Overnight Oats vs Oatmeal: Both Are Oats So Does It Matter?
As a Certified Health Coach, many clients ask me about overnight oats and oatmeal. People wonder if they’re the same or if there’s a difference. Let’s answer, what’s the difference between overnight oats and oatmeal?
Overnight oats and oatmeal are made from oats but prepared and served differently. Overnight oats are soaked in milk, water or yogurt overnight. Overnight the oats absorb the liquid, soften and it’s ready to be served cold in the morning. Oatmeal is made by cooking oats in water or milk and immediately served warm.
The rest of this article details all the differences between the two, the pros and cons of each and how they’re prepared. In addition, I’ll include a side-by-side comparison of their nutrients and health benefits.
In addition to coaching clients about oatmeal, I’ve researched and consumed both prior to, during and after writing this article. I personally consume both varieties on a regular basis.
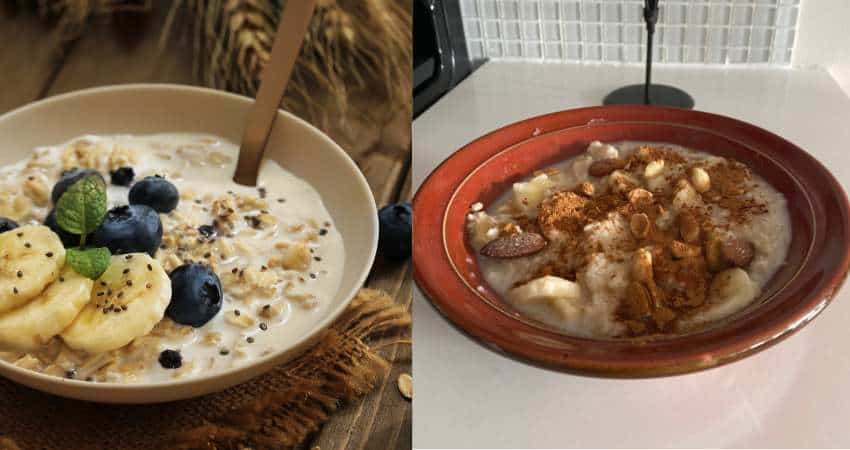

Are Overnight Oats and Oatmeal the Same?
Overnight oats and oatmeal are not the same. Overnight oats are prepared in advance and must soak overnight before its edible. However, oatmeal is cooked with heat to soften the grains quicker and is consumed shortly after. Overnight oats are served cold, and oatmeal is served hot.
Overnight Oats
Pros
- Saves time in the morning because it is ready to be consumed without any preparation. The steps are taken the night before.
- It’s like magic because they prepare themselves overnight already in the bowl.
- Since overnight oatmeals are not boiled they retain more nutrients.
- Soaking decreases phytic acid more. Phytic acid can prevent the body from absorbing nutrients. Cooking breaks them down as well, but research shows soaking does a better job.
- They are easier to transport. Since they’re chilled, you can easily pack them in a jar or container to take with you as a breakfast on the go.
- Easier preparation: There is no heating or cooking, they are uncooked oats. The ingredients can be added into the bowl with the liquid chosen the night before.
- Fewer dishes to wash. There is no pot to clean because they’re not cooked on the stove.
- More versatile. They can be prepared in batches and can be refrigerated up to four days. When ready, add the ingredients prior to eating them. Cooked oatmeal can be refrigerated but need to cool first.
Cons
- Most people prefer a warmer food to eat in the morning (comfort food).
- The texture is slightly different, and some people may not enjoy it as much as cooked.
- If you enjoy the crunch, leave out the seeds, granola, etc. until it’s time to eat the oats.
- More calories per serving, especially important if you’re looking to lose weight.
- This process is much longer and slower.

Oatmeal
Pros
- Heartier taste and texture.
- Comfort food. Many people like eating a warm breakfast, especially on a cold morning.
- Satisfy your immediate cravings. The ingredients added to overnight oats the night before may not satisfy your cravings in the morning.
- Less calories. Important if you’re dieting or looking to drop a few pounds.
Cons
- Require more time in the morning.
- Provide a lower percentage of nutrients.
- The hot preparation is more difficult to package and take with you.
Ultimately, which one is best for you depends on how much time you have in the morning and your taste preferences.
Some people enjoy alternating from one day to the next. This helps break the boredom of eating the same type all the time.
I also alternate between the two depending on my schedule for the morning. If I know I have more time for breakfast, like on my days off, I’ll cook them. If not, I’ll prepare them for overnight.
Overnight Oats vs Oatmeal: Nutrition
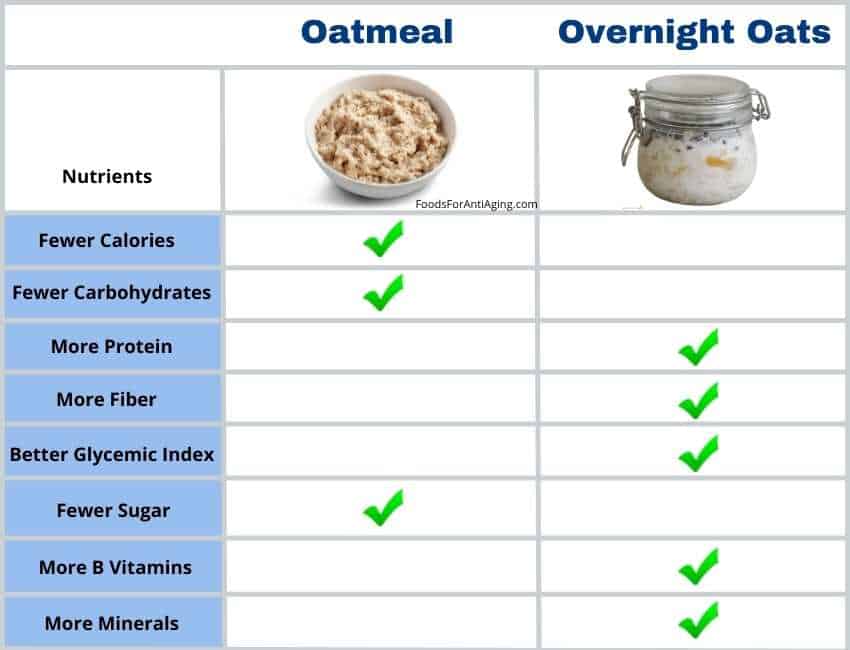
They both have the same nutrients, just in different percentages. The differences between the two can greatly affect which one you choose.
The following table is a side-by-side comparison of the nutrients contained in a 100-gram serving of each one. It’s almost 1/2 cup.
| Oatmeal (100 g)
Cooked |
Overnight Oats (100 g) | |
| Calories | 71 | 375 |
| Protein | 2.54 g | 12.5 g |
| Carbohydrates | 12.0 g | 67.5 g |
| Fiber | 1.7 g | 10.0 g |
| Fat | 1.52 g | 7.50 g |
| Sugar | 0.27 g | 2.50 g |
| Vitamin A | 0 IU | 0 IU |
| Beta-carotene | 0 mcg | 0 mcg |
| Vitamin C | 0 mg | 0 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.005 mg | 0.07 mg |
| Vitamin B9 (Folate) | 6 mcg | 28 mcg |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 0.07 mg | 0.38 mg |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0.01 mg | 0.12 mg |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | 0.22 mg | 1.09 mg |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | 0.31 mg | 1.08 mg |
| Magnesium | 27 mg | 100 mg |
| Phosphorous | 77 mg | 325 mg |
| Potassium | 70 mg | 375 mg |
| Iron | 0.90 mg | 3.75 mg |
| Copper | 0.07 mg | 0.39 mg |
| Calcium | 9 mg | 50 mg |
| Zinc | 1.00 mg | 3.42 mg |
They both contain the same types of nutrients. This causes many people to wonder if one is healthier for nutrition and benefits.
Overnight oats are healthier than oatmeal due their higher percentage of protein, fiber, B vitamins and minerals. They provide more B6, folate, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, B5, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, iron, copper, calcium and zinc than oatmeal.
Oatmeal is healthy also and contains the same nutrients but less of them. It contains fewer calories and carbohydrates.
Choosing between the two may come down to your specific goals. Both of them for a healthy breakfast. One of those goals may be weight loss.
Weight Loss
Oatmeal is better for weight loss due to its fewer calories, total fat and sugar. Overnight oats are bad for weight loss because they contain 430% more calories per 100 grams.
Fiber
Overnight oats contain more fiber. They provide 10.0 grams of fiber per 100 grams, almost 1/2 cup.
Protein
Overnight oats contain more protein per serving. They provide 12.5 grams of protein per 100 gram serving.
Bodybuilding
Overnight oats are better for building muscle and athletic performance due to its higher percentage of protein, carbohydrates and calories. The extra calories and protein per 1/2 cup help to gain weight, muscle and repair muscle. The extra carbs help to provide energy while lifting weights.
Low Carb
Overnight oats contain 67.5 grams of carbohydrates per 100 gram serving, almost 1/2 cup. Over 50 grams more than oatmeal which is the better choice if you’re on a low carb or Keto diet.
Find out how Cream of Wheat compared in my article here.
Why Overnight Oats Contain More Nutrients
Cooking oats degrades the amount of available nutrition the consumer can benefit from. The heat from cooking can cause them to lose approximately 25% or more of their nutritional value. So, soaking them overnight softens the grain without losing any of the healthy benefits.
However, if you prefer to eat your oats warm and don’t like the texture of the overnight meal, you may want to try this. Cooking them at a lower and consistent temperature, and for a short period, will help them retain more of their nutrients.
The grain may not get as soft, but you’ll still benefit from more of the available nutrients within the oats.
Find out how brown rice compared in my article here.
Taste and Texture
It’s not always about the nutrients provided. Many times, people choose one food over the other because of its taste or according to their mood. Or, it may be the limited time in the morning at breakfast.
Since there are some similarities between the two, like both being oats, many people wonder about the taste of both.
Overnight oats and oatmeal have a similar bland taste, but overnight oats are cold while oatmeal is hot. They both take on the flavor of any ingredients added to them. Oatmeal’s texture is not smooth but overnight oats are a little chewier.
Overnight oats have a bland and earthy taste. Adding ingredients or seasonings will add more flavor similar to the addition. Preparing them results in a chewier texture.
Old-fashioned rolled oats have a chewier texture than the smoother instant oatmeal.
To conduct some research, I polled some of my readers and people in food groups I belong to. I asked, which do you prefer the taste of for breakfast?
- 57% said they preferred the taste of oatmeal.
- 34% said they preferred the taste of overnight oats.
- 9% said they had no preference.
I thought it would be fun to set up my own taste test at home. I prepared both varieties for breakfast with the same ingredients added to both of them. Three out of four people chose the oatmeal.
Find out how white rice compared in my article.
Preparation Tips
How To Cook Overnight Oats
Overnight is prepared without cooking. Instead, they are mixed with liquid (usually milk, water or yogurt, or some combination of both) and other ingredients for taste. The oats soak in the refrigerator overnight.
Easy Overnight tips:
- Use old-fashioned rolled oats. They have the perfect texture, whereas instant oats may result in a soggy mixture.
- Mix them with your favorite milk or yogurt. These can be dairy, or plant based. It is possible to make them with just milk and skip the yogurt, but if you want the classic creamy texture, the yogurt will help accomplish this.
- The right ratio of liquid to oats. You’ll need adding the right ratios of ingredients to avoid drying out the mixture. Most people add a 1:1 ratio. Some people feel a liquid to oats ratio of 2:1 is more ideal for a creamier result. I also prefer using a 2:1 ratio.
- Add your desired flavorings. Many people choose to mix in fruit, seeds, sweeteners and spices to give them more taste.
- Store them in a sealed container in the refrigerator. Mason jars with lids or plastic containers with tight seals are ideal for storing.
It’s possible to get creative with your mix-ins and toppings as well. However, if you’re on a diet or trying to reduce your sugar intake, you’ll want to be sure to omit the syrups, artificial sweeteners and other high-calorie toppings.
The calories can up quickly, especially since they have more calories to begin with.
Find out if grits have the better satiety in my article.
Preparation Tips for Oatmeal
Here are some tips to get you started on preparing them:
- It can be cooked on the stovetop or in the microwave. The method you choose will depend on your preference and how much time you have for breakfast.
- Monitor them to avoid burning. You’ll have to keep an eye on it as they’re cooking so the mixture isn’t ruined. You should also avoid using high heat and instead use low-medium heat to cook them gradually.
- Ensure you’ve added enough liquid. A dry result can congeal after cooling, resulting in an undesirable texture. Using enough milk will keep them smooth and creamy.
- Add your toppings after it has cooled. Wait for it to cool a bit before adding any ingredients. This is to prevent the toppings from cooking, burning or losing their texture and taste.
Glycemic Index
The Glycemic Index (GI) is a scale measuring how fast a particular food raises the blood sugar in the blood3. Blood sugar spikes can lead to health complications with the heart, nerves, kidneys and eyes4.
Foods on the GI scale are categorized as:
- Low-GI foods: 55 or under
- Medium-GI foods: 56-69
- High-GI foods: 70 or over
How blood sugars levels are affected:
- Foods with a glycemic index 70 or more cause a quicker spike in blood sugar levels.
- Foods with a glycemic index 56 to 69 cause a moderate spike in blood sugar levels.
- Foods with a glycemic index 55 or less cause a slow spike in blood sugar levels.
Having more knowledge of the glycemic index of food and how it raises blood sugar, many people wonder which type has a better GI score.
Overnight oats have a lower glycemic index than oatmeal. Whether a food is consumed hot or cold have significant effects on glucose and insulin responses after consumption. Oats soaked overnight in skim milk was shown to have a lower glycemic index than cooked oatmeal in a 2019 study.
Steel-cut has a lower GI because they are the least processed. Rolled oats are a little higher because they’ve been partially cooked. Quick or instant have been steamed and rolled into thinner pieces to cook quicker. This process increases their GI.
Find out how quinoa compared in my article.
Health Benefits
Overnight oats provide more nutrients and therefore the greater benefits. Since both contains the same nutrients, the benefits are the same, just in different degrees. Let’s take a look at how each nutrient benefits health.
Fiber
- Overnight oats contain more fiber per 100 grams.
Both foods are high in soluble fiber, which is helpful for many reasons ((National Center for Biotechnology Information: Mechanisms linking dietary fiber, gut microbiota and colon cancer prevention)). What makes fiber soluble is it dissolves in water.
Soluble fiber is known for the following:
- Manage the blood glucose levels which helps decrease the risk of diabetes.
- Helps avoid constipation and have a more regular stool.
- Help overall digestive health.
- Aids greatly in weight management because it allows you to feel full faster and eat less.
Potassium
- Overnight oats contain 375 mg of potassium per 100 grams.
Some medical experts recommend the potassium to sodium ratio of 4:1. Consuming too much sodium or not enough potassium throws off the delicate balance the kidneys need to remove the excess water5.
Potassium helps the body get rid of excess sodium reducing fluid build-up. These help keep systolic and diastolic blood pressure lower helping with heart health6.
According to Harvard Health, a number of university health studies have shown a connection between low potassium levels and high blood pressure7. The more potassium, the more sodium your body will lose.
Magnesium
- Overnight oats contain more magnesium per 100 grams.
Magnesium helps keep blood pressure levels stable and balanced. Recent scientific research examined previous studies and concluded magnesium supplementation decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure8.
Magnesium helps control the following:
- Muscle
- Blood pressure
- Blood sugar
- Nerve function
- Insomnia
In the heart and muscles, magnesium competes with calcium to help the muscles relax after contracting. When the body is low in magnesium, calcium can over stimulate the heart muscle’s cells causing a rapid or irregular heartbeat9.
One reason many people supplement with magnesium in the evening is because it helps calm the whole body including blood vessels.
Phosphorus
- Overnight oats contain more phosphorus per 100 grams.
Phosphorus has been shown in scientific studies to help with the following:
- Promote bone and teeth strength.
- Help the body store and manage energy.
- Promote healthy nerve conduction.
- Muscle contraction.
- Muscle recovery.
- Help the kidneys remove waste.
Find out if granola has more nutrients in my article.
B Vitamins
Of the six B vitamins listed below, overnight provides a higher percentage of all of them.
The B vitamins provided include the following:
- B1 (thiamin)
- B2 (riboflavin)
- B3 (niacin)
- B5
- B6
- B9 (folate)
B vitamins help support the following:
- Brain function.
- Red blood cells.
- Digestion.
- Nerve function.
- Cardiovascular disease.
- Energy levels.
A lack of B vitamins has been associated with oxidative stress and neural inflammation. In a study released in 2018 32 healthy adults were given B vitamin supplementation for six months. The results indicated preliminary evidence B vitamin supplementation reduced oxidative stress and inflammation10
Iron
- Overnight oats contain 3.75 mg of iron per 100 grams.
Much higher in iron than other grains, it is an excellent choice if you need getting your daily value of iron. Iron is essential in the creation of red blood cells and is a necessary part of any healthy diet.
Iron is also vital for growth and development, as some hormones need iron to be appropriately balanced11.
Calcium
- Overnight contains five times more calcium per 100 grams.
Calcium is important for the heart and blood pressure. Harvard Health reports calcium helps maintain blood pressure by helping in the controlling of the relaxing and tightening of blood vessels12.
Calcium also helps the following:
- Help the muscles to function properly.
- Helps nerve function.
- Build and maintain strong bones.
Find out if there is a difference in benefits between these two varieties in my article, Steel Cut Oatmeal vs Oatmeal: Which Is Better? Let’s Compare.
Gluten-Free Benefits
Oatmeal and overnight oats are both made with oats which are naturally gluten-free and might be a great substitute to other gluten-heavy items of a similar taste. Even those who don’t have a completely gluten-free diet may benefit from cutting down on their gluten.
Recently it has been discussed many more people have at least a small amount of gluten intolerance and are unaware of it. Having less gluten in your diet is a good choice for most.
Important: Although both are made from gluten free oats, they may come in contact with gluten-containing grains in storage or during transportation. Most of the Quaker products have solved this issue and label those products gluten free. Always check the label of your products to determine if its gluten free.
FAQs
Which cost more, overnight oats or oatmeal?
Overnight oats and oatmeal costs the same. They are both prepared with the same type of oats purchased in the store.
How to store overnight oats or oatmeal?
Prepared overnight oats and oatmeal are both stored in a sealed container in the refrigerator up to four days. The ingredients added may change the storage time depending on the ingredient used.
If you have any questions about this article don’t hesitate to email us. You can find an email on our contact page.

Solve this ongoing battle, is it better than eggs? Find out in my article here.
Read Next – More Food Articles!
Muesli vs Oatmeal – What’s The Difference? Let’s Compare
Instant Oatmeal vs Oatmeal: What’s The Difference?
- USDA: Cereals, oats, regular and quick, unenriched, cooked with water (includes boiling and microwaving), without salt [↩]
- USDA: Rolled Overnight Oats [↩]
- Harvard Health Publishing: Glycemic index for 60+ foods [↩]
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Know Your Blood Sugar Numbers: Use Them to Manage Your Diabetes [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: The Effect of the Sodium to Potassium Ratio on Hypertension Prevalence: A Propensity Score Matching Approach [↩]
- American Heart Association: How Potassium Can Help Control High Blood Pressure [↩]
- Harvard Health: Potassium lowers blood pressure [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure: a meta-analysis [↩]
- National Institutes of Health: Magnesium [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: The Effect of a High-Dose Vitamin B Multivitamin Supplement on the Relationship between Brain Metabolism and Blood Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress: A Randomized Control Trial [↩]
- National Institutes of Health: Iron [↩]
- Harvard Health: Key minerals to help control blood pressure [↩]
