Spinach vs Romaine: Which is Better? An Ultimate Comparison
Part of my job as a Certified Health Coach is to inform people about healthy foods like spinach and romaine lettuce. Many of my clients ask me if one is superior to the other. Let’s answer which is better, spinach or romaine?
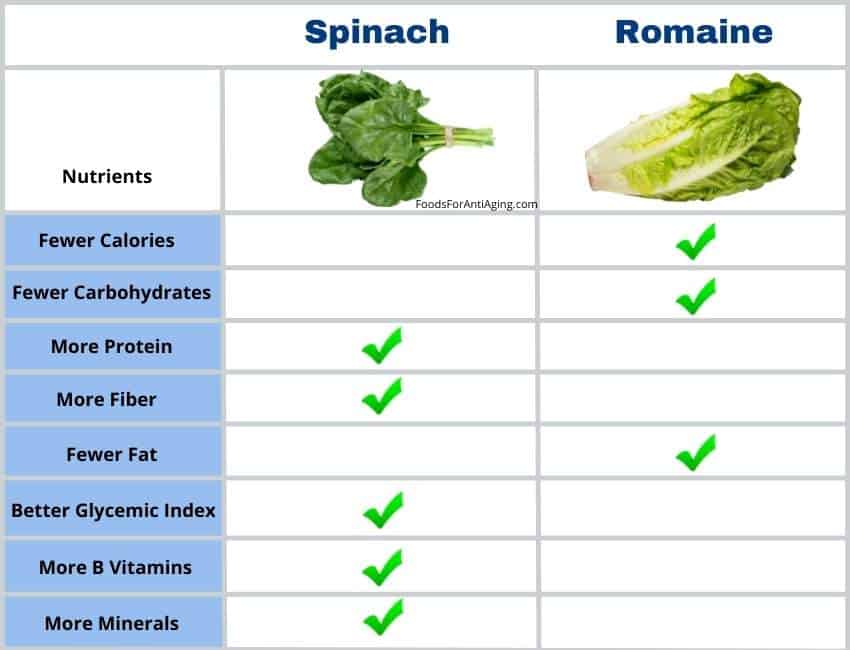
Spinach is better than romaine due to its higher percentage of vitamins, minerals, protein and fiber. Spinach provides 600% more vitamin C, 200% more calcium and 477% more iron than romaine. Spinach is easier to find in stores and costs less per ounce making it slightly more affordable.
This article will start with a side-by-side nutrient comparison of the two leafy greens. In addition, I’ll examine their tastes, textures, prices, glycemic indexes, health benefits and whether one can substitute for the other.
I’ve purchased, researched and consumed both leafy greens prior to, during and sometimes after writing this article.
Spinach vs Romaine Lettuce: Nutritional Profile Comparison
The following table compares the nutrients contained in each one per 100 grams.
| Spinach, raw (100 g) | Romaine, raw (100 g) | |
| Calories | 23 | 17 |
| Protein | 2.86 g | 1.23 g |
| Carbohydrates | 3.63 g | 3.29 g |
| Fiber | 2.2 g | 2.1 g |
| Fat | 0.39 g | 0.30 g |
| Sugar | 0.42 g | 1.19 g |
| Vitamin A | 9,380 IU | 8,710 IU |
| Beta-carotene | 5,630 mcg | 5,230 mcg |
| Vitamin C | 28.1 mg | 4.0 mg |
| Vitamin K | 483 mcg | 102 mcg |
| Vitamin D | 0 IU | 0 IU |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.19 mg | 0.07 mg |
| Vitamin B9 (Folate) | 194 mcg | 136 mcg |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 0.08 mg | 0.07 mg |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0.19 mg | 0.07 mg |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | 0.72 mg | 0.31 mg |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | 0.07 mg | 0.14 mg |
| Magnesium | 79 mg | 14 mg |
| Phosphorous | 49 mg | 30 mg |
| Potassium | 558 mg | 247 mg |
| Iron | 2.71 mg | 0.97 mg |
| Copper | 0.13 mg | 0.05 mg |
| Calcium | 99 mg | 33 mg |
| Zinc | 0.53 mg | 0.23 mg |
Both contain many of the same nutrients. After examining the table above let’s determine which is healthier.
Spinach is healthier than romaine lettuce because it provides more protein, fiber, vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin K, B6, folate, riboflavin, niacin, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, iron, copper, calcium and zinc.
Romaine provides more B5 and fewer calories, carbohydrates and total fat.
I typically use spinach at home for salads, smoothies and entrees due to its nutrients.
In almost every category, spinach is nutritionally superior to lettuce. Find out how these nutrients benefit health further down in this article.
The following video compares the benefits of spinach and romaine lettuce.
Which to Choose
Based on the nutrients just discussed, one of the two foods may be more beneficial for your particular goal. Let’s take a look at the more popular goals and which food is better for them.
Weight Loss and Green Vegetables
If weight loss is the goal, the number of calories per serving is important. Let’s examine how many calories per serving each one contains.
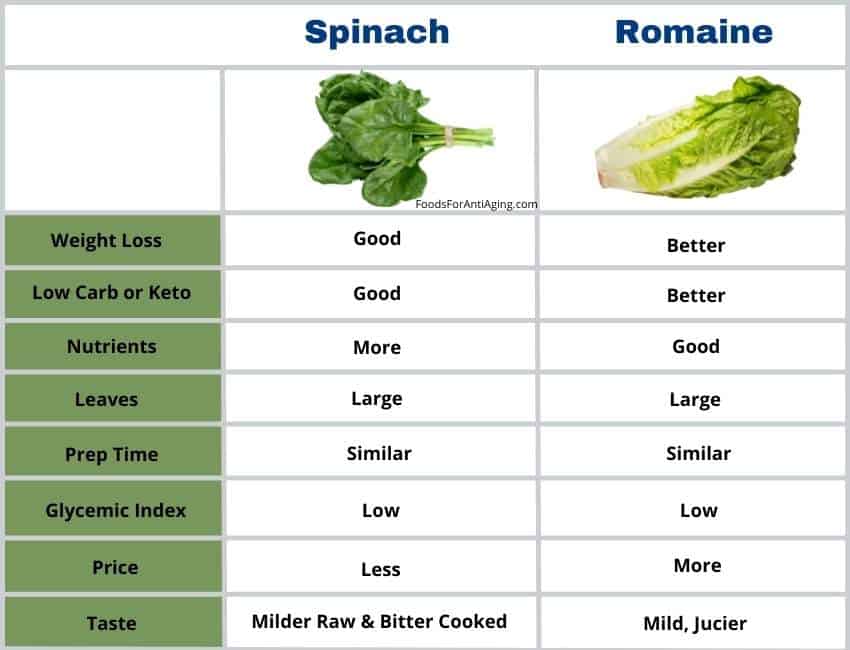
Spinach has 23 calories, and romaine lettuce has 17 calories per 100 grams. Romaine provides 6 fewer calories. While this number may not seem like much, it equals 35% less calories making it better for weight loss.
When counting calories every little bit may help as the total is calculated for the day.
Low-carb or Keto Diets
If you’re currently consuming low-carb foods or considering one of these diets, the number of carbohydrates may make a huge difference. Therefore, let’s examine which one has more carbohydrates.
Spinach has 3.63 grams of carbohydrates, and romaine has 3.29 per 100 grams, 10% fewer making it better for low-carb diets.
The difference isn’t large but when limiting the total amount, every gram can make a difference at the end of the day.

Gluten Free
For people who have celiac disease, whether one food contains gluten will automatically make the decision which to choose. Some people prefer following a gluten free diet, therefore it’s important also.
Spinach and romaine lettuce are gluten free. Therefore, both foods are good options for a gluten free diet.
Bodybuilding and Spinach Nutrition
If gaining lean muscle mass is your goal then the amount of protein and carbohydrates may matter to you.
Healthy carbohydrates help to increase performance and fuel energy when exercising or lifting weights. It’s why marathon runners consume many carbs the day and night before the big race.
Any extra protein helps to build and repair muscle after putting them through a good workout. Therefore, let’s take a closer look at which is better for bodybuilding.
Spinach is better than romaine for bodybuilding due to its higher percentage of protein and carbohydrates. It provides 2.86 grams of protein and romaine 1.23 grams per 100 grams. It provides 133% more protein per 100 grams.
In addition, it provides 10% more carbohydrates and 35% more calories which may help when trying to bulk up.
Tastes and Textures
Some foods taste undesirably to some people. In this situation, no matter how many nutrients the food has, that food may remain on the store shelf instead of in the shopping cart.
Therefore, let’s take a close look at how the taste and texture of each one compares.
Romaine has a refreshing, juicy taste and is a little bitter like spinach. Raw spinach is drier and tastes grassier than romaine lettuce. Romaine is crispier than raw spinach which is softer raw or cooked.
I wanted to get the opinion of real people like you by conducting some original research. So I reached out to some of my clients, readers and members of food groups and asked, which one tastes better?
- 34% said they preferred the taste of spinach.
- 58% said they preferred the taste of romaine.
- 8% said it depended on their mood.
To conduct more original research I setup a blind taste test at home. We chopped both into equal size leaves to help avoid detection. I chose the romaine due to its crispier texture and moist content.
In the battle of taste, romaine was the winner. Many people also stated, if health or nutrients were the priority, they would choose spinach first even though they preferred the taste of the other.

Substituting for Lettuce
Sometimes you may only have one available at home and don’t want to run out to the store. In this situation or any other time when you may want to substitute, you’ll wonder if they can be used for each other.
Spinach and romaine lettuce can substitute for each in raw or cooked dishes. They can also substitute for one another in gluten free recipes. When substituting, use a one to one ratio. When cooking, both of them will shrink in volume.
Other substitutes include the following:
- Swiss chard
- Bok choy
- Green leaf lettuce
- Butterhead lettuce
- Watercress
- Collard greens
- Iceberg
- Kale
- Arugula
- Beet greens
Which Cost More?
The price of foods commonly purchased is important to most people, especially with the inflation we’re experiencing lately. Let’s take a detailed look at how much each one costs.
Romaine lettuce costs more than spinach. The average price for romaine is $0.22 per ounce. The average price for spinach is $0.18 per ounce.
To conduct some original research, I visited some local supermarkets and compared the prices of both. Here are my findings.
First I checked Walmart:
- Marketside bagged fresh spinach
- 10 ounce bag $1.98. Equals $0.20 per ounce
- Marketside bagged leafy romaine lettuce
- 10 ounce bag $2.78. Equals $0.28 per ounce
I then checked my local Shoprite supermarket:
- Fresh spinach bundle
- 12 ounces for $1.87. Equals $0.16 per ounce
- Romaine lettuce bundle
- 20 ounces for $3.11. Equals $0.16 per ounce
Glycemic Index
Blood sugar spikes may lead to health complications over time ((National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Know Your Blood Sugar Numbers: Use Them to Manage Your Diabetes)). For this reason, avoiding blood sugar spikes as often as possible is an important part of a healthy diet.
The glycemic index measures how fast food raises blood sugar levels ((Harvard Health Publishing: Glycemic index for 60+ foods)). Foods on the GI scale are categorized as:
- Low-GI foods: 55 or under
- Medium-GI foods: 56-69
- High-GI foods: 70 or over
How blood sugars levels are affected:
- Foods with a glycemic index 70 or more cause a quicker spike in blood sugar levels.
- Foods with a glycemic index 56 to 69 cause a moderate spike in blood sugar levels.
- Foods with a glycemic index 55 or less cause a slow spike in blood sugar levels.
Let’s examine which food has a higher glycemic index.
Spinach and romaine lettuce have low glycemic indexes and are considered low glycemic index foods. Therefore, either food is a good choice to avoid blood sugar spikes.
Find out if collard greens are better in my article.

Health Benefits
This section will examine the health benefits of the nutrients provided by both foods. Each section includes the benefits of each nutrient and a breakdown of the percentages provided by each food.
Spinach Health Benefits
In the following video an accredited hospital and doctor explain the spinach nutrition and benefits.
Vitamin C
- Spinach contains more vitamin C (an antioxidant) per 100 grams, 600% more.
Vitamin C acts as an antioxidant and helps with the following:
- Prevent cell damage.
- May help boost the immune system.
- Collagen production.
- Help heal wounds.
- Increases iron absorption.
- Help maintain health gums.
Magnesium
- Spinach provides 460% more magnesium per 100 grams.
Magnesium helps the body control the following:
- Nerve function
- Blood pressure
- Muscle function
- Insomnia
- Blood sugar
Magnesium helps keep blood pressure levels stable and balanced. Recent scientific research examined previous studies and concluded magnesium supplementation decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure3.
Many people supplement with magnesium in the evening because it helps calm the whole body including blood vessels.
Find out if Swiss chard has more nutrients in my article. You may be surprised.

Potassium
- Spinach provides 126% more potassium per 100 grams.
According to Harvard Health, a number of studies have shown a connection between low potassium levels and high blood pressure4. The more potassium, the more sodium your body will lose.
Calcium
- Spinach provides 110% more calcium per 100 grams.
Calcium helps the following:
- Helps nerve function.
- Help the muscles to function properly.
- Build and maintain strong bones.
In addition, calcium is important for the heart and blood pressure. Harvard Health reports calcium helps maintain blood pressure by helping in the controlling of the relaxing and tightening of blood vessels5.
Vitamin K
- Spinach provides 374% more vitamin K per 100 grams.
Vitamin K comes in two forms. Phylloquinone is the one found in both vegetables.
Vitamin K helps to make various proteins needed to help with the following:
- Heart disease
- Blood clotting
- Bone health
Vitamin K, through the production of proteins, help to prevent hardening or calcification of the arteries6.
Iron
- Spinach provides 477% more iron per 100 grams.
Iron is a necessary part of any healthy diet7 and may help with the following:
- Vital for development and growth.
- Is essential the creation of red blood cells.
- Help some hormones remain balanced.
- Help the immune system.
Find out if kale has more nutrients in my article. It’s a veggie powerhouse comparison.
The following video describes the best way to cut lettuce.
B Vitamins
Spinach provides a higher percentage of B6, folate, thiamin, niacin and riboflavin. Romaine provides a higher percentage of B5 but also contains the other B vitamins.
The B vitamins provided include the following:
- B1 (thiamin)
- B2 (riboflavin)
- B3 (niacin)
- B5
- B6
- B9 (folate)
B vitamins help support the following:
- Brain function.
- Digestion.
- Nerve function.
- Cardiovascular disease.
- Red blood cells.
- Energy levels.
Vitamin A & Beta Carotene
- Spinach provides 7.7% more vitamin A per 100 grams.
Spinach provides 7.6% more beta carotene per 100 grams.
Beta-carotene is a compound present in both foods. The body converts beta-carotene into vitamin A.
According to scientific studies, vitamin A helps the eyes when it comes to dim light vision and dry eyes ((National Center for Biotechnology Information: Nutrients for the aging eye)).
Besides eye health, an increased number of vitamin A has been shown to fight and prevent cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of death in the United States8.
In addition, vitamin A is a powerful antioxidant that can help reduce cellular damage by controlling the negative effects of free radicals9.
Dietary Fiber
Both green vegetables contains almost an equal number of dietary fiber. When examining each one’s nutritional profile, this is one of the few where the lettuce romaine holds its own.

Compare the benefits of baby spinach and regular in my article.
If you have any questions about this article don’t hesitate to email us. You can find an email on our contact page.
Read More Spinach Food vs Food Articles
Spinach vs Broccoli: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison
Frozen Spinach vs Fresh: Which is Better? A Comparison
Raw Spinach vs Cooked Spinach: Which is Better? A Comparison
Arugula vs Spinach: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison
Organic Spinach vs. Regular Spinach: What’s The Difference?
Spinach vs Lettuce: Which is Better? A Complete Comparison
- USDA: Spinach, raw [↩]
- USDA: Lettuce, cos or romaine, raw [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure: a meta-analysis [↩]
- Harvard Health: Potassium lowers blood pressure [↩]
- Harvard Health: Key minerals to help control blood pressure [↩]
- Harvard T.H. Chan: Vitamin K [↩]
- National Institutes of Health: Iron [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Antioxidant potentials of vitamin A and carotenoids and their relevance to heart disease [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health [↩]
