Sweet Potato vs Russet Potato: Which Potato is Better?
Russet potatoes and sweet potatoes are popular varieties. During my Health Coaching sessions, the topic about which one is better often come up. Let’s answer, which is better sweet potatoes or russet potatoes?
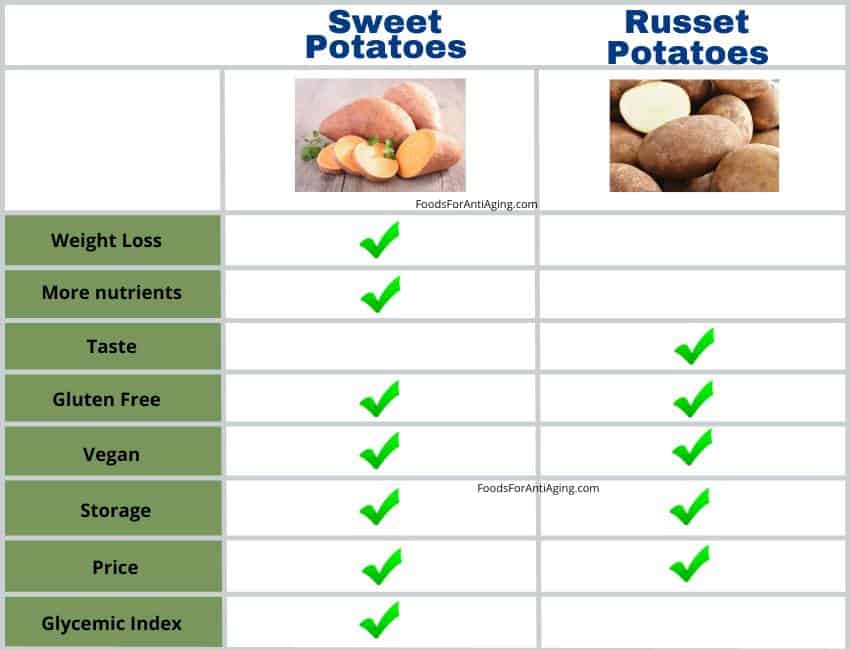
Sweet potatoes are better than russet potatoes due to their higher percentage of antioxidants, fiber, vitamins A and C. They have a better glycemic index and fewer carbohydrates. Sweet potatoes taste sweeter and are slightly more affordable than russet.
This article will compare both potatoes nutrients, tastes, costs and whether one can substitute for the other in recipes. In addition, I’ll examine their benefits and if one is easier to store than the other.
I’ve purchased, researched and consumed both potatoes prior to, during and sometimes after writing this article.
Differences Between a Sweet Potato and a Russet
- A sweet potato has a redder skin.
- A russet potato has a lighter color flesh.
- The flavor of a russet sweet potato is milder.
- Sweet potatoes have a sweeter flavor.
- The russet potato has a harder skin.
- Russet potatoes cost slightly more.
- Sweet potatoes have a better glycemic index.
- Sweet potatoes contain more antioxidants.

Sweet Potato vs Russet Potato Nutritional Content
Let’s take a look at the nutrients contained in each potato. The following table is a side-by-side comparison of the nutrients:
| Sweet Potato Cooked (100 g) | Russet Potato Cooked (100 g) | |
| Calories | 90 | 95 |
| Protein | 2.01 g | 2.63 g |
| Carbohydrates | 20.7 g | 21.4 g |
| Fiber | 3.3 g | 2.3 g |
| Fat | 0.15 g | 0.13 g |
| Sugar | 6.48 g | 1.08 g |
| Vitamin A | 19,200 IU | 10 IU |
| Beta-carotene | 11,500 mcg | 6 mcg |
| Vitamin C | 19.6 mg | 8.3 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.29 mg | 0.35 mg |
| Vitamin B9 (Folate) | 6 mcg | 26 mcg |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 0.11 mg | 0.07 mg |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0.11 mg | 0.05 mg |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | 1.49 mg | 1.35 mg |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | 0.88 mg | 0.38 mg |
| Magnesium | 27 mg | 30 mg |
| Phosphorous | 54 mg | 71 mg |
| Potassium | 475 mg | 550 mg |
| Iron | 0.69 mg | 1.07 mg |
| Copper | 0.16 mg | 0.11 mg |
| Calcium | 38 mg | 18 mg |
| Zinc | 0.32 mg | 0.35 mg |
| Manganese | 0.48 mg | 0.23 mg |
Both contain a wide variety of nutrients. At first it may be difficult to figure out which one is healthier than the other. Therefore, let’s examine which is healthier.
Sweet potatoes are healthier than russet potatoes due to their higher percentage of antioxidants, fiber and vitamins. They provide more vitamin A, vitamin C, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, B5, copper, calcium and manganese than russet. In addition, they have a lower glycemic index which helps keep blood sugar levels lower.
At the same time, russets are no slouch either. They provide more protein, B6, folate, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, iron and zinc.
I often choose regular sweet potatoes due to their nutrients. Of all the potatoes, I prefer them for this reason. If there’s not a good selection of sweet at the supermarket, I’ll buy russet.
Calories
- Sweet potatoes contain 5.5% fewer calories per 100 grams.
Protein
- Russet contains 31% more protein per 100 grams.
Carbohydrates
- Sweet potatoes contain 3.4% fewer carbohydrates per 100 grams.
Dietary Fiber
- Sweet potatoes contain 44% more fiber per 100 grams.
Vitamin A
- Sweet potatoes contain 190,000% more vitamin A per 100 grams.
Vitamin C
- Sweet potatoes contain 136% more vitamin C per 100 grams.
Saturated Fat
- Russet contains 0.02 fewer grams of saturated fat per 100 grams.
The following video compares both potatoes and their benefits.
Which to Choose
Some people may alternate between the two or choose one due to their particular goals. Let’s take a look at some of the popular goals.
Low Carb or Keto Diets
The goal for most low-carb diets is consuming few carbohydrates while adding more healthy fat and protein. With such a restrictive carbohydrate intake, every gram of carbs may make a difference.
Therefore, let’s examine which one has fewer carbohydrates.
- Sweet potatoes are better for low-carb diets than russet due to its fewer carbohydrates. Russet contains 3.4% more carbohydrates per 100 gram serving.
Weight Loss
Weight loss may be the most popular goal. If you’re trying to lose extra pounds from the midsection area, the number of calories may matter to you.
Therefore, let’s examine which is better for weight loss.
- Sweet potatoes are better for weight loss than russet potatoes due to its fewer calories and more fiber per serving. Russet contains 5.5% more calories per 100 grams.
- In addition, they provide 44% more fiber which has been associated with weight loss. Fiber makes a body feel fuller and as a result less food is consumed later.
Gluten Free
Avoiding any gluten is the main goal for people who wish to follow a gluten free diet or have Celiac disease. Therefore, let’s answer which one is gluten free?
- Sweet and russet potatoes are both gluten free and good for gluten free diets.
Vegan or Vegetarian
If you’re thinking about following a vegan or vegetarian diet consuming dairy products or animal-derived products is important. Knowing which one is vegan or vegetarian friendly may help you choose between the two.
- Russet and sweet potatoes do not contain animal products making them both beneficial for vegans and vegetarians.
Bodybuilding
- Russet potatoes are better than sweet potatoes for bodybuilding due to its great number of proteins, carbohydrates and calories.
Regardless of whether a bodybuilder is in a cutting, bulking or maintenance phase, they need much protein to repair their muscles and elicit a hypertrophy effect. 100 grams of cooked russets have 31% more grams of protein.
Bodybuilders need a good number of carbohydrates as well. The majority of their macronutrient balance should be made up of healthy carbohydrates. Carbohydrates help to fuel energy and increase performance during exercise.
The white potato contains 3.4% more grams of carbohydrates for every 100 grams.
They also contain more calories which are important for a bodybuilder when trying to gain lean muscle mass. The extra calories may prove beneficial during a bulking phase.
On the evenings before I go to the gym, I’ll often pick which potato I have because I feel like I have more energy the following day due to the carbs.
Taste and Texture
Due to their different color flesh, one would think they don’t taste the same. Let’s examine the taste and texture of both.
Sweet potatoes taste sweeter and nuttier than russet potatoes. Russet potatoes have a mild, neutral taste. A Russet has a thicker skin with a creamy flesh compared to sweet potatoes stringy, crumbly texture.
The orange potatoes hold their sweetness consistently. There’s a subtle starchy undertone with rich sweet flavor. They have a stringy, soft, crumbly texture.
A Russet has a neutral, mild flavor which is unsweet. There’s a starchy undertone and the flesh is creamy. If you eat the skin, it’s thicker than other potatoes.
I wanted to get the opinion of real people like you by conducting some original research. Therefore, I reached out to some clients, members of food groups and readers. I asked, what potato tastes better?
- 43% said they preferred the taste of russet potatoes.
- 42% said they preferred the taste of sweet potatoes.
- 15% said it depended on their mood.
I also participated in my own taste test. I mashed both potatoes and seasoned them the same way. I chose the taste of the russet even though I consume the orange potato more often.
Can You Substitute Sweet Potatoes for Russet Potatoes?
Sweet potatoes can substitute for russet potatoes in recipes. When substituting with sweet potatoes, the cooking time will be increased due to their denser flesh which takes longer to cook. They both can both be baked, mashed, roasted or grilled.
There are a few things you should consider before substituting these potatoes with each other.
- Increased cooking times is recommended for sweet potatoes. This is due to their denser flesh. The longer cooking time will make it moister.
- If you’re substituting russet, remember shortening the cooking time.
- The quantity of each doesn’t change when substituting one for the other.
If a recipe requires a sweet taste, it may need to be modified when using russet to add other ingredients which will increase the sweetness.

Find out how Yukon Gold compared in my latest article.
Which Potato Costs More
With the rising prices of just about everything, the cost of food certainly matters to most people. The price may sway your decision about which one to use. Therefore, let’s take a close look at which one is more expensive.
Sweet potatoes and russet potatoes have a similar price. Both potatoes average cost is $0.99 per pound.
To conduct my own research, I checked three different supermarkets located in my area. Both supermarkets are on different levels of pricing. Walmart is the most economical and Stop and Shop being more expensive.
Here are my findings, first I visited Shoprite:
Shoprite:
- Sweet potatoes
- $0.99 per pound
- Russet
- $0.99 per pound
Walmart:
- Sweet potatoes
- $0.98 per pound
- Russet
- $0.98 per pound
Stop & Shop:
- Sweet potatoes
- $1.19 each
- Russet
- $1.26 each
How to Store
How to store a particular food may make a difference when choosing one over the other. If you have both and routinely buy one or the other, you’ll want to know how to properly store them for longevity and quality.
Store sweet potatoes or russet potatoes in a dark place away from heat. They should be kept out of the refrigerator. A humid basement or root cellar is the best area. They should be kept in a ventilated container or burlap bag and stored between 55°F and 60°F.
Storing either one in a refrigerator can make the center hard, change the cell structure and diminish the flavor. If you don’t have a cool basement, be sure to store them in a ventilated place, away from heat and light.
I used to store them in my refrigerator because I didn’t have any other spare room for them. If you can, it’s better to keep them somewhere else.
Find out how these two sweet varieties compared in my article here.
Glycemic Index
Knowing the glycemic index of certain foods is important especially if blood sugar levels is a concern. Diabetic or not, blood sugar is an important thing people should be aware of.
The Glycemic Index (GI) is a scale measuring how fast a particular food raises or spikes the blood sugar in the blood3. Blood sugar spikes can lead to health complications with the heart, kidneys, eyes and nerves4.
Foods on the GI scale are categorized as:
- Low-GI foods: 55 or under
- Medium-GI foods: 56-69
- High-GI foods: 70 or over
How blood sugars levels are affected:
- Foods with a glycemic index 70 or more cause a more quicker spike in blood sugar levels.
- Foods with a glycemic index 56 to 69 cause a moderate spike in blood sugar levels.
- Foods with a glycemic index 55 or less cause a slow spike in blood sugar levels.
Now we know what GI is, and how it affects blood sugar, let’s examine the GI of both potatoes.
Sweet potatoes have a lower GI than russet. A boiled sweet potato has a GI of 44, and a boiled russet has a GI of 54. A baked sweet spud has a GI of 94, and a baked russet potato has a GI of 111.
Find out how the red potato compared in my comparison article.
Health Benefits
The doctor in the following video explains the health benefits of sweet potatoes.
Sweet Potatoes
Eye Health
For eye health, sweet potatoes is more beneficial and offer more carotenoids than white potatoes.
There are two nutrients the body converts into vitamin A. Most notably, Beta Carotene, which is easily absorbed by the body.
According to scientific studies, vitamin A helps the eyes when it comes to dim light vision and dry eyes ((National Center for Biotechnology Information: Nutrients for the aging eye)). Consuming one regular sweet potato provides 730% of the daily value for vitamin A.
The Anthocyanins found in sweet potatoes have been found in studies to protect eye cells from damage improving overall eye health5.
If you’re interested about how they held up against pumpkin for health and nutrition, check out my article here.
The Immune System
Although vitamin C is widely talked about for the immune system, vitamin A is important also. According to Harvard University, vitamin A is a great source to stimulate healthy white blood cells6.
These cells have the responsibility of keeping the immune system as healthy as possible to fight viruses and illnesses effectively. Other nutrients like the antioxidant anthocyanin and vitamin C possess anti-inflammatory properties protecting against disease and illness.
Gut Health and Digestion
Fiber remains in the digestive tract and provides gut related health benefits. Fiber rich diets have been linked to regular bowel movements and a lower risk of colon cancer7.

Russet Potatoes
Potassium
Potassium helps the body get rid of excess sodium reducing fluid build-up. These help keep systolic and diastolic blood pressure lower ((American Heart Association: How Potassium Can Help Control High Blood Pressure)).
According to Harvard Health, a number of studies have shown a connection between low potassium levels and high blood pressure8.
The more potassium, the more sodium your body will lose. Consuming too much sodium or not enough potassium throws off the delicate balance the kidneys need to remove the excess water9.
B Vitamins
The B vitamins provided include the following:
- B1 (thiamin)
- B2 (riboflavin)
- B3 (niacin)
- B5
- B6
- B9 (folate)
- B12
B vitamins help support the following:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Energy levels.
- Brain function.
- Digestion.
- Nerve function.
- Red blood cells.
A lack of B vitamins has been associated with oxidative stress and neural inflammation. In a study released in 2018 32 healthy adults were given B vitamin supplementation for six months. The results indicated preliminary evidence B vitamin supplementation reduced oxidative stress and inflammation10.
Find out how purple yams compared in my comparison article here.
The following video explains how to prepare baked sweet potatoes.
If you have any questions about this article don’t hesitate to email us. You can find an email on our contact page.
Read Next – More Potato vs Food Articles!
Sweet Potato vs. Butternut Squash: A Comparison
Purple Sweet Potato vs Sweet Potato: What’s The Difference?
Are Sweet Potatoes Healthier Than Regular Potatoes?
Sweet Potato vs Yam Nutrition and Benefit Differences
- USDA: Sweet potato, cooked, baked in skin, flesh, without salt [↩]
- USDA: Potatoes, Russet, flesh and skin, baked [↩]
- Harvard Health Publishing: Glycemic index for 60+ foods [↩]
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Know Your Blood Sugar Numbers: Use Them to Manage Your Diabetes [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Review on nutritional composition of orange-fleshed sweet potato and its role in management of vitamin A deficiency [↩]
- Harvard Health: Vitamin A [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Mechanisms linking dietary fiber, gut microbiota and colon cancer prevention [↩]
- Harvard Health: Potassium lowers blood pressure [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: The Effect of the Sodium to Potassium Ratio on Hypertension Prevalence: A Propensity Score Matching Approach [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: The Effect of a High-Dose Vitamin B Multivitamin Supplement on the Relationship between Brain Metabolism and Blood Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress: A Randomized Control Trial [↩]
