Herring vs Sardines – What’s The Difference? Let’s Compare
Herring and sardines look similar and are from the same family. For this reason many people wonder about their differences. Let’s answer the question, what is the difference between herring and sardines?
Sardines tastes fishier, oilier and saltier than herring. Sardines have a meatier texture than herrings texture which is more tender. They are different species of fish although from the same family. Herring provides a higher percentage of B vitamins and omega-3 fatty acids.
This article will compare their tastes, textures, cooking methods, costs, mercury levels and whether one can substitute for the other in recipes. In addition, I’ll do a side-by-side comparison of their nutrients, habitats, size, weight and more.
For the comparison below I’ll be comparing Atlantic herring and the Atlantic sardine otherwise noon as the European pilchard.
Herring and Sardines Nutritional Value
As a Certified Health Coach I’m asked all the time about seafood and their nutrients. I’ve been researching the nutrients of food, including herring and sardines for over 20 years. I’ve purchased and consumed them also.
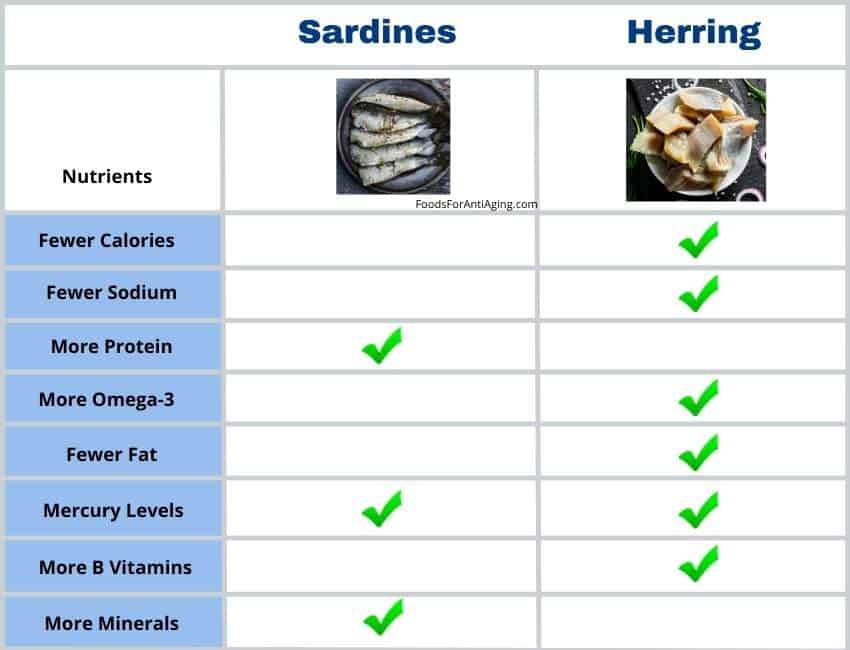
For the nutrient comparison, the table below compares 4 ounces of each. The sardines are canned, packed in water, boneless and skinless.
Sardines are extremely perishable, which is why it’s difficult to find them fresh. Almost everywhere, you’ll find them canned which is why I compare the canned ones first.
| Nutrient | Sardines, raw
Canned, water (4 Ounces) |
Herring, raw
Fresh, Atlantic (4 Ounces) |
| Calories | 210 | 170 |
| Fat | 12 g | 10 g |
| Saturated Fat | 3.0 g | 2.3 g |
| Cholesterol | 69 mg | 68 mg |
| Protein | 24 g | 20 g |
| Sodium | 469 mg | 102 mg |
| Omega-3 | 1.65 g | 1.84 g |
| B-6 | 0.1 mg | 0.3 mg |
| B-12 | 10.2 mcg | 15.5 mcg |
| Thiamin | 0.05 mg | 0.10 mg |
| Riboflavin | 0.26 mg | 0.28 mg |
| B5 | 0.6 mg | 0.7 mg |
| Iron | 2.6 mg | 1.2 mg |
| Niacin | 4.7 mg | 3.6 mg |
| Folate | 27.2 mcg | 11.3 mcg |
| Potassium | 386 mg | 370 mg |
| Magnesium | 38 mg | 36 mg |
| Phosphorus | 415 mg | 267 mg |
| Calcium | 272.1 mg | 64.6 mg |
| Zinc | 1.5 mg | 1.1 mg |
| Selenium | 46.0 mcg | 41.3 mcg |
Nutrient Sources ((Nutrition Value: Sardines, packed in water, boneless, skinless))1
Both fish contain a good number of minerals and vitamins. At first glance it’s difficult to determine which one provides more. Therefore, let’s examine which one is healthier.
Fresh herring is healthier than canned sardines due to its higher percentage of heart healthy omega-3 fatty acids and B vitamins. It contains less calories, total fat, saturated fat, cholesterol and sodium. Fresh herring provides more B6, B12, thiamin, riboflavin and B5.
Sardines offer many benefits and it’s difficult to argue against its healthy nutrients. They provide a higher percentage of niacin, folate, potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, calcium, zinc and selenium.
When both are available I prefer to eat herring. This is because of the nutrients and taste which is explained more further down in the article.
Both are good sources of vitamin D and zinc. Also, a high percentage of omega-3 fatty acids but herring contains a little more. To find out why they are important keep reading the next section below about health benefits.
Calories, Protein and Sodium
- Sardines contain 23.5% more calories, 20% more protein and 360% more sodium per 4 ounces.
Herring Health Benefits
Both fish provide the same nutrients and therefore the same benefits. Although I broke down the benefits by which fish offers the higher percentage of each nutrient ((FDA: Seafood Nutrition Facts)).
Omega 3 Fatty Acids
Both fatty fish are a great source of omega-3s. Herring contains approximately 13 percent more which leads to the question, why does omega-3 fatty acids matter so much?
Omega-3 fatty acids are important because they are heart healthy and help keep arteries healthy. The omega-3s may help with the following:
- Keeping bad cholesterol low.
- Keeping good cholesterol high.
- Reducing inflammation.
- Reducing plaque build-up.
- Lowering triglycerides
- Help keep the heart rhythms more normal.
DHA and EPA, polyunsaturated fatty acids, are associated with lowering blood pressure and improving the health of blood vessels ((National Center for Biotechnology: Marine Omega-3 Supplementation and Cardiovascular Disease)).
Studies suggest omega-3s can help reduce joint pain and stiffness in people with rheumatoid arthritis. They may also boost the effectiveness of anti-inflammatory drugs.
B Vitamins
The B vitamins in the table include B6, B12, B5, B1 (thiamin), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin) and B9 (folate). B vitamins help support the following:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Red blood cells
- Digestion
- Energy levels
- Brain function
- Nerve function
How does anchovies compare? I compare the two in my article.

Sardines Health Benefits
Magnesium
Adding magnesium to your diet could be instrumental in improving sleep related issues like insomnia. Magnesium relaxes and calms the whole body including the blood vessels ((National Institutes of Health: Magnesium)).
More so, it helps keep blood pressure levels balanced and stable. A recent study researched 22 studies and concluded magnesium supplementation decreased diastolic and systolic blood pressure2.
Magnesium helps control muscle and nerve function, blood sugar and blood pressure. In the muscles and heart, magnesium competes with calcium to help the muscles relax after contracting.
When the body is low in magnesium, calcium can over stimulate the heart muscle’s cells causing a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
Phosphorus
Phosphorus has been shown in studies to may help the following:
- Muscle contraction.
- Muscle recovery after exercise.
- Promoting healthy nerve conduction.
- Promote bone and teeth strength.
- Aids the kidneys in waste removal.
- Help the body manage and store energy.
Potassium
Since the recommended dietary intake is 4,700 mg, they both provide an excellent number.
Potassium is beneficial for reducing sodium intake. It helps the body reduce fluids and rids excess sodium ((American Heart Association: How Potassium Can Help Control High Blood Pressure)). This process helps to reduce blood pressure.
The more potassium you consume, the more sodium your body will lose. Consuming too much sodium or not enough potassium throws off the delicate balance the kidneys need to remove the excess water3.
According to Harvard Health, a number of studies have shown a connection between low potassium levels and increased blood pressure4.
Selenium
Selenium is an underreported nutrient. I’m unsure why many don’t write about it more because studies5 show selenium may help to protect the following:
- Heart disease
- Thyroid
- The immune system (Important for diseases like those who have a cancer risk)
- Cognitive issues
Calcium
Calcium is important for blood pressure and the heart.
Harvard Health reports calcium helps maintain blood pressure because it helps to control the relaxing and tightening of blood vessels6. Calcium also helps the following:
- Build and maintain strong bones.
- Muscles need calcium to function properly.
- Improve nerve function.
Mercury Levels
The EPA and The Food and Drug Administration have issued warnings and suggestions regarding mercury levels in fish and how often they should be consumed7. This is especially important for pregnant women, young infants and developing children.
They established a list of best fish, good choices and ones to avoid based on their mercury levels. Let’s examine which fish has more mercury.
Herring and sardines have similar levels of mercury. They are both listed on the FDA’s best choices of fish to consume regarding their mercury levels.
Always check with a physician prior to eating new foods or changing your dietary habits.
Find out how sprats compared in my article. Are they better?
Herring and Sardines: Tastes and Textures
One of the most important things people takes into consideration when choosing a fish is its taste. When comparing the two fish, herring vs sardines, let’s take a closer look at which one may taste better.
Sardines have a stronger and fishier flavor than herring. The fish herring is more mild to fishy. Sardines taste salty although herring is also salty but not as much. If a fishy taste is desired sardines is better. If a less fishy flavor is desirable, then herring is better. Sardines are meatier to chew while herring is softer.
I wanted to get the opinion of real people like you by conducting some original research. Therefore, I reached out to some clients, members of food groups and readers. I asked, which one tastes better?
- 51% said they preferred the taste of herring.
- 38% said they preferred the taste of sardines.
- 11% said they had no preference.
I conducted my own taste test between the two. I picked herring because I prefer less fishy when it comes to seafood.
If you’re wondering how salmon may differ, check out my article.
Food Substitutions
When preparing recipes for dinner it’s not always possible to locate the type of fish called for. If you have only one type on hand, you may wonder if you can substitute them.
Sardines can substitute for herring due to their similar oily, salty and fishy tastes. Herring can substitute for sardines also although their textures are different. They can be cooked using the same cooking methods like grilling, frying or baking.
The best sardine substitutes include the following:
- Herring
- Anchovies
- Mackerel
- Smelts
The best herring substitutes are:
- Sardines
- Anchovies
- Smelts
- Mackerel
When substituting try to stick to the following:
- Same size and weight.
- Stick with similar fillets, whole fillet or cross section.
- Stick with skinless or skin when the recipe calls for one.
- Texture is more important for certain cooking methods. Like using a firmer texture when grilling8.
Costs of Tinned Fish
When purchasing either fish, be sure to check the label to see if it is wild-caught, farm raised, smoked or marinated. Let’s take a close look at the prices of each one.
Canned wild herring is more expensive than canned wild sardines. The average cost for wild canned sardines is 0.52¢ per ounce while the average cost for wild canned herring is 0.64¢ per ounce. Fresh fillets of both are a similar price.
To conduct some original research on costs I visited various different stores and checked their prices.

First, I visited my local Shoprite supermarket and found the following prices for tinned fish:
- Canned sardines in olive oil (skinless and boneless)
- 0.38¢ per ounce
- Wild canned sardines in olive oil (skinless and boneless)
- 0.66¢ per ounce
- Wild canned smoked herring fillets (ready to eat)
- 0.46¢ per ounce
- Wild canned smoked herring fillets (ready to eat)
- 0.83 per ounce
I checked online at Freshdirect and found the following prices:
- Fresh marinated herring fillets
- $12.99 per pound
- Fresh sardines
- $11.99 per pound
Herring vs Sardines: Habitats, Size, Weight, Appearance
Herring and sardines are not the same, they are two different species of fish. The average herring is longer and weighs more than a sardine. Herring have a blueish green back while sardines have an olive to greenish color back. Herring lives longer.

For the comparison below I’ll be comparing Atlantic herring and the Atlantic sardine otherwise noon as the European pilchard.
Scientific Classifications, Families, Species
Herring is the species C. harangus and sardines are S. pilchardus although both members of the herring family – clupeidae.
Habitats
- Herring are found on both sides of the North Atlantic. Near the United States they are found from Labrador to Cape Hatteras, North Carolina.
- Sardines are found in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea.
Colors
- Herring are silvery in color with a bluish or greenish-blue back.
- Sardines are silvery in color with a greenish to olive colored back.
Appearance
- Herring are small schooling fish. Their bodies are long and narrow with one dorsal fin.
- Sardines are an elongated, small fish like the herring. They have one dorsal fin.
Size and Weight
- Herring are longer than sardines. They can grow up to 14″ long and weigh up to 2 pounds.
- Sardines grow up to 8-10″ long and weight from 0.33 to half a pound. They are the smaller fish.
Maybe one of the biggest differences is the size of the two.
Age
- Herring lives up to 12-16 years.
- Sardines live up to 10-12 years.
Diets
Herring consumes the following diet:
- Zooplankton
- Copepods
- Arrow worms
- Krill
- Fish larvae
Sardines consume the following diet:
- Zooplankton
- Phytoplankton
- Fish larvae
- Copepods
- Baby barnacles
Species Resources ((NOAA Fisheries: Atlantic Herring))9
As a Certified Health Coach, many of my clients ask me about seafood. In addition to coaching clients about herring and sardines, I’ve purchased, researched and consumed both fish for over 20 years.
If you have any questions about this article or other featured content, don’t hesitate to email and notify us. You can find an email on our contact page. We’ll do our best to reply as soon as possible.
Read Next – More Fish vs Fish Articles!
Brook Trout vs Brown Trout – Let’s Compare The Differences
Rainbow Trout vs Cod: Which Is Better? Let’s Compare
Alaska Pollock vs Atlantic Pollock: Which Is Better?
White Bass vs Striped Bass: The Key Differences
- Nutrition Value: Fish, raw, Atlantic, herring [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure: a meta-analysis [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: The Effect of the Sodium to Potassium Ratio on Hypertension Prevalence: A Propensity Score Matching Approach [↩]
- Harvard Health: Potassium lowers blood pressure [↩]
- National Institutes of Health: Selenium [↩]
- Harvard Health: Key minerals to help control blood pressure [↩]
- FDA: Advice about Eating Fish [↩]
- Sea Grant North Carolina: Fish Flavors and Substitutions [↩]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Sardina pilchardus [↩]
