Spinach vs Lettuce: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison
As a Certified Health Coach, part of my job is to educate people about the differences in certain foods, including spinach and lettuce. They are synonymous with healthy living and a happy waistline. So which is healthier, spinach or lettuce?
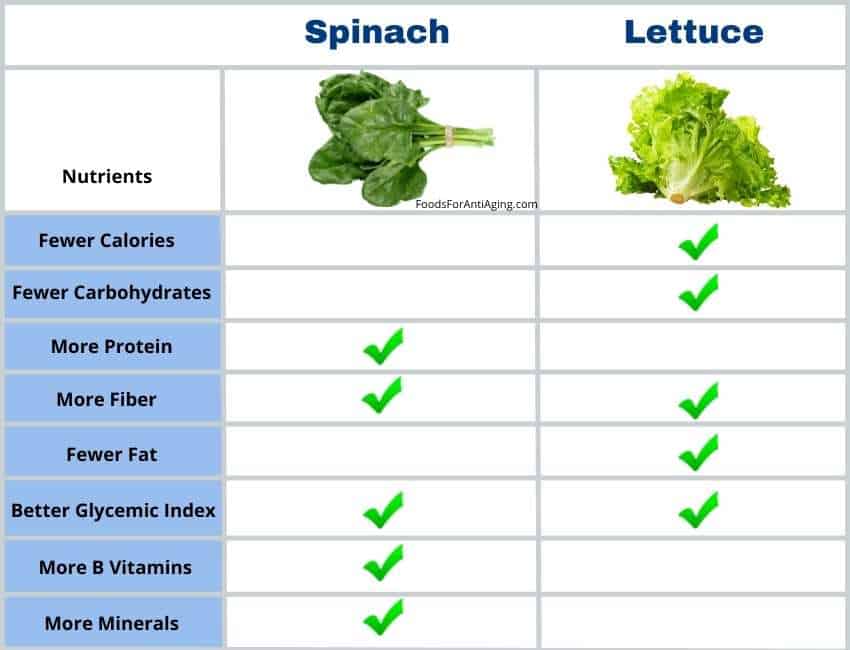
Spinach is healthier than lettuce due to its higher percentage of protein, fiber, vitamins and minerals. Spinach provides more vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin K, B6, folate, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, iron and zinc than lettuce.
This article will include a complete comparison of both including a side-by-side nutrient comparison. In addition, I’ll examine their prices, tastes, textures, glycemic index, health benefits and if one can substitute for the other.
In addition to coaching clients about them, I’ve purchased, researched and consumed both prior to, during and after writing this article.
What Is Spinach?
Spinach is part of the amaranth family, a group consisting of over 60 types of grains. To narrow it down further, it belongs to the Chenopodiaceae (or goosefoot) subgroup, to which Swiss chard, beets and quinoa also belong1
It is a dark, leafy, flowering green easily found in grocery stores and is versatile to use.
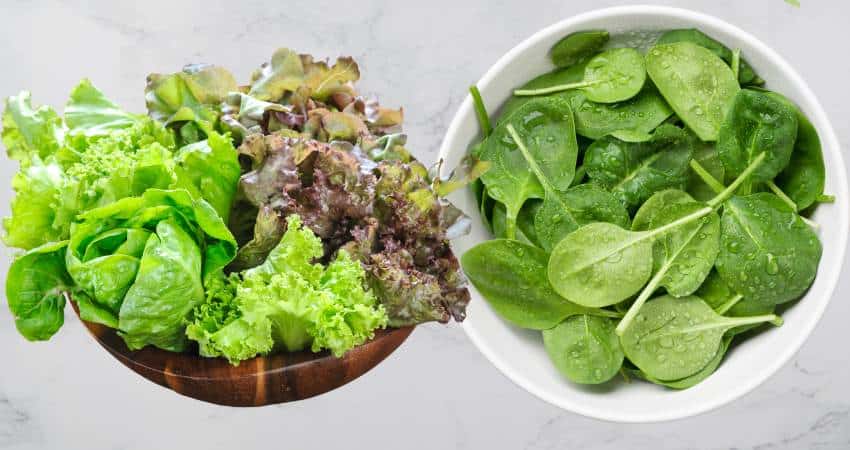

What Is Lettuce? Romaine, Green Leaf and Iceberg
Lettuce is part of the Asteraceae (or daisy) family and contains many different varieties. The most popular leafy types are:
- Romaine (or cos)
- Green leaf lettuce
- Iceberg
Other well-known varieties include chicory, endive, and artichoke2.
Spinach is a solid dark green leaf which is triangular and rounded. Most lettuce are different shades of green with larger and longer leaves. Some has some red or purple colors mixed in with the green coloring.
Spinach vs Lettuce: Nutritional Values
The following table is a side-by-side comparison of the nutrients contained in 100-grams.
| Spinach, raw (100 g) | Green leaf Lettuce, raw (100 g) | |
| Calories | 23 | 15 |
| Protein | 2.86 g | 1.36 g |
| Carbohydrates | 3.63 g | 2.87 g |
| Fiber | 2.2 g | 1.3 g |
| Fat | 0.39 g | 0.15 g |
| Sugar | 0.42 g | 0.78 g |
| Vitamin A | 9,380 IU | 7,400 IU |
| Beta-carotene | 5,630 mcg | 4,440 mcg |
| Vitamin C | 28.1 mg | 9.2 mg |
| Vitamin K | 483 mcg | 126 mcg |
| Vitamin D | 0 IU | 0 IU |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.19 mg | 0.09 mg |
| Vitamin B9 (Folate) | 194 mcg | 38 mcg |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 0.08 mg | 0.07 mg |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0.19 mg | 0.08 mg |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | 0.72 mg | 0.37 mg |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | 0.07 mg | 0.13 mg |
| Magnesium | 79 mg | 13 mg |
| Phosphorous | 49 mg | 29 mg |
| Potassium | 558 mg | 194 mg |
| Iron | 2.71 mg | 0.86 mg |
| Copper | 0.13 mg | 0.03 mg |
| Calcium | 99 mg | 36 mg |
| Zinc | 0.53 mg | 0.18 mg |
When examining the nutrients above, spinach is nutritionally superior to lettuce. While they both contain the same types, spinach and lettuce are nutritionally different because spinach contains a higher percentage of most.
Due to its nutrients and fiber I often consume more spinach. Although I consume both especially when I have a mixed green grilled chicken salad at my favorite cafe for lunch or dinner.
Which to Choose?
Weight Loss
If you’re counting calories to lose extra pounds, you may be wondering which one is better for weight loss.
Green leaf lettuce contains eight fewer calories than spinach per 100 grams. While this doesn’t sound like much of a difference, it results in 54% less calories. Therefore, green leaf lettuce may be better for weight loss if you’re counting calories.
Gluten Free
If you’re consuming a gluten free diet or have celiac disease, this can make or break your choice between the two. Between the two, which is gluten free?
Spinach and lettuce are gluten free. Therefore, if you have celiac disease, both are good options.
Low-carb or Keto Diet
If you’re consuming a low-carb diet, how many carbohydrates a food contains may be your priority. Therefore, lettuce vs spinach, which has more carbohydrates?
Spinach has 0.76 more carbohydrates than green leaf lettuce per 100 grams. While this doesn’t sound like much of a difference, it has 26% more carbohydrates. Therefore, green leaf lettuce is better for low-carb or keto diets.
Bodybuilding
If you’re trying to gain lean muscle mass, your diet and protein intake are important. Which is better for bodybuilding?
Spinach is better for bodybuilding due to its higher percentage of protein and carbohydrates. The extra protein helps to repair and build new muscle after a workout. The extra carbohydrates help to fuel energy and increase exercise performance when lifting weights.
It provides 1.5 more grams of protein per 100 grams. While this may not seem like much of a difference, it equals 110% more protein.
Health Benefits
Minerals
Spinach provides a higher percentage of every mineral listed in the table above. The difference in minerals is significant. Let’s examine these minerals a little closer and discuss how they may benefit health.
Calcium
- Spinach provides 175% more calcium per 100 grams.
Calcium is important for the heart and blood pressure. Harvard Health reports calcium helps maintain blood pressure by helping in the controlling of the relaxing and tightening of blood vessels5.
Calcium also helps the following:
- Helps nerve function.
- Help the muscles to function properly.
- Maintain and build strong bones.
Potassium
- Spinach provides 188% more potassium per 100 grams.
Potassium helps the body reduce excess fluid and blood pressure6.
Some medical experts recommend the potassium to sodium ratio of 4:1. Consuming too much sodium or not enough potassium throws off the delicate balance the kidneys need to remove the excess water7.
According to Harvard Health, a number of studies have shown a connection between low potassium levels and high blood pressure8. The more potassium, the more sodium your body will lose.
This video below examines the benefits of spinach and lettuce.
Iron
- Spinach provides 216% more iron per 100 grams.
Iron is essential in the creation of red blood cells and is a necessary part of any healthy diet. Iron is also vital for growth and development, as some hormones need iron to be appropriately balanced9.
Magnesium
- Spinach provides 510% more magnesium per 100 grams.
Magnesium helps the body control the following:
- Systolic and diastolic blood pressure
- Blood sugar
- Muscle
- Insomnia
- Nerve function
- Immune system
Magnesium helps keep blood pressure levels stable and balanced. Recent scientific research examined previous studies and concluded magnesium supplementation decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure10.
One reason many people supplement with magnesium in the evening is because it helps calm the whole body including blood vessels.
In the heart and muscles, magnesium competes with calcium to help the muscles relax after contracting. When the body is low in magnesium, calcium can over stimulate the heart muscle’s cells causing a rapid or irregular heartbeat11.
Phosphorus
- Spinach provides 69% more phosphorus per 100 grams.
Phosphorus has been shown in scientific studies to help with the following:
- Help the kidneys remove waste.
- Help the body store and manage energy.
- Promote healthy nerve conduction.
- Promote bone and teeth health.
- Muscle contraction and recovery.
Find out if Swiss chard has more nutrients in my article. Is it better overall?

Dietary Fiber
- Spinach provides 69% more fiber per 100 grams.
Soluble fiber is helpful for many reasons ((National Center for Biotechnology Information: Mechanisms linking dietary fiber, gut microbiota and colon cancer prevention)). What makes dietary fiber soluble is it dissolves in water.
Soluble fiber is known for the following:
- Manage the blood glucose levels which helps decrease the risk of diabetes.
- Aids greatly in weight management because it allows you to feel full faster and eat less.
- Help overall digestive health.
- Helps avoid constipation and have a more regular stool.
Vitamins
B Vitamins
For B vitamins spinach provides a higher percentage of folate, B6, thiamin, niacin and riboflavin. The B vitamins provided include the following:
- B1 (thiamin)
- B2 (riboflavin)
- B3 (niacin)
- B5
- B6
- B9 (folate)
B vitamins help support the following:
- Brain function.
- Red blood cells.
- Nerve function.
- Cardiovascular disease.
- Energy levels.
- Digestion.
A lack of B vitamins has been associated with oxidative stress and neural inflammation.
In a study released in 2018 32 healthy adults were given B vitamin supplementation for six months. The results indicated preliminary evidence B vitamin supplementation reduced oxidative stress and inflammation12.
Vitamin A & Beta Carotene
- Spinach provides 26% more vitamin A per 100 grams.
Beta-carotene is a compound present in both. The body converts beta-carotene into vitamin A.
Vitamin A is a powerful antioxidant that can help reduce cellular damage by controlling the negative effects of free radicals13. An increased number of vitamin A has been shown to fight and prevent cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of death in the United States14.
According to scientific studies, vitamin A helps the eyes when it comes to dim light vision and dry eyes ((National Center for Biotechnology Information: Nutrients for the aging eye)).
Find out if collard greens have more nutrients in my article.

They Both Contain All Essential Amino Acids
Essential amino acids are amino acids your body cannot produce by itself, so you must get them through the foods you consume.
Therefore, a diet low in them will result with low levels of aminos.
Amino acids are necessary for the body to repair itself and regulate several muscular and nerve functions. They are also required to break down fats and proteins properly.
Both contain trace amounts of each amino acid:
- Histidine
- Isoleucine
- Leucine
- Methionine
- Threonine
- Valine
- Phenylalanine
- Lysine
Neither Contains Vitamin D, B12, Cholesterol, Starch, Trans or Saturated Fat
With varying levels of other vitamins, unfortunately, neither one contains vitamin D or B12. They’re also free from cholesterol, starch and unhealthy trans fats on a more positive note.
They contain low levels of healthy saturated fat, which means you can eat a large portion of greens without worrying about many calories.
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index measures how fast food raises blood sugar levels ((Harvard Health Publishing: Glycemic index for 60+ foods)). Large blood sugar spikes may lead to health complications over time ((National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Know Your Blood Sugar Numbers: Use Them to Manage Your Diabetes)). For this reason, avoiding blood sugar spikes as often as possible is an important part of a healthy diet.
Foods on the GI scale are categorized as:
- Low-GI foods: 55 or under
- Medium-GI foods: 56-69
- High-GI foods: 70 or over
How blood sugars levels are affected:
- Foods with a glycemic index 70 or more cause a quicker spike in blood sugar levels.
- Foods with a glycemic index 56 to 69 cause a moderate spike in blood sugar levels.
- Foods with a glycemic index 55 or less cause a slow spike in blood sugar levels.
Spinach and lettuce are both low glycemic foods and have few carbohydrates per serving. All leafy greens have a low glycemic index, almost unmeasurable in some varieties.
Find out if romaine is healthier in my article.
The video below explains how to make sautéed spinach.
Taste, Flavor and Texture
In addition to the benefits and goals listed above, you may want to choose one of these healthy foods because of its flavor. Since there are some similarities between the two, many people wonder, which tastes better?
Spinach has a stronger, bitter taste than lettuce. Lettuce has a milder taste and almost no scent. Spinach is thicker than lettuce which tears apart easier. Iceberg lettuce is thicker than other lettuces and is crunchier than spinach.
To do some original research, I decided to poll my clients, readers and people in food groups I belong to. I asked them, which taste do you prefer?
- 51% said they preferred the taste of lettuce.
- 41% said they preferred the taste of spinach.
- 8% said they had no preference.
To conduct more research I setup and participated in a blind taste test at home. We made two salads, one with each leafy green. Two out of the three of us chose the salad with the lettuce.

Substituting in Recipes and Salad
Regardless of which one you choose, sometimes you may not have a choice. You may only have one available in the refrigerator or at the store. Therefore, many people wonder if they can substitute for each other.
Spinach and lettuce can substitute for each other in recipes, salads or side dishes. They both can be eaten raw, cooked or used in gluten free recipes. When substituting use equal amounts called for in the recipe.
Substitutes for spinach include:
- Green leaf lettuce
- Swiss chard
- Bok choy
- Romaine lettuce
- Arugula
- Butterhead lettuce
- Kale
- Mustard greens
- Beet greens
- Purslane
- Watercress
- Collard greens
- Iceberg lettuce
Substitutes for green leaf lettuce include all of the items above except for number one.
Find out the differences between these two spinach varieties in my comparison article.

Prices
Just when you thought the price of grocery items went to high, they keep getting higher. The cost of food certainly matters to most people. Therefore, let’s examine the prices of each one.
To conduct original research, I visited some local supermarkets and compared the prices. Here are my findings.
Fresh lettuce costs less money per ounce than spinach. The cost for fresh lettuce averages $0.12 per ounce and spinach averages $0.16 per ounce. Bagged spinach and lettuce have a similar price averaging $0.20 per ounce.
First I checked Walmart:
- Marketside bagged fresh spinach
- 10 ounce bag $1.98. Equals $0.20 per ounce
- Marketside bagged leafy romaine lettuce
- 10 ounce bag $2.78. Equals $0.28 per ounce
- Marketside bagged iceberg lettuce
- 12 ounce bag $1.48. Equals $0.12 per ounce
I then checked my local Shoprite supermarket:
- Fresh spinach bundle
- 12 ounces for $1.87. Equals $0.16 per ounce
- Green leaf lettuce bundle
- 9 ounces for $1.12. Equals $0.12 per ounce
- Red leaf lettuce bundle
- 9 ounces for $1.12. Equals $0.12 per ounce
- Iceberg lettuce fresh
- One head for $1.79. Equals $0. per ounce
Find out which spinach type has more nutrients in my comparison article.
If you have any questions about this article don’t hesitate to email us. You can find an email on our contact page.
Read More Food Articles
Spinach vs Broccoli: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison
Frozen Spinach vs Fresh: Which is Better? A Comparison
Kale vs Spinach: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison
Organic Spinach vs. Regular Spinach: What’s The Difference?
Arugula vs Spinach: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison
- Britannica: Amaranthaceae [↩]
- Britannica: Asteracae [↩]
- USDA: Spinach, raw [↩]
- USDA: Lettuce, green leaf, raw [↩]
- Harvard Health: Key minerals to help control blood pressure [↩]
- American Heart Association: How Potassium Can Help Control High Blood Pressure [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: The Effect of the Sodium to Potassium Ratio on Hypertension Prevalence: A Propensity Score Matching Approach [↩]
- Harvard Health: Potassium lowers blood pressure [↩]
- National Institutes of Health: Iron [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure: a meta-analysis [↩]
- National Institutes of Health: Magnesium [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: The Effect of a High-Dose Vitamin B Multivitamin Supplement on the Relationship between Brain Metabolism and Blood Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress: A Randomized Control Trial [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Antioxidant potentials of vitamin A and carotenoids and their relevance to heart disease [↩]
