Legumes vs. Nuts: What’s the Difference? A Comparison
As a Certified Health Coach specializing in nutrition, I’m often asked about legumes and nuts. Sometimes there are questions. Let’s answer the most common one asked, what’s the difference between legumes and nuts?
Legumes have multiple seeds within a pod typically attached to the inside walls. Nuts have a single seed in a hardened shell which is not attached inside. The legume outer shell will burst open on its own while a nut’s outer shell has to cracked open. Both are protein rich, legumes are low in fat while nuts are high in healthy fats.
This article will take a deep dive into all the differences between the two including some astonishing facts many people aren’t aware of. I’ll identify the most common legumes and nuts, their nutrition and common uses.
Legumes vs Nuts: The Differences
In addition to coating my clients about them, I purchase and consume legumes and nuts almost daily. Therefore, I have researched this topic in the past and present.
The table below indicates the differences between each one:
| Facts | Legumes | Nuts |
| Type of Pod or Shell | A soft shell which splits open during maturity revealing the seeds. | A hard shell which needs to be cracked open to reveal the seed. |
| Number of Seeds | Multiple seeds attached to the inner wall. | Typically one seed unattached to the inner wall. |
| Nutrition | High in protein, high in fiber, low in fat. | High in protein, fat and minerals. |
| Common Types | Beans, lentils, peas, peanuts. | Hazelnuts, chestnuts, acorns, macadamia. |
| Price | Less expensive. | More expensive. |
The Definition of a Legume
Legumes are edible seeds enclosed in a pod. It is a family of plants having flowers1. The seed and outer shell are both edible.
It is dehiscent meaning the outer shell opens up when mature to release the inner seeds. Most of the plants have flowers with five petals. The flowers carry both male and female parts.
One significant difference between their plants and others is their ability to restore and enrich nitrogen supplies into the soil. They are often planted in fields to increase the nitrogen left in the soil after the crop finishes.
Furthermore, this helps to enrich fields having previously grown another crop, which might pull nitrogen from the soil instead of enriching it.
The following are common species:
- Lentils
- Black beans
- Red beans
- Lima beans
- Kidney beans
- Navy beans
- Black-eyed peas
- Pinto beans
- Pink beans
- Lima soy
- Peanuts
- Soybeans
- Chickpeas
- Peas
- Snap beans (string beans)
Legumes are part of the pea family. Every bean is a legume.
The Definition Of A Nut
A nut is a fruit coming from a plant having an inedible hard shell encasing the seed2. The seeds are edible, and the shell is not edible. It is indehiscent meaning the outer shell does not open to release the inner seed.
The following are common types:
- Hazelnut
- Chestnut
- Acorn
- Brazil nut
- Macadamia
- Some pine nuts
What many people call nuts are not actually nuts but drupes.
Common drupes include the following:
- Cashew
- Almond
- Pistachio
Some called nuts are not actually a drupe or a nut, but a hybrid. They include the following:
- Walnut
- Pecan
The following video explains the differences between legumes and nuts and their benefits.
Nutritional Differences
Since there are so many different types, hundreds of comparisons can be made. The following are the typical differences.
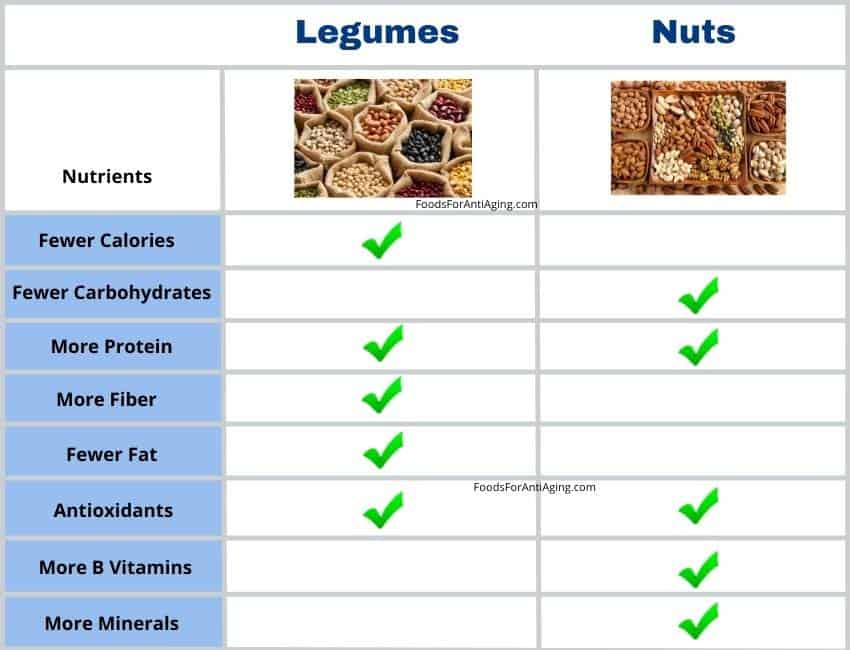
- Legumes and nuts typically contain a similar amount of protein.
- Legumes typically contain more carbohydrates and fiber.
- Nuts typically contain more calories, fats, B vitamins and minerals.
The following table compares the nutrients between two common legumes and two common nuts:
| Lentils (100 g) | Red Beans (100 g) | Macadamia (100 g) | Hazelnuts (100 g) | |
| Calories | 116 | 123 | 718 | 628 |
| Protein | 9.02 g | 9.49 g | 7.91 g | 15.0 g |
| Carbohydrates | 20.1 g | 21.8 g | 13.8 g | 16.7 g |
| Fiber | 7.9 g | 9.3 g | 8.6 g | 9.7 g |
| Fat | 0.38 g | 0.17 g | 75.8 g | 60.8 g |
| Sugar | 1.80 g | 0.87 g | 4.57 g | 4.34 g |
| Vitamin A | 8 IU | 3 IU | 0 IU | 20 IU |
| Beta-carotene | 5 mcg | 0 mcg | 0 mcg | 11 mcg |
| Vitamin C | 1.5 mg | 1.2 mg | 1.2 mg | 6.3 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.17 mg | 0.10 mg | 0.27 mg | 0.56 mg |
| Vitamin B9 (Folate) | 181 mcg | 74 mcg | 11 mcg | 113 mcg |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 0.16 mg | 0.09 mg | 1.20 mg | 0.64 mg |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0.07 mg | 0.06 mg | 0.16 mg | 0.11 mg |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | 1.06 mg | 0.55 mg | 2.47 mg | 1.80 mg |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | 0.63 mg | 0.21 mg | 0.75 mg | 0.91 mg |
| Magnesium | 36 mg | 42 mg | 130 mg | 163 mg |
| Phosphorous | 180 mg | 142 mg | 188 mg | 290 mg |
| Potassium | 369 mg | 378 mg | 368 mg | 680 mg |
| Iron | 3.33 mg | 2.77 mg | 3.69 mg | 4.70 mg |
| Copper | 0.25 mg | 0.26 mg | 0.75 mg | 1.72 mg |
| Calcium | 19 mg | 44 mg | 85 mg | 114 mg |
| Zinc | 1.27 mg | 0.90 mg | 1.30 mg | 2.45 mg |
There is much information in the table above. Both are considered healthy, but many people ask, which one is healthier?
Legumes are healthier than nuts due to their less number of calories, carbohydrates, fat and sugar. Although both foods provide a good percentage of B vitamins and minerals like potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, iron and calcium.
I choose to eat both of them. I’ll have beans or lentils at dinner time and snack on nuts throughout the day.
Deciding between the two may depend on which goal you have which I’ll examine next.
Which to Choose?
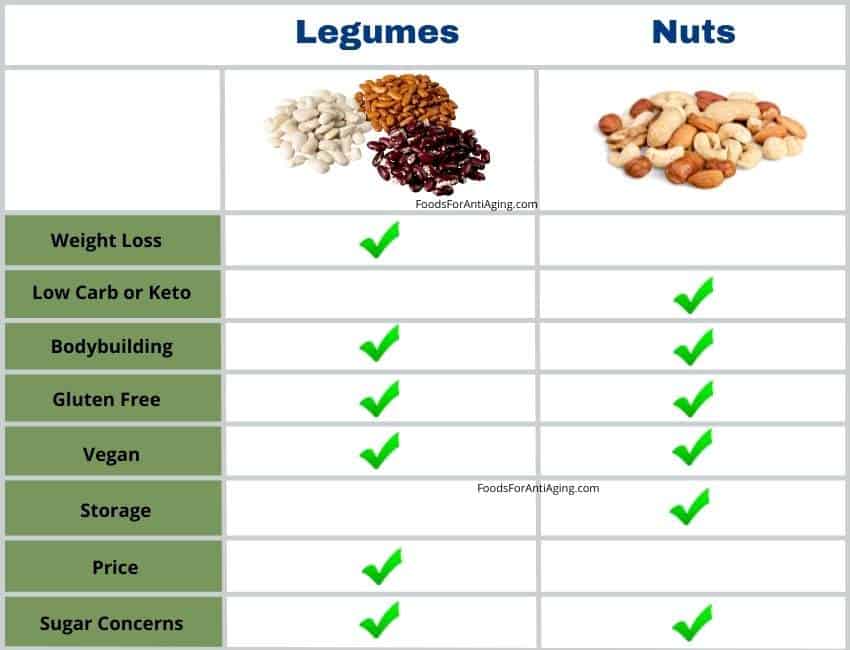
Weight Loss
Weight loss may be the most popular goal. If you’re trying to lose extra pounds from the midsection area, the number of calories may matter to you. Therefore, let’s examine which is better for weight loss.
- Legumes is better for weight loss than nuts due to its fewer calories and more fiber per serving. Nuts contain approximately six times the number of calories per 100 grams.
- Legumes typically provide more fiber which has been associated with weight loss. Fiber makes a body feel fuller and as a result less food is consumed later.
Low Carb or Keto Diets
The goal for most low-carb diets is consuming few carbohydrates while adding more healthy fat and protein. With such a restrictive carbohydrate intake, every gram of carbs may make a difference.
Therefore, let’s examine which one, nut vs legume, has fewer carbohydrates or more healthy fats and protein.
- Nuts are better for low-carb diets than legumes due to its fewer carbohydrates. Legumes contain approximately 43% more carbohydrates per 100 gram serving than nuts.
- Nuts contain more fat, and both contain a similar amount of protein.
Vegan or Vegetarian
If you’re thinking about following a vegan or vegetarian diet consuming dairy products or animal-derived products is important. Knowing if they are vegan or vegetarian friendly may help you choose between the two.
- Legumes and nuts do not contain animal products making them both beneficial for vegans and vegetarians.
Gluten Free
Avoiding any gluten is the main goal for people who wish to follow a gluten free diet or have Celiac disease. Therefore, let’s answer which one is gluten free?
- Legumes and nuts are both gluten free and good for gluten free diets.
Prices
It seems every trip to the supermarket results with more money spent at the checkout. For this reason and others, I’m sure the prices of food matters to most people.
A client of mine was complaining about the high cost and was saving money by buying peanuts.
I did some research and checked some supermarkets to compare the prices of both.
Nuts costs 184% more than legumes per serving. Legumes average cost per serving is $0.13 and the average price for mixed nuts is $0.37 per one ounce serving.
To conduct my own research, I checked two different supermarkets located in my area. Both supermarkets are on different levels of pricing. Walmart is the most economical and Shoprite being more expensive.
Here are my findings, I first visited Walmart:
Walmart:
- Small red beans (store brand) – 1 lb. bag $1.28 ($0.10 per 1/4 cup serving)
- Black beans (store brand) – 1 lb. bag $1.48 ($0.11 per 1/4 cup serving)
- Lentils (store brand) – 1 lb. bag $1.34 ($0.10 per 1/4 cup serving)
- Mixed nuts (store brand) – 27 ounce container $8.94 ($0.33 per 1 ounce serving)
Shoprite:
- Red beans (store brand) – 1 lb. bag $1.99 ($0.15 per 1/4 cup serving)
- Pinto beans (store brand) – 1 lb. bag $1.99 ($0.15 per 1/4 cup serving)
- Lentils (store brand) – 1 lb. bag $1.99 ($0.15 per 1/4 cup serving)
- Mixed nuts (store brand) – 30 ounce container $10.99 ($0.41 per 1 ounce serving)
Why a Peanut is a Legume
Peanuts are actually legumes because multiple peanuts grown inside pods. They are edible, and the outer pod or shell is inedible.
The main difference between peanuts and most nuts is most nuts grow on trees, called tree nuts. However, peanuts grow under the soil. When peanut harvest time comes, the peanut plants find themselves removed.
The hard and indigestible shell of the peanut helps to protect the seeds growing inside. The facts that they grow underground, do not grow on trees and have multiple seeds within their pod are why they make them a legume.
One of the most common mistakes is for people to assume a peanut is a nut. It’s a simple and common mistake, given the word is part of the peanut name.
However, due to its demanding nature, it is often considered a nut due to its consistency. As well, the shell is not known to be edible, like other legumes. That is to say, although the shell is not toxic to humans, it is indigestible.
Peanut shells can cause digestive problems due to this indigestible nature7. One of these issues is peanut shells can stick and build up within the gastrointestinal tract8.

The Difference Between Beans And Nuts
Most beans typically grow in pods where multiple beans reside9. In addition, these pods are often edible as in the form of green beans, for example.
Beans, as mentioned, are a legume. Legumes grow multiple seeds in an often edible pod. In contrast, nuts grow a single seed in a robust and inedible shell10. In addition, many nuts grow on trees, whereas beans grow on vines and other similar plants.
Check out how cashew butter compared to peanut butter in my article, Cashew Butter vs Peanut Butter: Which is Better? We Compare.
The Difference Between Seeds and Nuts
Seeds and nuts have more similarities than legumes and nuts do. Some seeds have an edible shell. Other seeds do not have an edible shell, and yet neither are considered nuts or legumes on their own.
However, one could note that both legumes and nuts technically are seeds. The definition of a seed is a pod of some sort growing from a plant for that plant to reproduce. Therefore, they both could find consideration as seeds.
Nuts are typically found to grow on trees and typically have a hard and inedible shell. Although many seeds also have hard and inedible shells, not all seeds have hard and inedible shells. Yet all nuts have hard and inedible shells.
Many seeds are soft where nuts are very firm compared to seeds. There are, however, many seeds crossing the boundary in terms of hardness.
For example, the sunflower seed could find consideration as it is hard. However, despite the inedible and hard shell, the sunflower seed is still considered a seed.
Find out how peanuts compared to almonds in my article, Peanuts vs Almonds: Which is Healthier? Let’s Compare.
Health Benefits
They both provide a wealth of health benefits. Many of the benefits are the same due to the similar nutrients provided by both.
The following Healthline video explains the benefits of nuts.
Health Benefits of Nuts
B Vitamins
The B vitamins provided help support the following11:
- Nerve function.
- Red blood cells.
- Brain function.
- Digestion.
- Cardiovascular disease.
- Energy levels.
Calcium
Calcium helps the following:
- Helps nerve function.
- Help the muscles to function properly.
- Build and maintain strong bones.
In addition, calcium is important for heart health and blood pressure. Harvard Health reports calcium helps maintain blood pressure by helping in the controlling of the relaxing and tightening of blood vessels12.
Magnesium
The magnesium provided helps the body control the following:
- Blood sugar
- High blood pressure
- Muscle function
- Insomnia
- Nerve function
Magnesium helps keep blood pressure levels stable and balanced. Recent scientific research examined previous studies and concluded magnesium supplementation decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure13.
Many people supplement with magnesium in the evening because it helps calm the whole body including blood vessels.
Phosphorus
Phosphorus has been shown in scientific studies to help with the following:
- Help the body store and manage energy.
- Muscle contraction.
- Muscle recovery.
- Help the kidneys remove waste.
- Promote healthy nerve conduction.
- Promote teeth and bone strength.
Health Benefits of Legumes
Fiber
Legumes typically provide more fiber than nuts. Fiber is helpful for many reasons ((National Center for Biotechnology Information: Mechanisms linking dietary fiber, gut microbiota and colon cancer prevention)). Fiber is known for the following:
- Help digestion.
- Aids in controlling weight because it allows you to feel full faster resulting in consuming less food.
- Manage the blood glucose levels which helps decrease the risk of diabetes.
- Helps avoid constipation and have a more regular stool.
Protein
Protein may help benefit the following:
- Reduce appetite.
- Build and repair muscle beneficial for bodybuilders.
- Boost metabolism.
- Weight loss.
Iron
Why is iron important? Iron is a necessary part of any healthy diet14 and may help with the following:
- Help the immune system.
- Is essential the creation of red blood cells.
- Help some hormones remain balanced.
- Vital for growth and development.
In the following video a panel of doctors explain the health benefits of beans (legumes).
Find out how almonds compared to pistachios in my article, Pistachios vs Almonds: Which is Better? Let’s Compare.
If you have any questions to ask me about this article don’t hesitate to comment below or email us. You can find an email on our contact page.
Read Next – More Food, Legume and Nut Articles!
Cashews vs Almonds: Which is Better? Let’s Compare
This is How You Store Nuts to Keep Them Fresh
Quinoa vs Lentils: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison
Organic Lentils vs Conventional Lentils: Which is Better?
- Wikipedia: Legume [↩]
- Wikipedia: Nut [↩]
- USDA: Lentils, mature seeds, cooked, boiled, without salt [↩]
- USDA: Beans, kidney, royal red, mature seeds, cooked, boiled, without salt [↩]
- USDA: Nuts, macadamia nuts, raw [↩]
- USDA: Nuts, hazelnuts or filberts [↩]
- Feedipedia: Peanut hulls [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Peanut shell colitis [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Legumes: Health Benefits and Culinary Approaches to Increase Intake [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Health Benefits of Nut Consumption [↩]
- Harvard T.H. Chan: B Vitamins [↩]
- Harvard Health: Key minerals to help control blood pressure [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure: a meta-analysis [↩]
- National Institutes of Health: Iron [↩]
