Plantain vs Potato – Which is Better? Let’s Compare
As a Certified Health Coach many of my clients bring up the topic of plantains and potatoes. They are versatile and have many nutrients. Due to their similarities many people want to know, which is better plantains or potatoes?
Plantains are better than potatoes for nutrients, athletic performance and provide a higher percentage of vitamins. They are beneficial for energy while having a lower glycemic index than potatoes. Plantains taste sweeter and are better for desserts.
This article will include a side-by-side comparison of their nutrients. In addition, I’ll examine their tastes, textures, costs, glycemic index and whether one can substitute for the other. We’ll also take a look at their health benefits.
In addition to coaching clients about them, I’ve purchased, researched and consumed both prior to, during and after writing this article.
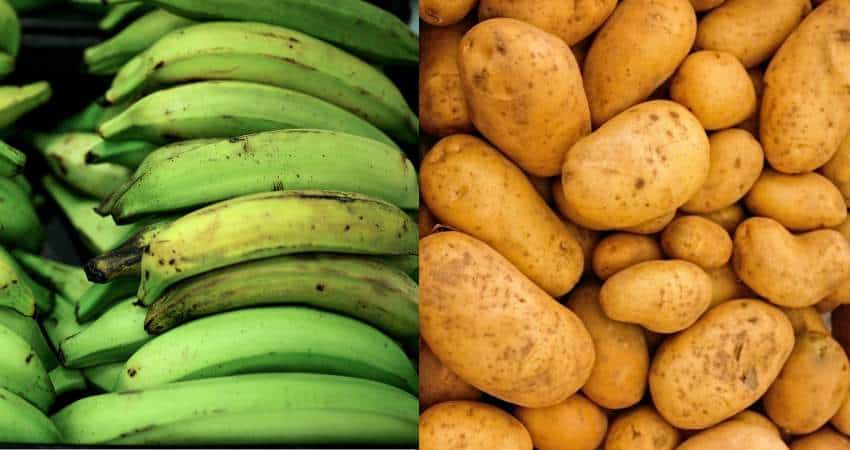

Overview
Plantains
A plantain has been a part of humanity’s diet for over 2,500 years since traders began transporting them around the seas. They’re exclusively grown in the tropics and the Caribbean where they are an important export for these developing countries.
People often substitute them for other starchy foods like potato, yam and cornmeal.
Due to their shape, appearance and taste, they are often compared to a banana. Are they part of the banana family?
A plantain is part of the same family of bananas. Both of them are from the genus known as Musa.
However, they cannot be consumed like a banana. Since they’re a lot starchier, they need to be cooked before eating. As they ripen, their starches are converted into natural sugars which give them their sweet taste.
What’s the difference between yellow and green?
A yellow and green plantain is the same fruit but is at different stages of ripeness. Green are unripe while yellow are ripe. Yellow tastes sweeter than the blander, starchier green plantain.
Potatoes
Potatoes originated in the South America Andes over 8,000 years ago. For this reason they are often associated with America. They were bought to Europe by early explorers in the 1500s.
Except for Africa, they are produced heavily and consumed all over the world. They are extremely popular and China alone produces approximately 101 million metric tones.
Plantain and potato are in different families and genus. Potato is in the genus Solanum, and plantain is in the genus Musa.
Plantain vs Potato: Nutrition
The following table is a side-by-side comparison of the nutrients:
| Potato Raw (100 g) | Yellow Plantain Raw (100 g) |
Green Plantain Raw (100 g) |
|
| Calories | 69 | 122 | 152 |
| Protein | 1.68 g | 1.30 g | 1.25 g |
| Carbohydrates | 15.7 g | 31.9 g | 36.7 g |
| Fiber | 2.4 g | 1.7 g | 2.2 g |
| Fat | 0.10 g | 0.35 g | 0.07 g |
| Sugar | 1.15 g | 17.50 g | 2.29 g |
| Vitamin A | 8 IU | 1,130 IU | 1,130 IU |
| Beta-carotene | 5 mcg | 457 mcg | 457 mcg |
| Vitamin C | 9.1 mg | 18.4 mg | 20.2 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.20 mg | 0.24 mg | 0.07 mg |
| Vitamin B9 (Folate) | 18 mcg | 22 mcg | 28 mcg |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 0.07 mg | 0.06 mg | 0.10 mg |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0.03 mg | 0.07 mg | 0.10 mg |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | 1.07 mg | 0.67 mg | 0.55 mg |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | 0.28 mg | 0.30 mg | 0.53 mg |
| Magnesium | 21 mg | 36 mg | 41 mg |
| Phosphorous | 62 mg | 32 mg | 31 mg |
| Potassium | 407 mg | 487 mg | 431 mg |
| Iron | 0.52 mg | 0.55 mg | 0.75 mg |
| Copper | 0.11 mg | 0.07 mg | 0.11 mg |
| Calcium | 9 mg | 3 mg | 2 mg |
| Zinc | 0.29 mg | 0.19 mg | 0.18 mg |
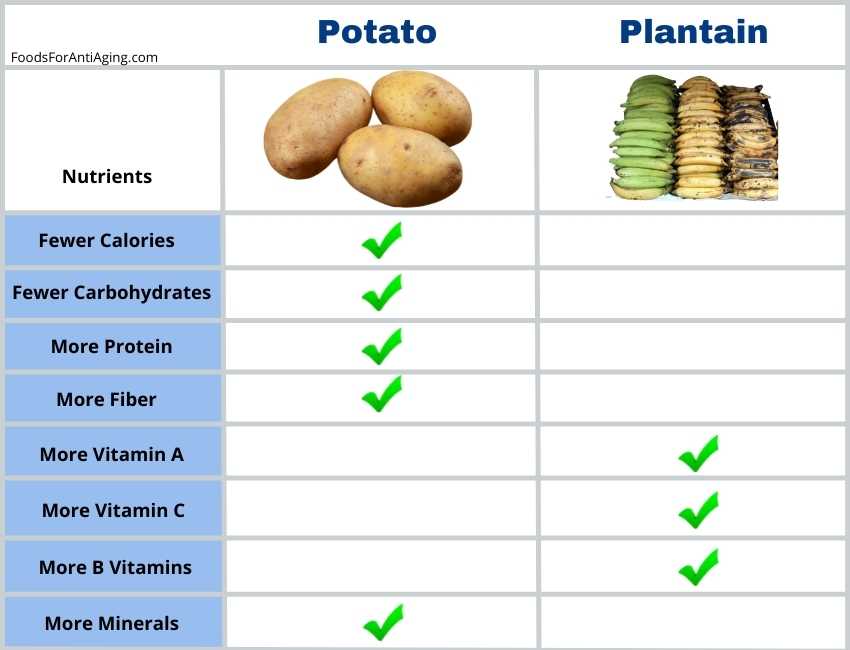
They both contain the same types of nutrients. At first glance it’s difficult to determine which one contains a higher percentage than the other. In regards to total nutrients, let’s examine which one is healthier.
Plantains are healthier in nutrients due to their higher percentage of vitamin A, vitamin C, beta carotene and B vitamins. They have a lower glycemic index than potatoes even though they contain more carbohydrates. They provide a higher percentage of magnesium, potassium and iron than potatoes.
On the other hand, potatoes are healthy too. They contain fewer calories, sugar and carbohydrates. They provide a higher percentage of fiber, thiamin, niacin, phosphorus, copper, calcium and zinc.
Both contain many of the same essential amino acid profile.
Which to Choose?
Choosing between the two may be difficult considering how healthy both of them are. A person’s particular goals may sway their decision, one way or the other.
Weight Loss and Calories
One of those goals may be the most popular one, weight loss.
Potatoes are better for weight loss than plantains due to their fewer calories, sugar and carbohydrates. A yellow plantain contains approximately 78% more calories. A green plantain contains approximately 120% more calories.
Some people like to snack on chips. Always choose the healthier ones baked and always check the labels of store bought for sodium intake.

Bodybuilding and Muscle
If your goal is to gain weight, like when bulking up for building muscle, plantains are better than potatoes. The greater percentage of calories make it easier to increase calories more than how many are burned. This is necessary to gain weight and muscle.
The extra carbohydrates provide more energy for the body and athletic performance.
Low Carb Diet and Carbohydrates
Potatoes contain approximately 50% fewer carbs per 100 grams. Therefore, if you’re on a low carb or Keto diet, potatoes are the better choice.
Check out the Keto tip just below.
Keto Bread Tip: Great News! Did you know, you don’t have to give up your favorite bread, pizza or sandwiches to follow a 100% Keto diet. Find out more in the KetoBreads website by clicking here, Keto Breads.
Paleo Diet
A Paleo friendly diet consists of fruits, vegetables, meats, fish, eggs, nuts, healthy fats and oils.
Unprocessed potatoes without any additives are good for those following a Paleo diet. A plantain is also a good carbohydrate source in a balanced Paleo diet.
Taste and Texture
People often choose one food over the other because of its taste. Since there are some similarities between the two, many people wonder if they taste the same or which one is better.
Green plantains taste starchy and bland similar to a potato. Yellow or black plantains taste sweeter due to their higher sugar content. Partially ripe plantains taste more like a sweet potato. Both foods have a smooth, creamy texture depending on the cooking method.
We’re all familiar with the flavor and texture of potatoes. When they are baked or fried, they get a golden, crispy crust with a pillowy inside. They get very soft when boiled, so people love turning them into silky smooth mashed potatoes.
The flavor is nothing extreme. It’s somewhat earthy and slightly sweet from the naturally occurring sugars. Some people prefer the taste of a red potato.
A ripe plantain which is yellow or black taste slightly sweet and a little starchy. An unripe green ones is unsweet and taste starchier.
To conduct some original research, I polled clients, readers and members of food groups I belong to. I asked them which of the two foods taste better.
- 41% said they preferred the taste of a plantain.
- 50% said they preferred the taste of potatoes.
- 9% said they had no preference.
To conduct more research, I thought it would be fun to have my own taste test at home. Yellow ones were used and potatoes were mashed. 75% picked the potatoes making them the winner in the poll and my taste test.
Find out how cassava’s taste and texture compared in my article.
Substitutions
There are times when you only have one available at home. Other times the supermarket doesn’t have what you need. In these situations you’ll wonder if you can replace one with the other.
A plantain can substitute for a potato, especially the green type. The green ones have a similar taste and texture than potatoes. Both of them can be used using similar cooking methods like boiling, frying, roasting, baking, mashing or making chips.
Can You Substitute Plantain Chips for Potato Chips?
Plantain chips and potato chips are two popular snack foods. They’re especially great when on the run or while doing an activity like hiking.
Plantain chips and potato chips can substitute for each other. Any type of dish used for one of the chips could be used for the other, especially for potato chips.
The following can substitute for plantains in recipes:
- Sweet potato
- Yams
- Potato for green
- Slightly ripe bananas
- Yuca roots
- Jackfruits
- Breadfruits
The following can substitute for potatoes:
- Sweet potato
- Taro
- Red potatoes
- Any type of white potato
- Cassava
- Green plantain
Find out how turnips compared in my article here.
Plantain Chips vs Potato Chips
I’ve already covered either one can substitute for the other, including plantain chips and potato chips. Therefore, if you prefer one for chips over the other, go right ahead.
The nutrition content of both chips is similar giving plantain chips the slight edge and making them healthier. For a healthier version of both, bake the chips instead of frying them in an unhealthy oil.

Costs
With the rising prices of just about everything, the cost of food certainly matters to most. The price may sway your decision about which one to use. Therefore, let’s take a close look at the prices of each one.
Plantains cost more than potatoes. The average price for potatoes is $0.99 per pound, and the average price for plantains is $1.68 per pound.
Both foods are readily available and affordable to purchase in most supermarkets.
To conduct more research, I decided to visit a few local supermarkets and check the prices of each one.
I first visited the Shoprite supermarket and found the following prices:
- Plantain
- $1.17 per pound
- Potatoes
- $0.99 per pound
I then checked Walmart:
- Potatoes
- $0.99 per pound
Lastly, I checked Freshdirect online:
- Plantain
- $1.98 per pound
- Russet potatoes
- $1.49 per pound
To find out the differences compared to taro, check out my comparison article here.

How To Store
Whichever you choose or have on hand, proper storage is crucial. How you store fruits or vegetables can affect how long they last before going bad and how they taste.
Store potatoes in a dark, cool place away from heat and do not store them in the refrigerator. A humid basement or root cellar is the best area. They should be kept in a burlap bag or ventilated container and stored between 40°F and 60°F.
Storing them in a refrigerator can make the center hard and change the cell structure. This can diminish the flavor. If you don’t have a cool basement, store them in a ventilated place, away from heat and light.
Unripe or ripe plantain can be stored in a cool, dry place between 45-50°F. They should be turned over every day. Finding a place somewhere out of the sun or away from a heat source is ideal. To extend the life of one already ripened, place it in the refrigerator up to five days.
They can be frozen to extend their life. Wrap a whole plantain in plastic and place it into the freezer up to one year.
They are sensitive to ethylene gas which ripens them faster. If you want them to last longer, keep them away from apples, bananas, avocado, kiwi, tomatoes and peppers4.
If you’re looking to speed up the ripening process, store one in a brown paper bag with one of the fruits listed above.
At home I store my spuds in a burlap bag in the coolest area of my home.
If you’re interested about how sweet potatoes held up against pumpkin for health and nutrition, check out my article.
Glycemic Index
Knowing the glycemic index of food is important especially if blood sugar levels are a concern. Avoiding blood sugar spikes is an important part of consuming healthy food.
The Glycemic Index (GI) is a scale measuring how fast a particular food raises the blood sugar in the blood5.
Foods on the GI scale are categorized as:
- Low-GI foods: 55 or under
- Medium-GI foods: 56-69
- High-GI foods: 70 or over
How blood sugars levels are affected:
- Foods with a glycemic index 70 or more cause a quicker spike in blood sugar levels.
- Foods with a glycemic index 56 to 69 cause a moderate spike in blood sugar levels.
- Foods with a glycemic index 55 or less cause a slow spike in blood sugar levels.
Now we know what the glycemic index is, and how it affects blood sugar, let’s find out which one of the two has a higher GI.
The green plantain GI index of 45 and the yellow GI of 54 is lower than potatoes. A boiled russet potato has a GI of 54, and a boiled Yukon Gold has a GI of 58.
Potatoes all have different GI scores. In addition to how one is cooked, the heat of the spud when eaten affects the GI.
A study published in the Journal of the Diabetic Association found boiled potatoes eaten cold had a GI score of 56. When eaten hot and boiled, it had a GI score of 896.
Find out if rice have more nutrients in my article here.
The following video explains how to air fry plantains.
Health Benefits
As noted in the nutrient section of this article earlier, the nutrients provided by both are similar. For this reason some of the health benefits are the same and the nutrients have many health benefits.
Let’s examine how each one of these nutrients benefit health.
Vitamins
Vitamin A
For eye health, plantain is more beneficial. They provide 1,130 IU of vitamin A and 457 mcg of beta carotene per 100 grams.
There are two nutrients the body converts into vitamin A. Most notably, Beta Carotene, which is easily absorbed by the body. According to scientific studies, vitamin A helps the eyes when it comes to dim light vision and dry eyes ((National Center for Biotechnology Information: Nutrients for the aging eye)).
Vitamin C
Plantain provides 18.4 mg of vitamin C per 100 grams.
The body can’t make vitamin C, so it must come from the foods ate every day. Vitamin C has been shown in studies to help with the growth and repair of tissues throughout the body7.
Vitamin C helps heal and repair wounds, maintain healthy bones, skin and cartilage. Vitamin C acts as an antioxidant and fights free radicals which damage the cells. Helping to prevent cell damage can help with the following:
- Certain diseases like cancer.
- Heart disease.
- Promote healthy aging.
B Vitamins
Of the six B vitamins listed below, plantain provides a higher percentage of four of them.
The B vitamins provided include the following:
- B1 (thiamin)
- B2 (riboflavin)
- B3 (niacin)
- B5
- B6
- B9 (folate)
B vitamins help support the following:
- Red blood cells.
- Brain function.
- Nerve function.
- Cardiovascular disease.
- Digestion.
- Energy levels.
A lack of B vitamins has been associated with oxidative stress and neural inflammation. In a study released in 2018 32 healthy adults were given B vitamin supplementation for six months. The results indicated preliminary evidence B vitamin supplementation reduced oxidative stress and inflammation8.
Find out how bread compared to spuds for health and nutrients in my comparison article.
Fiber
Potatoes provide 2.4 grams per 100 gram serving.
They both contain soluble and insoluble fiber. Fiber remains in the digestive tract and provides gut related health benefits. Fiber rich diets have been linked to regular bowel movements and a lower risk of colon cancer9.
Magnesium
Plantain provides 36 mg of magnesium per 100 grams.
Magnesium helps keep blood pressure levels stable and balanced. Recent scientific research examined previous studies and concluded magnesium supplementation decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure10.
Magnesium helps control the following:
- Insomnia
- Muscle
- Nerve function
- Blood pressure
- Blood sugar
One reason many people supplement with magnesium in the evening is because it helps calm the whole body including blood vessels.
In the heart and muscles, magnesium competes with calcium to help the muscles relax after contracting. When the body is low in magnesium, calcium can over stimulate the heart muscle’s cells causing a rapid or irregular heartbeat ((National Institutes of Health: Magnesium)).

Calcium
Potatoes provide 9 mg per 100 grams.
Calcium is important for the heart and blood pressure. Harvard Health reports calcium helps maintain blood pressure by helping in the controlling of the relaxing and tightening of blood vessels11.
Calcium also helps the following:
- Help the muscles to function properly.
- Build and maintain strong bones.
- Helps nerve function.
Potassium
Plantain provides 487 mg of potassium per 100 grams raw.
Potassium helps the body get rid of excess sodium reducing fluid build-up. These help keep systolic and diastolic blood pressure lower ((American Heart Association: How Potassium Can Help Control High Blood Pressure)).
According to Harvard Health, a number of studies have shown a connection between low potassium levels and high blood pressure12. The more potassium, the more sodium your body will lose.
Consuming too much sodium or not enough potassium throws off the delicate balance the kidneys need to remove the excess water13.
If you have any questions about this article don’t hesitate to email us. You can find an email on our contact page.
Read Next – More Food Articles!
Red Potatoes vs Yukon Gold Potatoes: What’s The Difference?
Are Sweet Potatoes Healthier Than Regular Potatoes?
Idaho vs Russet Potatoes – Are They The Same? Let’s Compare
Yukon Gold Potato vs Russet Potato: What’s The Difference?
- USDA: Plantains, yellow, raw [↩]
- USDA: Plantains, green, raw [↩]
- USDA: Potatoes, white, flesh and skin, raw [↩]
- University of San Diego: Ethylene in Fruits and vegetables [↩]
- Harvard Health Publishing: Glycemic index for 60+ foods [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Glycemic index of potatoes commonly consumed in North America [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Vitamin C and Immune Function [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: The Effect of a High-Dose Vitamin B Multivitamin Supplement on the Relationship between Brain Metabolism and Blood Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress: A Randomized Control Trial [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Mechanisms linking dietary fiber, gut microbiota and colon cancer prevention [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure: a meta-analysis [↩]
- Harvard Health: Key minerals to help control blood pressure [↩]
- Harvard Health: Potassium lowers blood pressure [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: The Effect of the Sodium to Potassium Ratio on Hypertension Prevalence: A Propensity Score Matching Approach [↩]
