Red Quinoa vs White Quinoa: What’s The Difference?
As a Certified Health Coach specializing in nutrition informing clients about healthy foods like quinoa is part of my role. Since white and red quinoa are two popular colors many of my clients ask how they’re different. Let’s answer, what’s the difference between red quinoa and white quinoa?
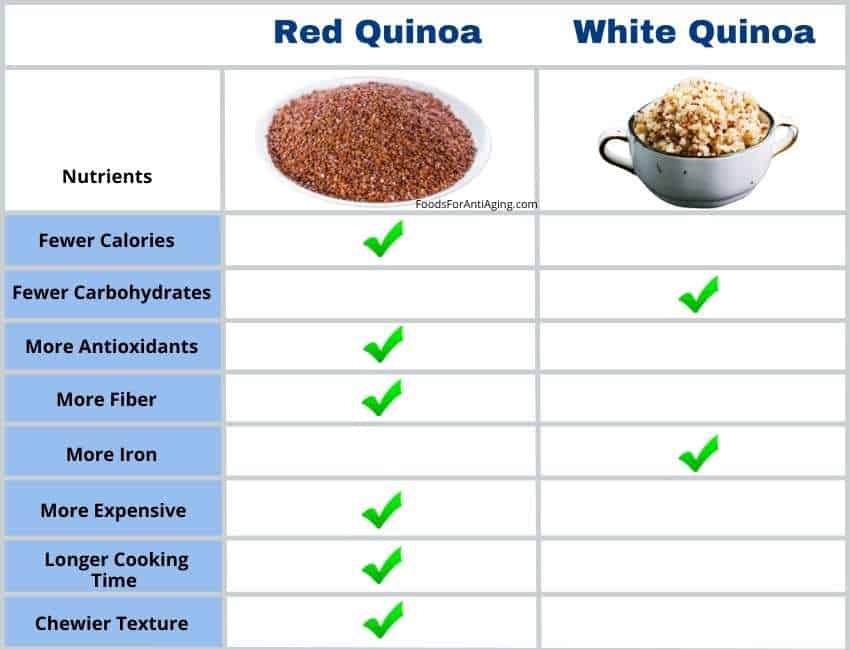
Red quinoa has a stronger flavor, is chewier and takes a few more minutes to cook than white quinoa. Red quinoa is colored red while white quinoa is colored an off white. Red and white quinoa contain a similar number of calories, protein, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals, although red quinoa has more antioxidants.
This article will cover all the differences between the two types starting with a side-by-side nutrient comparison. In addition, I’ll compare their tastes, textures, prices, glycemic index and health benefits.
I have research quinoa for my clients and personal use. I’ve purchased, researched and consumed both prior to, during and after writing this article.
Red Quinoa vs White Quinoa: Nutrient and Antioxidant Comparison
Red and white quinoa (pronounced KEEN-WAH) have similar nutritional profiles. The following table is a side-by-side comparison of the nutrients contained in 100-grams raw.
To keep things as equal as possible, both are organic and from the same brand, Inca’s Gold.
| Red Quinoa (100 g) | White Quinoa (100 g) | |
| Calories | 373 | 376 |
| Protein | 13.3 g | 13.3 g |
| Carbohydrates | 71.1 g | 68.9 g |
| Fiber | 8.2 g | 7.1 g |
| Fat | 4.44 g | 5.56 g |
| Sugar | 0 g | 0 g |
| Vitamin A | 0 IU | 0 IU |
| Vitamin C | 0 mg | 0 mg |
| Iron | 4.8 mg | 6.0 mg |
| Calcium | 67 mg | 67 mg |
| More antioxidants | X |
At first, it’s difficult to determine which one provides a higher percentage of nutrients than the other. This causes many people to ask, which one is healthier?
Red quinoa is healthier than white quinoa due to its higher percentage of antioxidants, antioxidant activity and fiber than white quinoa. Studies published in 2012 and 2015 in Food Chemistry and Food and Nutrition Sciences found red quinoa has more phenolic and antioxidant profiles than white quinoa.
The remaining macronutrients, protein, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals are similar between the two types. Therefore, white quinoa is healthy also, it just contains a little less antioxidants.
Red has more antioxidants due to its darker color. It gets its color from a plant pigment called betacyanins3.
Betacyanins are powerful antioxidants giving many red and purple plants their color4.
The two main betacyanins are:
- Betanin
- Isobetanin
Both types share the following antioxidant phenolic compounds:
- Phenolic acids
- Vanillic acid
- Ferulic acid
- Quercetin
- Kaempferol
- Glycosides

Which to Choose
Both are considered healthy, and you really can’t go wrong choosing either one. Some people will alternate between the two to avoid boredom. They even sell a tricolor version.
Some people have different goals which may sway your decision, one way or the other. Let’s take a look at the most common goals.
I consume both as part of my nutrition plan. I probably consume the white variety more often due to its price and texture.
Weight Loss
The most popular goal may be weight loss. If you want to shed some extra pounds, you may ask, which one is better for weight loss?
Red and white quinoa are similar for weight loss due to their similar number of calories per serving. Red quinoa contains 168 calories per 1/4 cup dry. White quinoa contains 169 calories per 1/4 cup dry.
The one calorie difference between the two isn’t large enough to make a difference when the goal is weight loss.
Including both as part of a well-balanced nutrition plan will help gain the maximum weight loss benefits.
Low-carb or Keto Diet
If your goal is a Keto or low-carb diet, then carbohydrates are your number one concern. If you’re on a low-carb diet, you may ask which has more carbohydrates?
Red and white quinoa is similar for a low-carb, Keto diet due to its similar amount of carbohydrates per serving. Red quinoa contains 32 grams of carbohydrates per 1/4 cup dry. White quinoa contains 31 grams of carbohydrates per 1/4 cup dry.
Another consideration for low-carb diets is the amount of fat. The total fat contained in each color is also similar.
Bodybuilding
If your goal is to gain lean muscle mass, there’s a good chance you’re lifting weights at home or in the gym. Which one is better for bodybuilding?
Red quinoa and white quinoa are similar for bodybuilding due to its similar number of protein, carbohydrates and calories. Red and white quinoa contain 5.8 grams of protein per 1/4 dry.
Supplements for bodybuilding are expensive, and the costs add up pretty fast. Considering the price of both, one type is a little higher and more difficult to find.
The higher priced color which is also more difficult to find may sway your decision to white for bodybuilding.
For more details about the prices check out the price section below.
I often eat quinoa during the morning on the days I train at the gym. The carbs help fuel my workout and I’m getting protein at the same time.
Gluten Free
Red and white quinoa are naturally gluten free. In addition, both of them can be made into flour and used as a substitute for regular flour in gluten free recipes.
My Vitamix blender I use at home can make the gluten free flour, almond, cashew or any nut flour in seconds. Check out my blender review here, Vitamix Venturist V1220 Review.
Red Quinoa vs White Quinoa: Taste and Texture
Many times people choose one food over the other because of its taste. Since there are some similarities between the two, many people wonder and ask, red vs white quinoa, do they taste the same?
Red and white quinoa have a nutty and earthy flavor, but the red quinoa is nuttier. The difference between the two is the texture. Although both are fluffy, the red quinoa has a heavier texture compared to white and is slightly chewier and less fluffy. If both types aren’t rinsed before cooking, they may taste bitter.
To conduct some original research and get the opinions of real people like you, I decided to poll my clients, readers and people in food groups I belong to. I asked them, do prefer the taste of red or white quinoa?
- 58% said they preferred the taste of white quinoa.
- 39% said they preferred the taste of red quinoa.
- 3% said they had no preference.
To conduct more research I thought it would be fun to setup and participate in a blind taste test at home. I cooked each food and served it in a bowl with the same exact seasonings. All three of us chose the white variety. The main reason was the texture.

Cooking Differences
How to Cook Quinoa
Most store-bought is pre-rinsed, if it is not pre-rinsed it should be rinsed to avoid a bitter taste.
- In a pot combine 1 cup with 2 cups of water or broth.
- Bring to a rolling boil.
- Reduce heat, cover and simmer until liquid is evaporated (about 10-15 minutes).
- Let stand 5 minutes then fluff with a fork and serve.
- Salt or add spices to taste.
Cooking tips:
- Red quinoa takes about 3-5 minutes longer to cook.
- It is done when the liquid is absorbed.
- If it’s properly cooked, you can see little, curled ends.
- 1 cup of dry makes about 3 1/2 to 4 cups cooked.
- It should be cooked and not eaten raw.
- For finicky kids, consider adding small amounts to cookies, salads, meatballs or even macaroni and cheese.
The following video informs you how to make three healthy recipes including red white and black.
Typically, the package of each type of quinoa has the cooking directions. Also, some of the stores, like IGA directions, post them on their websites with extra directions for seasoning..
Substitutions for Quinoa Recipes
When someone can’t find one of the two types called for in quinoa recipes, a common question asked is, can I substitute one for the other?
Red and white quinoa are interchangeable with each other in quinoa recipes. They can both be used in recipes, side dishes, salads and baking. Red quinoa holds its texture better and is used more for salads but is not as good for baked goods.
Price
It seems every time I check out at the supermarket the price is higher than the last. The cost of food certainly matters to most, especially with the rising costs of everything.
The price may sway your decision about which one to use in your meals more often. Therefore, which one costs more?
Red quinoa costs more than white quinoa per serving. The average price for red quinoa is $13.48 per 1 pound bag. The average cost for white quinoa is $10.99 per 1 pound bag.
The prices for both types vary depending on the store, location and sales offered. Therefore, to conduct original research, I searched various different stores to compare the price of both foods.
There didn’t seem to be a difference in price between white or tri-color in every store I checked.
I checked Shoprite supermarket:
- Wholesome Pantry White
- $3.99 per 12 oz bag (7 servings) equaling $0.57 per 1/4 cup serving
- Wholesome Pantry Tri-Color (White, Red, Black)
- $3.99 per 12 oz bag (7 servings) equaling $0.57 per 1/4 cup serving
I then checked Walmart:
- Food to Live White
- $10.99 per 1 pound bag
- Food to Live Organic Red
- $13.48 per 1 pound bag
Find out how bulgur compared, including black in my article, Bulgur vs Quinoa: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison.
I also checked the prices at Costco but was unable to make a fair comparison between the same size packaging.
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of food is important especially if blood sugar levels are a concern. Avoiding blood sugar spikes is an important part of consuming healthy food. This is true for diabetics or anyone worrying about their health5.
The Glycemic Index (GI) is a scale measuring how fast a particular food raises the blood sugar in the blood6. Blood sugar spikes can lead to health complications with the heart, nerves, kidneys and eyes7.
Foods on the GI scale are categorized as:
- Low-GI foods: 55 or under
- Medium-GI foods: 56-69
- High-GI foods: 70 or over
How blood sugars levels are affected:
- Foods with a glycemic index 70 or more cause a quicker spike in blood sugar levels.
- Foods with a glycemic index 56 to 69 cause a moderate spike in blood sugar levels.
- Foods with a glycemic index 55 or less cause a slow spike in blood sugar levels.
Having more knowledge of the glycemic index of food and how it raises blood sugar, many people ask, which one has a higher glycemic index?
Red quinoa has a higher glycemic index than white quinoa although both are considered low-GI foods. Red and white quinoa cooked in boiling water for 15 minutes has a glycemic index of 54 and 50.
After boiling for 15 minutes they have glycemic loads of 24 and 23.
Find out how black quinoa compared in my article.

The Satiety Index of Red Quinoa and White Quinoa
Satiety is a term used to explain the feeling of being full and the loss of appetite which occurs after eating food. The satiety index is a scale showing how full a person feels after eating a certain food.
The satiety index was developed in 1995 from a study which tested 38 foods. The foods were ranked how they satisfied a person’s hunger. Foods scoring under 100 are considered less filling and foods scoring above 100 are considered more filling ((National Center for Biotechnology Information: A satiety index of common foods)).
The table below shows the satiety scores of some grains, oats, rice and a few other filling foods.
| Food | Satiety Index Score |
| White bread | 100% |
| Brown rice | 132% |
| White rice | 138% |
| Lentils | 133% |
| Wholemeal Bread | 157% |
| Brown pasta | 188% |
| Oatmeal w/milk | 209% |
Unfortunately, quinoa was not one of the 38 foods tested. A study in 2005, by the University of Milan, tested the satiety of quinoa, oats and buckwheat compared to eating rice. All three had a higher satiating efficiency than rice8.
The study, or any other study I was able to find about satiety, didn’t reference whether the types tested was red or white. Since rice has satiety scores of 132% and 138%, we may be able to assume quinoa has a higher satiety score than 138%.
High satiety foods are likely to have a high satiety score for the following reasons:
- High in protein.
- High in fiber.
- High in volume (foods containing a lot of water or air).
- Low in energy density (foods low in calories for their weight).
Quinoa seems to fit into all four listed above.
Health Benefits and Disease
The nutrients provided by both types are similar. For this reason, the health benefits offered are also similar.
Although the red variety contains more antioxidants and antioxidant activity than white. Red quinoa may help better fighting cell damage and prevent disease. Let’s take a closer look at the nutrients and how they may benefit health.
In the following video a doctor informs you about quinoa and its health benefits.
Dietary Fiber
Both colors are high in dietary fiber, which is helpful for many reasons9. What makes dietary fiber soluble is it dissolves in water.
Dietary fiber is known for the following:
- Decrease the risk of diabetes by managing the blood glucose levels.
- Helps avoid constipation and have a more regular stool.
- Help overall digestive health.
- Aids greatly in weight management because it allows you to feel full faster and eat less.
Find out how lentils compared in my article, Quinoa vs Lentils: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison. The article includes all colors including black.
Protein
Both are a good source of protein. Protein may help benefit the following:
- Reduce appetite
- Build and repair muscle
- Boost metabolism
- Weight loss
B Vitamins
The B vitamins provided include the following:
- B1 (thiamin)
- B2 (riboflavin/0.11 mg per 100 grams)
- B3 (niacin)
- B5
- B6
- B9 (folate)
B vitamins help support the following:
- Digestion.
- Brain function.
- Cardiovascular disease.
- Nerve function.
- Red blood cells.
- Energy levels.
A lack of B vitamins has been associated with oxidative stress and neural inflammation. In a study released in 2018 32 healthy adults were given B vitamin supplementation for six months. The results indicated preliminary evidence B vitamin supplementation reduced oxidative stress and inflammation10.
Iron
Quinoa is an excellent choice if you need to get your daily value of iron. Iron is essential in the creation of red blood cells and is a necessary part of any healthy diet.
Iron is also vital for growth and development, as some hormones need iron to be appropriately balanced.
Find out how millet compared in my article, Millet vs Quinoa: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison. All colors including black were compared.

Calcium
Calcium is important for the heart and blood pressure. Harvard Health reports calcium helps maintain blood pressure by helping in the controlling of the relaxing and tightening of blood vessels11.
Calcium also helps the following:
- Help the muscles to function properly.
- Helps nerve function.
- Build and maintain strong bones.
Potassium
Potassium helps the body get rid of excess sodium reducing fluid build-up. These helps keep systolic and diastolic blood pressure lower12.
According to Harvard Health, a number of studies have shown a connection between low potassium levels and high blood pressure13. The more potassium, the more sodium your body will lose.
Consuming too much sodium or not enough potassium throws off the delicate balance the kidneys need to remove the excess water14.
Magnesium
Magnesium helps keep blood pressure levels stable and balanced. Recent scientific research examined previous studies and concluded magnesium supplementation decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure15.
Magnesium helps control the following:
- Muscle
- Insomnia
- Blood sugar
- Blood pressure
- Nerve function
One reason many people supplement with magnesium in the evening is because it helps calm the whole-body including blood vessels.
In the heart and muscles, magnesium competes with calcium to help the muscles relax after contracting. When the body is low in magnesium, calcium can over stimulate the heart muscle’s cells causing a rapid or irregular heartbeat ((National Institutes of Health: Magnesium)).

Phosphorus
Phosphorus has been shown in scientific studies to help with the following:
- Help the body store and manage energy.
- Muscle contraction.
- Muscle recovery.
- Help the kidneys remove waste.
- Promote healthy nerve conduction.
- Promote teeth and bone strength.
If you have any questions about this article don’t hesitate to email us. You can find an email on our contact page.
Read Next – More Food vs Food Articles!
Couscous vs Rice vs Quinoa: Which is Better? Let’s Compare
Brown Rice vs Quinoa: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison
Couscous vs Quinoa: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison
Barley vs Quinoa: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison
Quinoa Vs Oatmeal: Which is Better? Let’s Compare
Organic Lentils vs. Conventional Lentils: Which is Better?
Brown Rice vs White Rice: Which is Better for Bodybuilding?
- USDA: Organic White Quinoa [↩]
- USDA: Organic Red Quinoa, Red [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Characterisation of phenolics, betanins and antioxidant activities in seeds of three Chenopodium quinoa Willd. genotypes [↩]
- Scientific Research Journals: Total Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity of Red and Yellow Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Seeds as Affected by Baking and Cooking Conditions [↩]
- The University of Sydney: Your GI Shopping Guide [↩]
- Harvard Health Publishing: Glycemic index for 60+ foods [↩]
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Know Your Blood Sugar Numbers: Use Them to Manage Your Diabetes [↩]
- Pub Med: Effect on appetite control of minor cereal and pseudo cereal products [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Mechanisms linking dietary fiber, gut microbiota and colon cancer prevention [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: The Effect of a High-Dose Vitamin B Multivitamin Supplement on the Relationship between Brain Metabolism and Blood Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress: A Randomized Control Trial [↩]
- Harvard Health: Key minerals to help control blood pressure [↩]
- American Heart Association: How Potassium Can Help Control High Blood Pressure [↩]
- Harvard Health: Potassium lowers blood pressure [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: The Effect of the Sodium to Potassium Ratio on Hypertension Prevalence: A Propensity Score Matching Approach [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure: a meta-analysis [↩]
