Olive Oil vs Coconut Oil: Is Coconut Better? Let’s Compare
Many of my health coaching clients ask me about cooking oils. Two popular ones mentioned are olive oil vs coconut oil. Many people want to know, which is better?
Olive oil is better than coconut oil due to its higher percentage of healthy fats, minerals and vitamins. Coconut oil is much higher in saturated fat, 497% more per tablespoon. Olive oil costs less money and has a stronger, more desirable flavor.
This article will explain all the differences between the two oils including a side-by-side nutrient comparison. In addition, I’ll examine their smoke points, when one can substitute for the other, tastes, prices, storage and health benefits.
The Differences
They’re both cooking oils but what is the difference between the two?
Refined coconut oil is made from dried coconut while virgin coconut oil is made from fresh coconut kernels. Olive oil is made by extracting the oil from olives. The finished refined olive oil is a blend of refined olive oil and extra virgin olive oil.
Coconut Oils
- Made from coconut kernels or dried coconut flesh.
- Has a mild, neutral flavor.
- Cost more money.
- Has a lower smoke point.
- Typically white and cloudy color.
Refined coconut oil is made by the following method:
- Dried coconut (copra) is pressed in a machine to release the oil.
- The oil is steamed or heated to deodorize the oil.
- The oil is filtered to remove impurities.
- It’s then bottled and shipped for sale.
Olive Oil
- Refined is made from olives using heat and chemicals.
- Has a mild, peppery flavor.
- Cost less money.
- Has a higher smoke point.
- Typically a light yellow to golden color.
Made by the following method:
- Olive oil is made by using the leftover paste from making extra virgin olive oil.
- The leftover paste is heated and kneaded with chemicals to release more oil, water and residue from the paste.
- It is separated from the water and residue.
- The oil is filtered and bottled as olive oil.
Olive Oil vs Coconut Oil: Nutrient Comparison
The following table compares the nutrients contained in one tablespoon of each one:
| Olive Oil (1 Tbsp/13.5 g) | Coconut Oil (1 Tbsp/13.5 g) | |
| Calories | 119 | 120 |
| Protein | 0 g | 0 g |
| Carbohydrates | 0 g | 0 g |
| Fiber | 0 g | 0 g |
| Fat | 13.5 g | 13.5 g |
| Sugar | 0 g | 0 g |
| Sodium | 0.27 mg | 0 g |
| Vitamin K | 8.13 mcg | 0.08 mcg |
| Vitamin E | 1.94 mg | 0.01 mg |
| Potassium | 0.135 mg | 0 mg |
| Iron | 0.076 mg | 0.007 mg |
| Calcium | 0.135 mg | 0.135 mg |
| Omega-3 | 103 mg | 0 g |
| Omega-6 | 1,318 mg | 234 g |
| Saturated Fat | 1.86 g | 11.12 g |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 9.86 g | 0.85 g |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 1.42 g | 0.23 g |
Both contain many of the same nutrients but in different numbers. This leads many to ask if one is healthier.
Olive oil is healthier than coconut oil due to its higher percentage of vitamins, minerals and healthy fats. It provides a higher percentage of vitamin K, vitamin E, potassium and iron. It also contains 1,060% more healthy monounsaturated fats, more omega-3 fatty acids and fewer unhealthy saturated fats than coconut oil.
For these reasons I always use olive oil myself at home. I’ll add extra virgin to my salads and use it for low temperature cooking.
Let’s examine each nutrient closer and determine the percentage differences between the two oils.
Calories
- They contain a similar number of calories per one tablespoon.
Vitamin K
- Olive oil contains 10,063% more vitamin K per one tablespoon.
Vitamin E
- Olive oil contains 19,200% more vitamin E per one tablespoon.
Potassium
- Olive oil contains more potassium per one tablespoon.
Iron
- Olive oil contains 986% more iron per one tablespoon.
Calcium
- Both contain the same amount per one tablespoon.
Saturated Fat
One of their biggest differences is in their saturated fat content.
- Coconut oil contains 497% more saturated fat per one tablespoon.
Monounsaturated Fat
- Olive oil contains 1,060% more monounsaturated fat per one tablespoon.
Polyunsaturated Fat
- Olive oil contains 517% more polyunsaturated fat per one tablespoon.
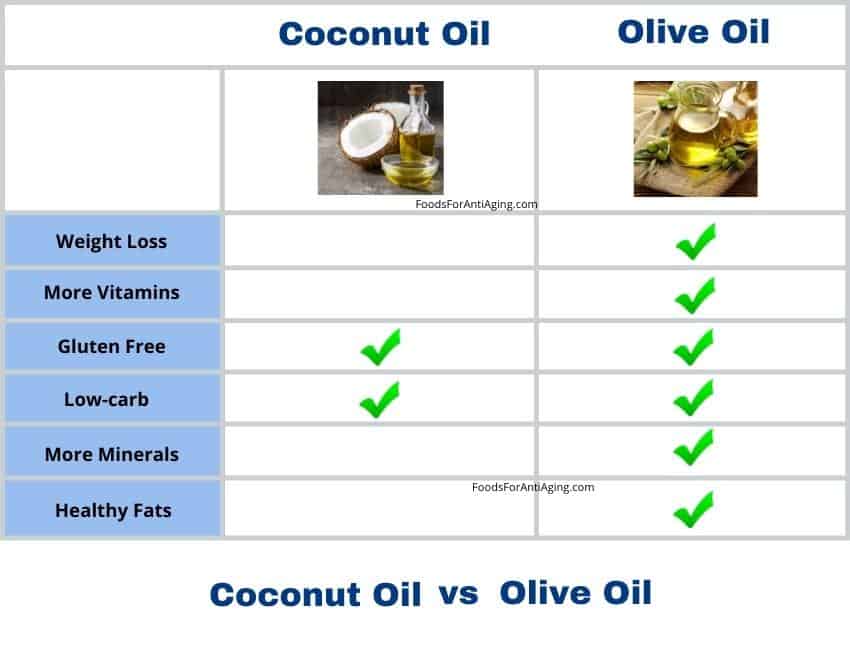
Which to Choose Based on Your Goals
In this section I examine the most common goals people have and determine if one is the better choice for each one.
Low Carb or Keto Diets
The goal for most low-carb diets is consuming few carbohydrates while adding more healthy fat and protein. With such a restrictive carbohydrate intake, every gram of carbs may make a difference.
Therefore, let’s examine which one has fewer carbohydrates or more healthy fats and protein.
- Olive oil is better for low-carb diets than coconut oil due to its higher percentage of healthy fats. They both provide 13.5 g of total fat per tablespoon. Both have an equal number of carbohydrates per tablespoon which is zero grams.
- A higher percentage of the fat contained in olive oil is the healthier monounsaturated fatty acids (mufas 1,060% more than coconut oil per tablespoon) making it the better choice.
- It contains 497% fewer unhealthy saturated fats.
Olive Oil vs Coconut Oil for Weight Loss
Weight loss may be the most popular goal. If you’re trying to lose extra pounds from the midsection area, the number of calories may matter to you.
Therefore, let’s examine which is better for weight loss.
- Olive oil is better for weight loss than coconut oil due to its overall healthy fat content, although they have the same number of calories. A diet based on the healthy fats provided, like the Mediterranean diet, is associated with weight loss.
- It contains a good number of medium-chain triglycerides which has been associated with weight loss and maintenance in studies3.
- The monounsaturated fats has been shown to increase good cholesterol and both have been associated with weight loss in studies4.
- A high percentage of saturated fats has been associated with weight gain5.
It should be noted to be careful about how much is added to a dish like salads. It’s easy to add multiple tablespoons. At 119 calories per, adding four tablespoons would equal 476 calories. Always be aware of the number of tablespoons and try not to overdo it.
Vegan or Vegetarian
If you’re thinking about following a vegan or vegetarian diet consuming dairy products or animal-derived products is important. Knowing which one is vegan or vegetarian friendly may help you choose between the two.
Olive oil and coconut oil do not contain animal products making them both beneficial for vegans and vegetarians.
Gluten Free
Avoiding any gluten is the main goal for people who wish to follow a gluten free diet or have Celiac disease. Therefore, let’s examine which one is gluten free.
- Olive oil and coconut oil are both gluten free and good for gluten free diets.
Bodybuilding
If you’re trying to gain muscle mass or just tone up, the amount of protein and carbohydrates may make a difference. Let’s take a look at both and determine which is better for bodybuilding.
Although they both contain the same number of proteins and carbohydrates, olive oil is better for bodybuilding. This is due to its higher percentage of healthy fats and antioxidants.
- Olive oil contains oleic acid which has been shown to stimulate protein production and synthesis.
- One of its antioxidants, oleocanthal, is an anti-inflammatory that also reduces pain in joints. Pain in the joints may affect workouts or the amount of weight lifted.
- The antioxidants help fight free radicals and prevent cell damage. It’s difficult to build and repair muscle cells with free radicals.
- It is associated with decreases in inflammation which can benefit the joints.
- When bulking up, the calories may prove beneficial.
On the days I workout at the gym, I’ll often have a grilled chicken salad for lunch. When I do, I always add olive oil mixed with balsamic vinegar.
Taste
Let’s face it, if you’re like me I won’t eat a food considered healthy unless I can tolerate the taste. I think if someone doesn’t like the flavor of a food they won’t purchase it.
Therefore, let’s examine how the taste of both compare.
Olive oil has a stronger flavor than the milder coconut oil. Coconut oil has a neutral taste with a slight tropical sweetness, while olive oil has a hint of olives and is peppery. The virgin oils have more flavor than the refined versions.
I wanted to get the opinion of real people like you by conducting some original research. Therefore, I reached out to some clients, members of food groups and readers. I asked, which one tastes better?
- 82% said they preferred the taste of olive oil.
- 15% said they preferred the taste of coconut oil.
- 3% said they had no preference.
I also participated in my own blind taste test. I had a small spoon of each one. The difference in taste was obvious and I picked the olive oil as the winner.
In the taste poll and my own taste test, olive oil was found to taste better and was the winner.
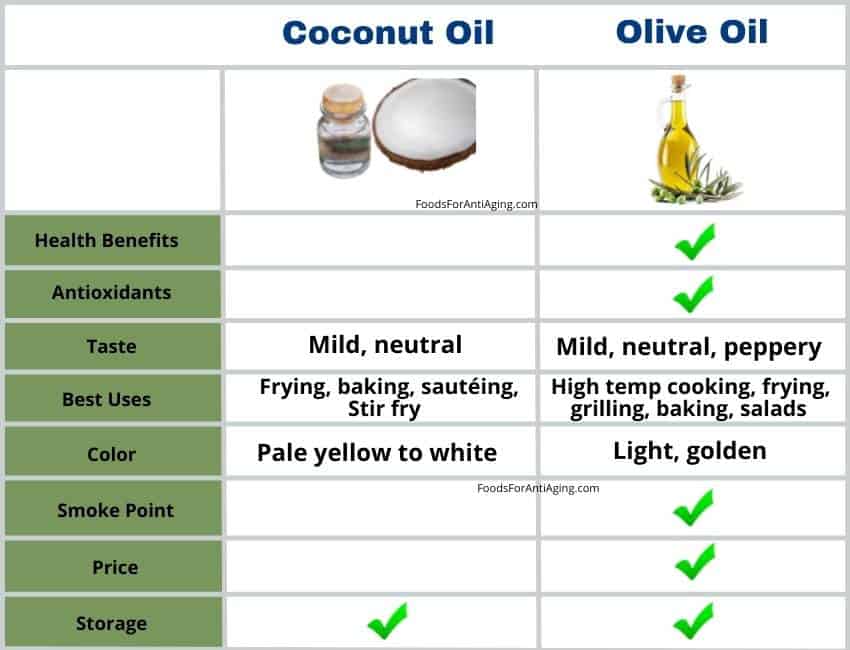
Substitutions
I think it’s happened to all us, at the last minute you find out you’re out of the food needed in a recipe. Unable to go out to the store or just don’t want to, you’ve probably wondered if you can use another type in its place.
Reasons why people will want to substitute one for the other in a recipe:
- Availability
- Taste
- Smoke point
- Price
- Variety
This makes people wonder is it okay to substitute one for the other. Let’s answer, can I use coconut oil instead of olive oil?
Coconut oil and olive oil can substitute for each other in cold recipes although the flavor will be stronger when using olive oil. In hot recipes refined can substitute for each other up to 400°F. Refined olive oils can substitute for coconut oils up to 470°F due to its smoke point.
When substituting both use an equal amount. Both can substitute for each other in vegan or gluten free recipes.
Smoke Points
The following are the smoke points for both oils which is important for frying:
| Type of Oil & Fats | Smoke Point (Fahrenheit) |
| Coconut Oil – Refined | 400°F |
| Coconut Oil – Virgin | 350°F |
| Olive Oil – Refined | 470°F |
| Olive Oil – Virgin | 410°F |
| Olive Oil – Extra virgin | 375°F |
Smoke point source ((Wikipedia: Smoke point))
- Extra virgin and refined olive oil has a higher smoke point than virgin coconut oil or coconut oil.
The types more refined or processed always have a higher smoke point than virgin oils, no matter which type.
Olive Oil and Coconut Oil for Cooking
Coconut Oil
Some people like using it because it doesn’t overpower the other flavors in a recipe.
Using it results in a neutral flavor and more people use it for cooking or baking than for dipping, salads or drizzling.
Sometimes using it instead of olive oil can give you a richer flavor. This is because it has a higher fat content.
Because many baked goods rely on the fat content found in butter, it is a substitute for baking. When substituting for butter, use the solid type at room temperature.
Solid has a texture similar to butter and can be mixed with flour the same way.
Is Virgin Coconut Better?
To bring out more of the flavor and retain benefits, use virgin instead of refined. Virgin retains more flavor and odor because it goes through less processing.
Use coconut oil for the following:
- Use when cooking in temperatures up to 400 degrees (the smoke point of refined coconut oil).
- Sauteing
- Frying
- Baking
- Stir fry
Olive Oil
- Use refined for any cooking in temperatures up to 470 degrees.
- Use extra virgin for cooking in temperatures up to 375 degrees.
- Dipping
- Dressings
- Salads
- Grilling
- Frying
- Stir-frying
- Baking
- Pasta

The Prices
Its seems every trip to the supermarket results with more money spent at the checkout. For this reason and others, I’m sure the prices of food matters to most people.
I checked the price of store brand and refined to keep things on an even playing field. I divided the price by the number of ounces. Therefore, let’s examine the prices.
Coconut oil costs 12% more than olive oil per ounce. Olive oil average cost per ounce is $0.24 and the average price for coconut oil is $0.27 per ounce.
To conduct my own research, I checked two different supermarkets located in my area. Both supermarkets are on different levels of pricing. Walmart is the most economical and Stop and Shop being more expensive.
Here are my findings, I first visited Walmart:
Walmart:
- Olive oil (Store brand) – 51 ounce $10.98 ($0.21 per ounce)
- Coconut oil (Store brand) – 56 ounce $13.63 ($0.24 per ounce)
Stop and Shop:
- Olive oil (Store brand) – 25.3 ounce $6.79 ($0.27 per ounce)
- Coconut oil (Store brand) – 27 ounce $8.19 ($0.30 per ounce)
Find out what is the healthiest oil to cook with in my article, Avocado Oil vs Olive Oil: Which is Better? A Comparison.
Storage
Storing food often gets overlooked. The shelf life you get out of the food is important, especially with the prices of a good quality types. In addition, improper storage may lessen the taste and quality.
Let’s examine how each should be stored.
Store coconut oil or olive oil the same way which is in a cool, dark location away from light. It’s best to store either one in a tinted glass container. Both should should be kept at a temperature between 55-60℉, although they can be refrigerated or frozen if needed.
If the temperature of a room rises above 70℉, they should be stored in the refrigerator. Leaving either one in warmer temperatures affects shelf life and lessens the quality.
Coconut oil is solid at room temperature below 76℉, above 76 degrees it will turn to liquid. It is perfectly fine if it turns to liquid. If you wish to freeze it I wrote a whole article dedicated to the freezing process, How to Freeze Coconut Oil.
Unrefined oil or extra virgin can go bad quicker than refined oils. For this reason, many people store them in the refrigerator regardless of the room temperature.
Kitchens are often warmer than most other rooms of the house due to cooking and the heat-creating appliances. Therefore, monitor the temperature of the room to ensure the best quality.
I have a cool kitchen away from the windows and sunlight. Therefore, I mostly store mine in the cabinet.
Find out how sesame oil compared in my article, Sesame Oil vs Olive Oil: Which is Better? Let’s Compare.
Health Benefits
Coconut Oil Benefits
There are some benefits and also some concerns if consumed too much.
Coconut oil has about six times the amount of saturated fat when compared to olive oil. Saturated fat should be limited because it can raise cholesterol numbers, good and bad. The increase in bad cholesterol, LDL, has been linked to plaque build-up in the arteries and cardiovascular disease risk6.
There’s emerging research redefining saturated fats healthy benefits. People have been replacing coconut oil with vegetable oil which may not be the better choice depending on the type used.
Some research has demonstrated consuming it may actually improve good cholesterol, despite its saturated fats7.
The USDA recommends limiting saturated fat intake to less than 10% of the daily calories. Until more is learned about coconut oil it’s best to treat it like a saturated fat. Always check with your physician about the proper diet for you.
Over half of the fatty acids are medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs). They have been shown to reduce the metabolic load on the liver compared to other fats.
One of the main MCTs is Lauric acid8.
Studies have shown it beneficial for the following:
- Anti-inflammatory properties.
- Antimicrobial properties.
- Insulin resistance.
- Immune system.
For further explanation about why many vegetable oils contain 100% soybean oil read about it in my article, Olive Oil vs Vegetable Oil: Which is Better? Let’s Compare.
Olive Oil and Extra Virgin Olive Oil Benefits
Cancer
The cancer rates in Mediterranean countries are lower than other places. As noted earlier, extra virgin olive consumption is a huge part of the diet.
Antioxidants are believed to contribute to the killing of cancer cells. In a 2015 study, oleocanthal, a phenolic compound, helped kill cancer cells in less than one hour9.
Another study published in 2015 evaluated the consumption of the Mediterranean diet, its nutrient profile and the incidence of breast cancer. For a six-year period, 4,282 women aged 60 to 80 years followed three different diets:
- Mediterranean diet supplemented with extra virgin olive oil
- Mediterranean diet supplemented with mixed nuts
- A reduced fat diet
After 4.8 years 35 of the women developed breast cancer. The lowest rate of breast cancer was seen in the women who supplemented with the EVOO10.
Oleic acid which it is rich in, has been associated with helping to reduce the risk of cancers.
Heart Disease
Heart disease is among the most common causes of death in the United States and throughout the world. Research has shown heart disease is lower in the Mediterranean countries where olive oil is a big part of their diets.
There are many ways it is beneficial for the heart including the following:
Lowering Blood Pressure
Studies have shown an association between lower blood pressure and an increase in its consumption. According to Harvard and others, the Mediterranean diet has been linked to lower blood pressure and cardiovascular disease11. This is more beneficial for the heart.
Blood Vessel Health
It has been shown to help improve the lining of blood vessels. A study published in 2015 showed blood vessels opened up and increased blood flow in people who included it in their diet12. Healthy blood vessels helps the heart work less harder.
Reducing Inflammation
It is associated with decreases in inflammation which is a main component of heart disease. An antioxidant in olive oil, oleocanthal, is an anti-inflammatory that also reduces pain13. It’s better for the heart to have less inflammation.
Brain Health
In addition to the heart, research has shown the Mediterranean diet may be associated with a reduced risk of cognitive problems and dementia14.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia causing problems with memory, thinking and behavior. Common conditions of the disease is the build-up of proteins known as beta-amyloid plaques in certain neurons in the brain.
Animal studies have shown extra virgin to clear the beta-amyloid proteins from the brain helping to prevent Alzheimer’s disease15.
Read More Oil Articles
Olive Oil vs Soybean Oil: Which is Better? Let’s Compare
Olive Oil vs Canola Oil: Which is Better? Let’s Compare
Grapeseed Oil vs Olive Oil: Which is Better? Let’s Compare
Butter vs Olive Oil: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison
Sunflower Oil vs Olive Oil: Which is Better? Let’s Compare
Extra Virgin Olive Oil vs Olive Oil: A Complete Comparison
- USDA: Oil, olive, salad or cooking [↩]
- USDA: Oil, coconut [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Effects of medium-chain triglycerides on weight loss and body composition: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: High Fat Diet with a High Monounsaturated Fatty Acid and Polyunsaturated/Saturated Fatty Acid Ratio Suppresses Body Fat Accumulation and Weight Gain in Obese Hamsters [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: A highly saturated fat-rich diet is more obesogenic than diets with lower saturated fat content [↩]
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute: Blood Cholesterol [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Randomised trial of coconut oil, olive oil or butter on blood lipids and other cardiovascular risk factors in healthy men and women [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Lauric acid ameliorates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced liver inflammation by mediating TLR4/MyD88 pathway in Sprague Dawley (SD) rats [↩]
- Taylor & Francis Online: (-)-Oleocanthal rapidly and selectively induces cancer cell death via lysosomal membrane permeabilization [↩]
- Jama Internal Medicine: Mediterranean Diet and Invasive Breast Cancer Risk Among Women at High Cardiovascular Risk in the PREDIMED Trial [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Virgin Olive Oil and Hypertension [↩]
- (National Center for Biotechnology Information: Effects of Olive Oil on Markers of Inflammation and Endothelial Function-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis [↩]
- National center for Biotechnology Information: Olive Oil-related Anti-inflammatory Effects on Atherosclerosis: Potential Clinical Implications [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease in the EPIC-Spain Dementia Cohort Study [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Attenuates Amyloid-β and Tau Pathologies in the Brains of TgSwDI Mice [↩]
