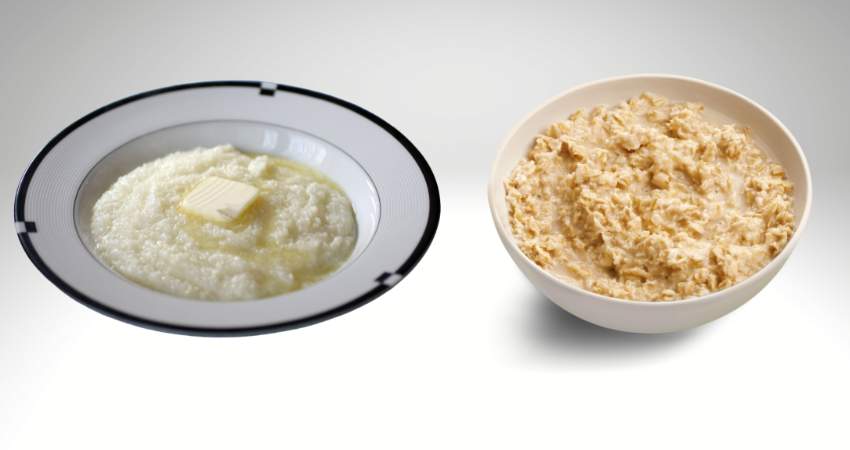

Grits
Grits are a type of porridge made from ground corn. Most of them found in stores are known as hominy. They are made by soaking corn kernels, typically dent corn kernels, in an alkali solution removing the hulls of the corn kernel.
The results are then ground down resulting in the finished product.
Stone-ground are made from grinding the whole dried corn kernel, but this kind is much rarer due to its short shelf life.
Oatmeal
Because oats are the primary ingredient, the different types come down to how the oat is flattened and sliced.
There are four main types:
- Rolled: Rolled oats are the classic type. These are also called regular or old-fashioned.
- Steel-cut: Steel-cut is typically chewier and heartier. You can also use these them as a substitution for traditional rice dishes, like risotto.
- Stone-ground: Stone-ground make a creamier dish.
- Quick: Quick oats, often called instant, are thinner rolled oats. These are often used in instant and microwavable versions because they don’t take as long to cook.
Nutrition Comparison
Both foods have a similar nutritional profiles, although there are key differences between the two. The following table is a side-by-side comparison of the nutrients contained in each one. Both are unenriched with no other ingredients.
The 100-gram amount is more than one cup and a serving but was used for an even comparison.
| Oatmeal Dry (100 g) | Grits Dry (100 g) | |
| Calories | 379 | 371 |
| Protein | 13.2 g | 8.8 g |
| Carbohydrates | 67.7 g | 79.6 g |
| Fiber | 10.1 g | 1.6 g |
| Fat | 6.52 g | 1.20 g |
| Sugar | 0.99 g | 0.64 g |
| Vitamin A | 0 IU | 214 IU |
| Beta-carotene | 0 mcg | 97 mcg |
| Vitamin C | 0 mg | 0 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.10 mg | 0.14 mg |
| Vitamin B9 (Folate) | 32 mcg | 5 mcg |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 0.46 mg | 0.13 mg |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0.15 mg | 0.04 mg |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | 1.12 mg | 1.20 mg |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | 1.12 mg | 0.48 mg |
| Magnesium | 138 mg | 27 mg |
| Phosphorous | 410 mg | 73 mg |
| Potassium | 362 mg | 137 mg |
| Iron | 4.25 mg | 1.00 mg |
| Copper | 0.39 mg | 0.07 mg |
| Calcium | 52 mg | 2 mg |
| Zinc | 3.64 mg | 0.41 mg |
At first it’s difficult to determine which one provides a higher percentage of nutrients than the other. This causes many people to wonder which one is healthier.
Oatmeal is healthier than grits due to its higher percentage of protein, fiber, B vitamins and minerals. It provides a greater number of folate, thiamin, riboflavin, B5, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, iron, copper, calcium and zinc.
Grits contain slightly fewer calories, less total fat and sugar. They provide a higher percentage of vitamin A, B6 and niacin.
Other than my trip to South Carolina, I rarely eat them. Although the experience and dishes tasted great. I always eat oatmeal due to its nutrient benefits.
You can’t go wrong with either option and which one you choose may come down to a specific goal.
Which to Choose
Some people may alternate between the two or choose one due to their particular goals. Let’s take a look at some of the popular goals.
Low Carb or Keto Diets
The goal for most low-carb diets is consuming few carbohydrates while adding more healthy fat and protein. With such a restrictive carbohydrate intake, every gram of carbs may make a difference.
Therefore, let’s examine which one has fewer carbohydrates or more healthy fats and protein.
- Oatmeal is better for low-carb diets due to its fewer carbohydrates. Corn grits are higher in carbohydrates per 100 gram serving.
- It provides 11.9 fewer grams of carbohydrates per 100 grams.
- In addition, it contains more fat and protein.
Weight Loss and Calories
Weight loss may be the most popular goal. If you’re trying to lose extra pounds from the midsection area, the number of calories may matter to you. Therefore, let’s examine which is better for weight loss.
- Oatmeal is higher in both fiber and protein than grits making it better for weight loss. The fiber may help increase the feeling of fullness and suppress the appetite.
How you prepare each food makes a huge difference when the goal is losing weight. Hominy is often combined with cheese, cream, butter, maple syrup, sausage, ham or bacon. Oatmeal is more often served with mixed nuts, pieces of fruit and cinnamon which is better.
Gluten Free
Avoiding any gluten is the main goal for people who wish to follow a gluten free diet or have Celiac disease. Therefore, let’s answer which one is gluten free.
- Oats and grits are naturally gluten-free although some may come into contact with gluten products, or cross-contamination is possible with machinery or during storage. Always check the label of your product for the gluten free label.
Vegan or Vegetarian
If you’re thinking about following a vegan or vegetarian diet consuming dairy products or animal-derived products is important. Knowing which food is vegan or vegetarian friendly may help you choose between the two.
- Oatmeal and grits do not contain animal products making them both beneficial for vegans and vegetarians.
Bodybuilding
- Oatmeal is better than grits for bodybuilding due to its greater number of proteins, calories and minerals.
Regardless of whether a bodybuilder is in a cutting, bulking or maintenance phase, they need much protein to repair their muscles and elicit a hypertrophy effect. Dry, oatmeal contains 50% more protein per 100 grams.
Bodybuilders need a good amount of carbohydrates as well. The majority of their macronutrient balance should be made up of healthy carbohydrates. Carbohydrates help to fuel energy and increase performance during exercise. Both options provide a good amount of carbs.
The difference between them will not make a difference when fueling energy for a workout session.
I always eat oatmeal for breakfast on the days I’m going to the gym to lift weights. The extra, healthy carbs gives me more energy and the weights just feel a little lighter when I do.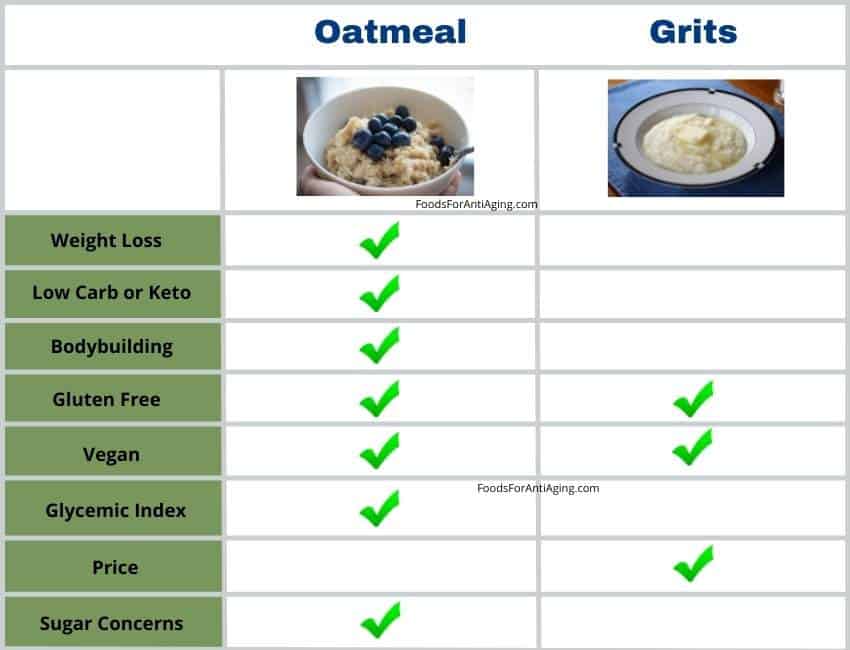
Health Benefits
Both foods provide nutrients in different amounts. For this reason the food with more of a particular nutrient offers the better benefit. Since oatmeal provides a greater number of many of the nutrients, we’ll start there first.
What Makes Oatmeal Healthy
Soluble Fiber
It contains 10.1 grams of fiber per 100 grams. It is high in soluble fiber, which is helpful for many reasons ((National Center for Biotechnology Information: Mechanisms linking dietary fiber, gut microbiota and colon cancer prevention)). What makes fiber soluble is it dissolves in water.
Soluble fiber is known for the following:
- Decrease the risk of diabetes by managing the blood glucose levels.
- Helps avoid constipation and have a more regular stool.
- Help overall digestive health.
- Aids greatly in weight management because it allows you to feel full faster and eat less.
High in Iron
It contains 4.25 mg of iron per 100 grams. Much higher in iron than other grains, it is an excellent choice if you need to get your daily value of iron. Iron is essential in the creation of red blood cells and is a necessary part of any healthy diet.
Iron is also vital for growth and development, as some hormones need iron to be appropriately balanced.
Calcium
It contains 52 mg of calcium per 100 grams: Calcium is important for the heart and blood pressure. Harvard Health reports calcium helps maintain blood pressure by helping in the controlling of the relaxing and tightening of blood vessels3.
Calcium also helps the following:
- Helps nerve function.
- Help the muscles to function properly.
- Build and maintain strong bones.
The following Healthline video explains the benefits of oats.
Potassium
Potassium helps the body get rid of excess sodium reducing fluid build-up. These help keep systolic and diastolic blood pressure lower ((American Heart Association: How Potassium Can Help Control High Blood Pressure)).
According to Harvard Health, a number of studies have shown a connection between low potassium levels and high blood pressure4. The more potassium, the more sodium your body will lose.
Consuming too much sodium or not enough potassium throws off the delicate balance the kidneys need to remove the excess water5.
Phosphorus
It contains 410 mg of phosphorus per 100 grams: Phosphorus has been shown in scientific studies to help with the following:
- Muscle contraction.
- Muscle recovery.
- Help the kidneys remove waste.
- Help the body manage and store energy.
- Promote healthy nerve conduction.
- Promote teeth and bone strength.
Magnesium
It contains 138 mg of magnesium per 100 grams: Magnesium helps keep blood pressure levels stable and balanced. Recent scientific research examined previous studies and concluded magnesium supplementation decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure6.
Magnesium helps control the following:
- Blood sugar
- Blood pressure
- Insomnia
- Muscle
- Nerve function
One reason many people supplement with magnesium in the evening is because it helps calm the whole body including blood vessels. In the heart and muscles, magnesium competes with calcium to help the muscles relax after contracting.
When the body is low in magnesium, calcium can over stimulate the heart muscle’s cells causing a rapid or irregular heartbeat ((National Institutes of Health: Magnesium)).
Find out if there is a difference in benefits between steel cut and regular in my article.
B Vitamins
Of the six B vitamins listed below, oatmeal provides a higher percentage of four of them.
The B vitamins provided include the following:
- B1 (thiamin)
- B2 (riboflavin)
- B3 (niacin)
- B5
- B6
- B9 (folate)
B vitamins help support the following:
- Digestion.
- Brain function.
- Cardiovascular disease.
- Nerve function.
- Red blood cells.
- Energy levels.
A lack of B vitamins has been associated with oxidative stress and neural inflammation.
In a study released in 2018 32 healthy adults were given B vitamin supplementation for six months. The results indicated preliminary evidence B vitamin supplementation reduced oxidative stress and inflammation7. 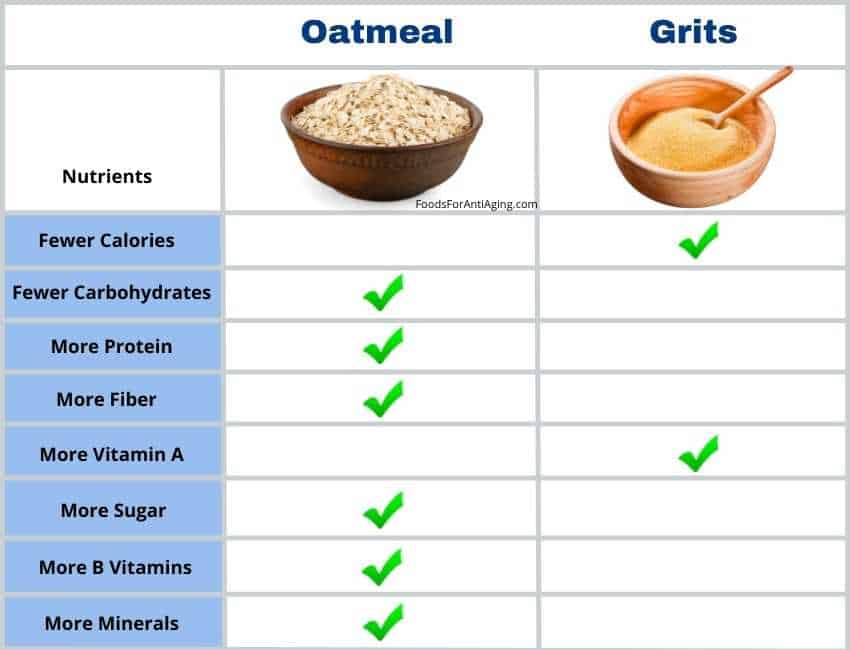
Why Grits Are Healthy Eating
Grits contain all of the nutrients listed above. Therefore, they provide a similar benefit but in smaller amounts due to their fewer percentages of those nutrients.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants are a very important part of any diet, and grits are rich in these. They protect the cells from free radical damage, which is the leading cause of cancer and other chronic diseases caused by cell damage.
They contain the following antioxidants:
- Lutein
- Zeaxanthin
- Syringic acid
- Caffeic acid
- 4-OH benzoic acid
Eye Health
Studies have shown the antioxidants lutein and zeaxanthin may protect against degenerative eye disorders like cataracts and may protect your skin from sun damage8.
Both antioxidants are found in high concentrations inside the retina part of the eye. The two antioxidants may help protect the eyes against potentially harmful blue light. Too much blue-wavelength light exposure can cause damage to the eye’s cornea9.
Gluten-Free Alternative
Grits and oats are naturally gluten-free and might be a great substitute to other gluten-heavy items of a similar taste. Even those who don’t have a completely gluten-free diet may benefit from cutting down on their gluten.
Recently it has been discussed many more people have at least a small amount of gluten intolerance and are unaware of it. Having less gluten in your diet is a good choice for most.
I compared Cream of Wheat in my article.

Taste and Texture
Many times people choose one food over the other because of its taste. Since there are some similarities between the two, many people wonder and ask, does grits taste like oatmeal?
Grits and oatmeal taste different. Cooked grits are blander and have less flavor. The ingredients added to them will make them taste more like the ingredient added. Oatmeal has an earthier flavor and the texture is not as smooth as grits.
Most food experts and chefs claim stone ground have more corn flavor and a better texture than instant. Old-fashioned rolled oats have a chewier texture than the smoother instant type.
I wanted to get the opinion of real people like you by conducting some original research. Therefore, I reached out to some clients, members of food groups and readers. I asked, which one tastes better?
- 59% said they preferred the taste of oatmeal.
- 34% said they preferred the taste of grits.
- 7% said they had no preference.
I also participated in my own blind taste test. I had two bowls made, one of each food. I didn’t add any extra ingredients and tasted them both plain. I chose the oatmeal as the tastier dish. I wonder if my choice would have been different if ingredients were added in.
In the taste poll and in my own taste test, the results were the same.
Find out how quinoa compared in my article here.
Glycemic Index and Diabetics
The glycemic index is important especially if blood sugar levels are a concern. Avoiding blood sugar spikes is an important part of consuming healthy food for diabetics or anybody. The Glycemic Index (GI) is a scale measuring how fast a particular food raises the blood sugar in the blood10.
Blood sugar spikes can lead to health complications with the heart, nerves, kidneys and eyes11.
How blood sugar levels are affected:
- Foods with a glycemic index 70 or more cause a quicker spike in blood sugar levels.
- Foods with a glycemic index 56 to 69 cause a moderate spike in blood sugar levels.
- Foods with a glycemic index 55 or less cause a slow spike in blood sugar levels.
Foods on the GI scale are categorized as:
- Low-GI foods: 55 or under
- Medium-GI foods: 56-69
- High-GI foods: 70 or over
Now we know what the glycemic index is, and how it affects blood sugar, let’s answer, which food has a higher GI?
The glycemic index of grits is higher than oatmeal. Grits made from fermented corn flour have a GI of 65 while those from non-fermented corn flour have a GI over 90. Rolled oats have a GI of 55. Instant has a GI of 79. Steel-cut oats have a low GI under 55.
Steel-cut has a lower GI because they are the least processed. Rolled oats are a little higher because they’ve been partially cooked. Quick and instant have been steamed and rolled into thinner pieces to cook quicker. This process increases their GI.
Find out if brown rice has the better satiety index in my comparison article.
Satiety Index
Satiety is a term used to explain the feeling of being full and the loss of appetite which occurs after eating food. The satiety index is a scale showing how full a person feels after eating a certain food.
The satiety index was developed in 1995 from a study which tested 38 foods. The foods were ranked how they satisfied a person’s hunger. Foods scoring under 100 are considered less filling and foods scoring above 100 are considered more filling ((National Center for Biotechnology Information: A satiety index of common foods)).
The table below shows the satiety scores of breakfast cereals with milk.
| Food | Satiety Index Score |
| Muesli | 100% |
| Sustain | 112% |
| Special K | 116% |
| Corn Flakes | 118% |
| Honey Smacks | 132% |
| All-Bran | 151% |
| Porridge | 209% |
| Oatmeal | 209% |
Oatmeal and porridge scored 209%. They scored the highest of the breakfast cereals tested. The study results didn’t mention what the porridge was made from. Technically, both foods or other similar dishes are a type of porridge.
Of all the 38 foods, it scored the fourth highest only beat by oranges, ling fish and boiled potatoes.
High satiety food is likely to have a high satiety score for the following reasons:
- High in protein.
- High in fiber.
- High in volume (foods containing a lot of water or air).
- Low in energy density (foods low in calories for their weight).
Check out how granola compared in my article here.
Prices
The cost of food certainly matters to most, especially with the rising costs of everything. The price may sway your decision about which one to use in your meals more often. Therefore, let’s examine which costs more.
Oatmeal costs more than grits. The average price for quick oats is $0.19 per serving. The average price for quick grits is $0.15 per serving.
To conduct more of my own research, I decided to visit various different stores to compare the prices.
I visited the Shoprite supermarket first for the prices:
- Quaker quick grits
- $2.39 per 24 oz container (14 servings) equaling $0.17 per 1/4 cup serving
- Quaker quick oats
- $4.99 per 18 oz container (13 servings) equaling $0.38 per 1/2 cup serving
I then checked Walmart:
- Quaker quick grits
- $2.00 per 24 oz container (14 servings) equaling $0.14 per 1/4 cup serving
- Quaker quick oats
- $4.98 per 42 oz container (30 servings) equaling $0.17 per 1/2 cup serving
- Quaker quick oats
- $2.73 per 18 oz container (13 servings) equaling $0.21 per 1/2 cup serving

How To Store
Whichever you choose or have on hand, proper storage is crucial. How you store food can affect how long they last before going bad and how they taste.
Store unopened dry grits in a cool, dry place away from the heat and sun. Opened it should be tightly covered in its original container, glass or plastic container or resealable bag. Opened, uncooked does not have to be refrigerated.
Opened it should be stored in a sealed container up to one year. Always check the date on the packaging. Cooked it should be stored in a sealed container in the refrigerator up to three days.
Store unopened dry oatmeal in a cool, dry place away from the heat and sun. Opened should be tightly covered in its original container, glass or plastic container or resealable bag. Opened, uncooked does not have to be refrigerated.
Opened it should be stored up to one year. Always check the dates on the packaging. Typically, the “best if used by date” is a quality suggestion. Cooked it should be stored in a sealed container in the refrigerator up to three days.
I buy the biggest oat container in the store. It’s cheaper and I eat enough of it so I know it won’t last too long. I store it in a cool, dry cabinet and never have an issue with it going bad.
Find out how overnight oats compared to regular in my article here.
Is oatmeal better than eggs? Find out in my article here.
If you have any questions about this article don’t hesitate to email us. You can find an email on our contact page.
Read Next – More Food Articles!
Muesli vs Oatmeal – What’s The Difference? Let’s Compare
Oatmeal vs Porridge: Are They The Same?
Oatmeal vs Rice: Which Is More Healthy? (We Find Out)
Oatmeal Vs. Oat Bran: A Comparison
Bread vs Oatmeal: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison
Oatmeal vs Cereal – Which is Better? Let’s Compare
- USDA: Cereals, oats, regular and quick, not fortified, dry [↩]
- USDA: Cereals, corn grits, yellow, regular and quick, unenriched, dry [↩]
- Harvard Health: Key minerals to help control blood pressure [↩]
- Harvard Health: Potassium lowers blood pressure [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: The Effect of the Sodium to Potassium Ratio on Hypertension Prevalence: A Propensity Score Matching Approach [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure: a meta-analysis [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: The Effect of a High-Dose Vitamin B Multivitamin Supplement on the Relationship between Brain Metabolism and Blood Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress: A Randomized Control Trial [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Overall skin tone and skin-lightening-improving effects with oral supplementation of lutein and zeaxanthin isomers: a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: The Photobiology of Lutein and Zeaxanthin in the Eye [↩]
- Harvard Health Publishing: Glycemic index for 60+ foods [↩]
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Know Your Blood Sugar Numbers: Use Them to Manage Your Diabetes [↩]
