Sunflower Oil vs Olive Oil: Which of the Two Oils is Better?
Many oils, like sunflower oil, are compared to olive oil for various reasons. During my health coaching sessions, clients often ask, is sunflower oil better than olive oil?
Olive oil is better than sunflower oil due to its higher percentage of vitamins and minerals. It contains 27.5% more heart healthy monounsaturated fats than sunflower oil. It also contains some nutrients sunflower oil doesn’t like potassium and calcium. In addition, it has a stronger, more favorable flavor.
This article will include a complete comparison of both oils like their tastes, smoke points, whether one can substitute for the other, prices, health benefits and a side-by-side nutrient comparison. In addition, I’ll examine their differences and how they’re made.
I’ve purchased, researched and consumed both prior to, during and sometimes after writing this article.
Sunflower Oil vs Olive Oil: The Differences
Olive oil is made by extracting the oils from olives using heat and/or chemicals. Sunflower oil is made by extracting the oils from sunflower seeds. The finished olive oil is a blend of refined olive oil and extra virgin.
Oleic Acid
There are 4 types of sunflower oil:
- High linoleic
- Mid-oleic
- High oleic
- High stearic/High oleic
High linoleic is the traditional one that has been produced for many years. It has limitations on frying and for that reason is being produced in small volumes. Its typical fatty acid ratio is:
- 68% linoleic acid
- 21% oleic acid
- 11% combined saturated
Mid-oleic was developed through traditional breeding methods and is currently the largest volume variety produced in the United States and Canada. It is now considered the standard.
It is much better for frying with excellent stability and has a better healthy fat profile. It has more monounsaturated fats and fewer polyunsaturated fats.
Since it’s the most common, the mid-oleic will be the oil used in this article for the nutrients and most comparisons. Its typical fatty acid ratio is:
- 65% oleic acid
- 26% linoleic acid
- 9% combined saturated

Sunflower oil facts:
- Made from pressed sunflower seeds.
- Has a mild, slightly nutty flavor.
- Cost less money.
- Has a slightly higher smoke point when refined, but lower when it’s cold pressed.
- Typical color is a pale yellow for refined or light amber for unrefined.
It is made by the following method:
- The sunflower seed is crushed or pressed to remove the oils from the seed.
- Chemical solvents are used for extraction or the seeds are cold pressed without the use of chemicals.
- The oil is filtered to make sure all the oil cakes or seeds are removed.
- It is then bottled for shipping and sale.
In 2018, 53% of the sunflower production was led by Ukraine and Russia. Currently, there is a shortage of it due to the events in the region.
Olive Oil
- Made from olives using heat and chemicals.
- Has a mild, peppery flavor.
- Cost more money.
- Has a higher smoke point than cold pressed.

It is made by the following method:
- Olive oil is derived from pressing olives.
- It is made by using the leftover paste from making extra virgin olive oil.
- The leftover paste is heated and kneaded with chemicals to release more oil, water and residue from the paste.
- The oil is separated from the water and residue.
- It is filtered and bottled.
All olive oils are held to certain USDA grade standards ((USDA: Grades of Olive Oil)). Extra virgin is certified as having the highest grade standards for excellent flavor, odor and free fatty acid content. It must not exceed 0.8 grams of oleic acid per 100 grams.
Nutrient Comparison
The following table compares the nutrients contained in one tablespoon of each one:
| Olive Oil (1 Tbsp/13.5 grams) | Sunflower Oil – Mid-oleic (1 Tbsp/13.5 grams) | |
| Calories | 119 | 119 |
| Protein | 0 g | 0 g |
| Carbohydrates | 0 g | 0 g |
| Fiber | 0 g | 0 g |
| Fat | 13.5 g | 13.5 g |
| Sugar | 0 g | 0 g |
| Sodium | 0.27 mg | 0 g |
| Vitamin K | 8.13 mcg | 0.73 mcg |
| Vitamin E | 1.94 mg | 5.55 mg |
| Potassium | 0.135 mg | 0 mg |
| Iron | 0.076 mg | 0.004 mg |
| Calcium | 0.135 mg | 0 mg |
| Omega-3 | 103 mg | 5 g |
| Omega-6 | 1,318 mg | 3,765 g |
| Saturated Fat | 1.86 g | 1.21 g |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 9.86 g | 7.73 g |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 1.42 g | 3.91 g |
The nutrients in the table above compare the mid-oleic sunflower oil. According to the National Sunflower Association this type is the largest volume produced in the United States and Canada4.
Since the mid-oleic is the most produced and found in the supermarkets, it is the reason for using it in the nutrient and benefit comparisons.
At first glance it may be difficult to determine which one has the most nutrients and healthy fats. Let’s answer a common question, which is healthier?
Olive oil is healthier than sunflower oil due to its higher percentage of vitamins, minerals and heart healthy monounsaturated fats. It contains more vitamin K, potassium, iron and calcium. In addition, it contains 1,960% more heart healthy omega-3 fatty acids than sunflower oil.
Sunflower oil is healthy but contains fewer nutrients. It provides a higher percentage of vitamin E. Sunflower oil is rich in some antioxidants while olive oil has more.
It has a higher percentage of omega-6 fatty acids compared to omega-3. This makes its omega-3 to omega-6 ratio less than the desired ratio.
I mostly use olive oil for everything due to its nutrients and taste. I use it for salads, dipping and lower temperature cooking.
The following video discusses health and sunflower oil.
Let’s examine the nutrients of both one by one.
Calories
- They both contain 119 calories per one tablespoon.
Vitamin K
- Olive oils contain 1,015% more vitamin K per one tablespoon.
Vitamin E
- Sunflower oils contain 186% more vitamin E per one tablespoon.
Potassium
- Olive oils contain more potassium per one tablespoon.
Iron
- Olive oils contain 1,800% more iron per one tablespoon.
Calcium
- Olive oils contain more calcium per one tablespoon.
Saturated Fat
- Olive oils contain 53% more saturated fat per one tablespoon.
Monounsaturated Fat
- Olive oils contain 27.5% more monounsaturated fat per one tablespoon.
Polyunsaturated Fat
- Sunflower oils contain 175% more polyunsaturated fat per one tablespoon.
Taste
Sometimes the nutrients and goals don’t matter much, and the taste is more important. After all, if someone doesn’t like how something tastes, they will probably leave it on the shelf.
Therefore, let’s examine how the taste of each one compares.
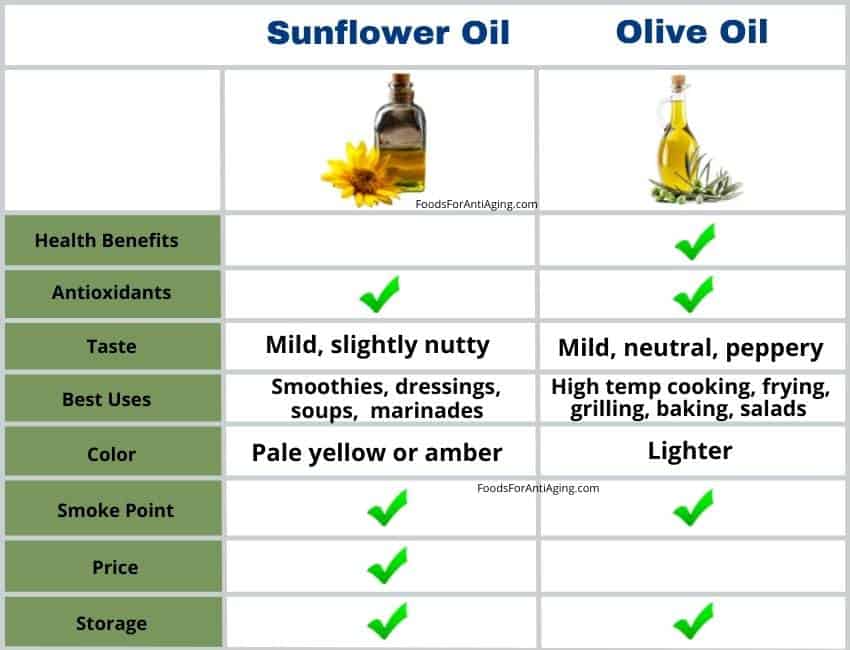
Olive oil has a slightly stronger flavor than the milder sunflower oil. Sunflower oil has a neutral, slightly nutty taste, while olive oil has a hint of olives and is peppery. The virgin olive oil and cold pressed sunflower oil have more flavor than the refined versions.
I wanted to get the opinion of real people like you by conducting some original research. Therefore, I reached out to some readers, clients and members of food groups. I asked, which one tastes better?
- 68% said they preferred the taste of olive oil.
- 28% said they preferred the taste of sunflower oil.
- 4% said they had no preference.
To conduct more research I setup and participated in my own taste test. I blindly tasted a teaspoon of each one and chose the olive oil for its better taste.
Substitutions
Have you ever wanted to try a new recipe the last minute and found out you didn’t have the correct ingredients at home? Unable to go out to the store or just don’t want to, you’ve probably wondered if you can use another one in its place.
Reasons why people will want to substitute one food for the other in a recipe:
- Availability
- Taste
- Variety
- Smoke point
- Price
This makes people wonder if they can substitute each one for the other.
Sunflower oil and olive oil can substitute for each other in cold recipes although the flavor will slightly differ. In hot recipes they can substitute for each other. If using cold pressed sunflower oil it can’t substitute for olive oil when using cooking temperatures above 225°F due to its low smoke point.
The following video explains what olive oil has the best taste.
Olive oil substitutes for high temperature cooking include the following:
- Refined avocado oil
- Safflower oil (refined and neutralized)
- Extra virgin avocado oil
- Pecan oil
- Sesame oil
- Corn oil
- Soybean oil
- Peanut oil
- Refined rice bran oil
- Refined sunflower oil
Sunflower oil substitutes for high temperature cooking include the following:
- Pecan oil
- Safflower oil refined
- Safflower oil neutralized
- Palm oil
- Soybean oil
- Refined rice bran oil
- Peanut oil
- Avocado oil
- Sesame oil
Smoke Points
The following are the smoke points for each one:
| Type of Oil & Fats | Smoke Point (Fahrenheit) |
| Sunflower Oil – refined | 486-489°F |
| Sunflower Oil – semi refined | 450°F |
| Sunflower Oil – cold pressed | 225°F |
| Olive Oil – Refined | 470°F |
| Olive Oil – Virgin | 410°F |
| Olive Oil – Extra virgin | 375°F |
Smoke point source ((Wikipedia: Smoke point))
Since traditional (high linoleic) sunflower oil is high in polyunsaturated fat, it shouldn’t be used in high temperature cooking5. These fats react with oxygen at high heat forming free radicals and harmful compounds.
How to Incorporate Them Into Your Diet
Sunflower Oil
Some people prefer using sunflower oil because it doesn’t overpower the other flavors. Using it results in a different flavor and variety.
Also, before using it, make sure you know which variety you have. It has a wide range of smoke points from 225 degrees up to 489 degrees.
Use cold pressed for the following:
- Dressings
- Marinades
- Salads
- Smoothies
Use refined for the following:
- Use it when cooking in low to moderate temperatures.
- Dressings
- Add a tablespoon to a smoothie.
- Baking
- Sauteing
- Marinades
- Soups
Olive Oil
- Use it for any cooking in temperatures up to 470 degrees.
- Frying
- Stir-frying
- Grilling
- Baking
- Dipping
- Salads
- Dressings

Which to Choose Based on Your Goals
Choosing which one may depend on your particular goal. Therefore, in this section I examine the most common goals people have, and determine which type is the better choice for each one.
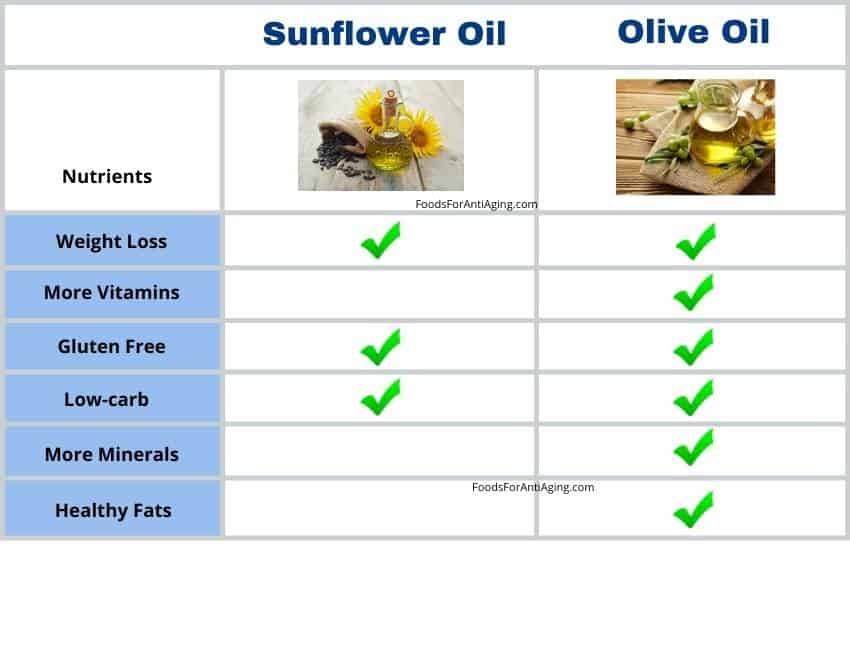
Weight Loss
If you’re looking to lose some weight, the number of calories may matter to you.
Therefore, let’s examine which is better for weight loss.
- Sunflower oil and olive oil are similar for weight loss because they contain the same number of calories per tablespoon.
Even though both are considered healthy additions to your diet, at 119 calories per tablespoon the calories can add up pretty fast.
It’s easy to add multiple tablespoons into a salad. Four tablespoons of either one equal 476 calories added to the salad. Always be aware of the number of tablespoons added and try not to overdo it.
Low Carb or Keto Diets
The goal of most low-carb diets is to consume few carbohydrates while adding more protein and fat. Every carbohydrate can make a difference depending on the diet followed.
Therefore, let’s examine which one has fewer carbohydrates or more fat.
- Sunflower oil and olive oil are both beneficial for keto or low-carb diets due to their similar amount of carbohydrates and fats. Both of them don’t contain any carbohydrates and are a healthy source of fats.
Bodybuilding
If you’re trying to gain lean muscle mass, the amount of protein and carbohydrates may make a difference. Let’s take a look at both varieties and determine which is better for bodybuilding.
Sunflower oil and olive oil are similar for bodybuilding because they both contain the same number of carbs and protein. Although they don’t contain any protein, both of them contain healthy fats and are a good addition to any bodybuilding diet.
When bulking up, the calories from both types may prove beneficial.
Gluten Free
Avoiding any gluten is the main goal for people who wish to follow a gluten free diet or have Celiac disease. Therefore, let’s take a look at which one is gluten free.
- Sunflower oil and olive oil are both gluten free and good for gluten free diets.
Find out how vegetable oil compares in one my recent articles.
The Prices
The price of groceries keeps rising, especially during the current atmosphere. Every trip to the supermarket seems to get more expensive than the last. For this reason and others, I’m sure the prices of food matters to most people.
Therefore, let’s examine the prices of each one.
Olive oil costs 22% more than sunflower oil per ounce. Sunflower oil average cost per ounce is $0.18 and the average price for olive oil is $0.22 per ounce.
To conduct my own research, I checked three different supermarkets located in my area. All the supermarkets are on different levels of pricing. Walmart is the most economical and Stop and Shop being more expensive.
Here are my findings, I first stopped at Walmart:
Walmart:
- Sunflower oil (Store brand) – 48 ounce $6.74 ($0.14 per ounce)
- Olive (Store brand) – 17 ounce $2.52 ($0.15 per ounce)
Stop and Shop:
- Sunflower oil (Store brand) – 24 ounce $4.79 ($0.20 per ounce)
- Olive (Store brand) – 25.3 ounce $6.79 ($0.27 per ounce)
Shoprite
- Sunflower oil (Store brand) – 25.4 ounce $4.99 ($0.20 per ounce)
- Olive (Store brand) – 25.5 ounce $6.49 ($0.25 per ounce)
You may want to check out the comparison with butter in my article.
How to Store and Time
Good quality food can be costly, therefore, the shelf life you get out of it is important. In addition, improper storage may lessen the taste and quality. Let’s examine how each one should be stored.
Sunflower oil, especially cold pressed, and extra virgin olive oil are more sensitive to temperature and can go bad quicker than refined oil. For this reason they should be refrigerated after they are opened.
Opened sunflower oil should be stored in the refrigerator and can also be frozen. Store it in a cool, dark place away from any heat or light. It’s best to store it in a tinted container. Unopened oil should be kept in temperatures between 55-60℉.
Store olive oil in a cool, dark location away from light. It’s best to store it in a tinted glass container. It should be kept at a temperature between 55-60℉, although it can be refrigerated or frozen if needed.
Both should be stored in the refrigerator if the room temperature rises above 70℉. Leaving either one in warmer temperatures affects shelf life and lessens the quality.
Due to heat-creating appliances and heated ovens, kitchens tend to be a bit warmer than most other rooms of the house. Therefore, be sure to monitor your oil and the temperature of the room.
I store mine in my kitchen cabinets but it’s in a cool area away from heat and sun.
Find out how sesame oil compared in my article.
The following video explains things to watch out for when shopping or olive oil.
Health Benefits
Both contain a wealth of antioxidants and healthy fats. The healthy fats and antioxidants provide many health benefits which I’ll examine in this section.
Sunflower Oil Benefits
Heart Disease
Much research suggests a diet rich in monounsaturated fatty acids may help reduce cholesterol levels and risk of heart disease.
In 2018, the FDA has determined there is evidence to support a health claim consuming oleic acid in edible oils, like sunflower oil, may reduce the risk of coronary heart disease6.
A study which involved 15 men and women were split up into two groups. Both groups consumed saturated and monounsaturated fats but one group consumed monounsaturated fats for a longer period of time.
The group which consumed more of the monounsaturated fats lowered their LDL (bad) cholesterol and fat cells more than the other group7.
Another study found people with high cholesterol improved their good cholesterol levels after consuming monounsaturated fats from sunflower oil. The group which didn’t consume it didn’t see any improvement in their good cholesterol8.
Brain and Nerve Health
It is very rich in vitamin E which has antioxidant properties. Research on vitamin E has found it may be helpful with the following:
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Liver disease
Some research has shown high doses of vitamin E might delay the progression of Alzheimer’s disease in people with mild to moderate diagnosis9.
Deficiencies in vitamin E has been shown to cause nerve pain10.
Find out how avocado oil compared in my comparison article.
Olive Oil Benefits
The doctor in the following video explains the benefits of using olive oil.
Cancer
The cancer rates in Mediterranean countries is lower than other places. Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) consumption is a huge part of the diet in those countries.
Antioxidants are believed to contribute to the killing of cancer cells. In a 2015 study, oleocanthal, a phenolic compound, helped kill cancer cells in less than one hour11.
Another study published in 2015 evaluated the consumption of the Mediterranean diet and the incidence of breast cancer. For a six-year period, 4,282 women aged 60 to 80 years followed three different diets:
- Mediterranean diet supplemented with EVOO.
- Mediterranean diet supplemented with mixed nuts.
- A reduced fat diet.
After 4.8 years 35 of the women developed breast cancer. The lowest rate of breast cancer was seen in the women who supplemented with the EVOO12.
Oleic acid has been associated with helping to reduce the risk of cancers.

Brain Health
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia causing problems with thinking, memory and behavior. A common feature of the disease is the build-up of proteins known as beta-amyloid plaques in certain neurons in the brain.
Animal studies have shown extra virgin to clear the beta-amyloid proteins from the brain helping to prevent Alzheimer’s disease13.
Several studies conducted on humans have shown the Mediterranean diet may be associated with a reduced risk of cognitive problems and dementia14.
Heart Disease
Heart disease and stroke are among the most common causes of death throughout the world. Studies have shown heart disease is lower in the Mediterranean countries.
There are many ways it is beneficial for the heart including the following:
Blood Vessel Health
It has been shown to help improve the lining of blood vessels. A study published in 2015 showed blood vessels opened up and increased blood flow in people who included olive oil in their diet15.
Lowering Blood Pressure
Studies have shown an association between lower blood pressure and an increase in olive oil consumption. The Mediterranean diet has been linked to lower blood pressure and cardiovascular disease16.
Reducing Inflammation
It is associated with decreases in inflammation which is a main component of heart disease. An antioxidant, oleocanthal, is an anti-inflammatory that also reduces pain17.
Grapeseed oil is another one compared in my article.
If you have any questions about this article don’t hesitate to email us. You can find an email on our contact page.
Read More Oil Articles
Olive Oil vs Coconut Oil: Which is Better? Let’s Compare
Olive Oil vs Soybean Oil: Which is Better? Let’s Compare
Olive Oil vs Canola Oil: Which is Better? Let’s Compare
The Complete Guide To Storing Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Can Extra Virgin Olive Oil Go Bad? What You Need To Know
Can I Replace Olive Oil With Coconut Oil?
This is the Best Way to Store Your Olive Oil
- USDA: Oil, olive, salad or cooking [↩]
- USDA: Oil, sunflower, linoleic, (approx. 65%) [↩]
- USDA: Oil, industrial, mid-oleic, sunflower [↩]
- National Sunflower Association: Types of Sunflower Oil Available [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Oxidative Stability of Selected Edible Oils [↩]
- USDA: FDA Completes Review of Qualified Health Claim Petition for Oleic Acid and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: A diet rich in high-oleic-acid sunflower oil favorably alters low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, and factor VII coagulant activity [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Adding monounsaturated fatty acids to a dietary portfolio of cholesterol-lowering foods in hypercholesterolemia [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Effects of Vitamin E on Cognitive Performance during Ageing and in Alzheimer’s Disease [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Analgesic effect of vitamin E is mediated by reducing central sensitization in neuropathic pain [↩]
- Taylor & Francis Online: (-)-Oleocanthal rapidly and selectively induces cancer cell death via lysosomal membrane permeabilization [↩]
- Jama Internal Medicine: Mediterranean Diet and Invasive Breast Cancer Risk Among Women at High Cardiovascular Risk in the PREDIMED Trial [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Attenuates Amyloid-β and Tau Pathologies in the Brains of TgSwDI Mice [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease in the EPIC-Spain Dementia Cohort Study [↩]
- (National Center for Biotechnology Information: Effects of Olive Oil on Markers of Inflammation and Endothelial Function-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis [↩]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Virgin Olive Oil and Hypertension [↩]
- National center for Biotechnology Information: Olive Oil-related Anti-inflammatory Effects on Atherosclerosis: Potential Clinical Implications [↩]
